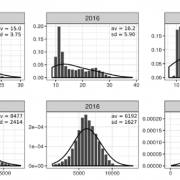
Improvement of predictive ability in maize hybrids by including dominance effects and marker x environment models ($) (Crop Sci.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHeterosis is phenomenon that occurs when crossbred individuals show qualities (such as such as size, growth rate, fertility, and yield) that are superior to those of both parents. In maize, heterosis can be explained in terms of hybrid vigor, and this has been well studied using traditional breeding.…
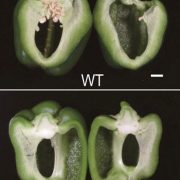
A gene knock-out that leads to seedless parthenocarpic fruits in Solanaceae plants ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParthenocarpy, or the ability to make fruit without fertilization, is desirable for many reasons including the opportunity to make seedless fruits and a greater resiliency in crop production in the face of climate change. Matsuo et al. identified a new gene involved in parthenocarpy, starting with a…
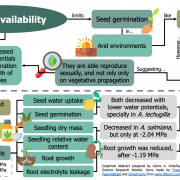
Water availability effects on germination, membrane stability and initial root growth of Agave lechuguilla and A. salmiana (Flora)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLow water availability limits seed germination in arid environments, such as the ones that Agave plants inhabit. As a result, vegetative propagation has been considered their most effective and successful method of reproduction. However, agaves produce several hundreds of seeds, and their natural populations…
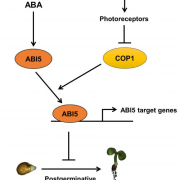
Post germination seedling establishment by ABA in response to light (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA), is implicated in reversible inhibition of seed germination (emergence of radicle) and post-germination seedling establishment (formation of green open cotyledons) during unfavorable conditions. Yadukrishnan et al. analyzed the role of light in ABA- mediated inhibition of post germination…
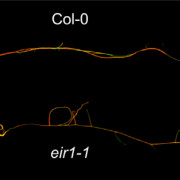
PIN FORMED 2 modulates the transport of arsenite in Arabidopsis thaliana (Plant Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPIN FORMED (PIN) proteins are known for their directional auxin transport capacity. Ashraf et al. found that auxin transporter PINs have sequence similarity to bacterial arsenite transporter arsB, yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae arsenite transporter SsAcr3, and arsenic hyperaccumulator fern Pteris vittata…
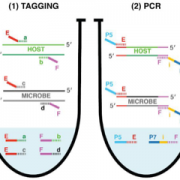
Measuring both microbial load and diversity with a single amplicon sequencing library (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmplicon sequencing of microbial DNA is a gold standard for analyzing the relative abundance of microbes in host-associated microbiomes. To gain more accurate insights into microbiome changes, it is crucial to know the absolute abundance of microbes, which can be analyzed by integrating relative abundance…
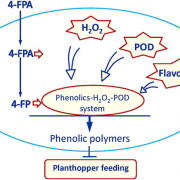
A chemical elicitor, 4- fluorophenoxyacetic acid suppresses insect pest populations and increases crop yields (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant strengtheners, synthetic chemical elicitors, have been shown to enhance plant resistance against various insect pests without toxic effects on the environment, but evidence is lacking for a significant increase in crop growth and yield after using these elicitors. To address this, Wang et al. studied…
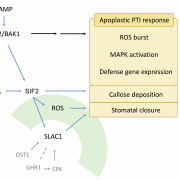
STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2 regulates arabidopsis stomatal immunity through phosphorylation of the anion channel SLAC1 ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants detect microbes by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that sense common conserved structures called microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and trigger the innate immunity responses. Chan et al. identified a new player in the Arabidopsis immune response known as STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2…

Plant Science Research Weekly: June 5th
WWR Full PostReview: Functions of anionic lipids in plants
Moving materials within and out of cells requires that membranes carry identification labels, but when the membrane itself moves, that ID label must be updated. These requirements are met ingeniously by the anionic lipids, which are both a modifiable information…

