
Did you know? This January is the Global Plant Science Event Calendar's First Anniversary!
BlogOur Global Calendar project was initiated on January 2nd, 2019 in an effort to collect and curate all of the plant science events of interest to our community. Agrisera, our calendar sponsor, recognized the need for scientists and exhibitors to have a comprehensive list of events and approached us with…
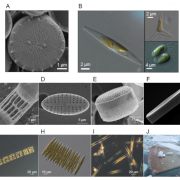
Review. Diatom molecular research comes of age: Model species for studying phytoplankton biology and diversity (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDiatoms are photosynthetic eukaryotes and contribute substantially to global carbon fixation. They are distantly related to green plants, having shared the same primary endosymbiotic event, although they subsequently underwent additional secondary endosymbioses. There are over 100,000 species of diatoms,…
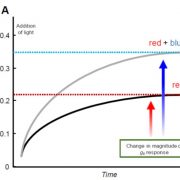
Review: Role of blue and red light in stomatal dynamic behaviour (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGuard cells are extremely sensitive and dynamic, and their behaviour controls rates of gas exchange and transpiration, which affect evaporative cooling and transport in the xylem. Matthews et al. review the roles of light signalling pathways in guard cell responses. Cues that control guard cell ion channels…
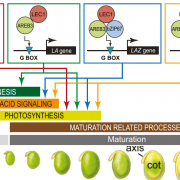
Combinatorial interactions of the LEC1 transcription factor specify diverse developmental programs during soybean seed development (PNAS) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLEC1 (LEAFY COTYLEDON 1) transcriptional factor regulates multiple developmental processes during different stages of seed development including macromolecule accumulation, inhibition of germination and morphogenesis. In this paper Jo et al., have uncovered the mechanism of LEC1 functioning with other…
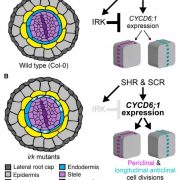
The Arabidopsis receptor kinase IRK is polarized and represses specific cell division (Devel. Cell) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrientation of cell division decides daughter cell fate and is fundamentally important for tissue patterning and morphology. For instance, asymmetric cell division leads to the generation of new cell types; in contrast, symmetric division produces cells with similar identity in a proliferative manner.…
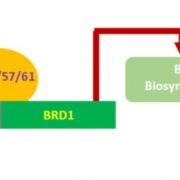
Promotion of BR biosynthesis by miR444 is required for ammonium-triggered inhibition of root growth (Plant Physiol.) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen, as one of the most important plant nutrients, profoundly affects root growth. Nitrogen is usually taken up in one of two forms, nitrate (NO3-) or ammonium (NH4+), and the two forms affect root growth differently. Here, Jiao et al. demonstrate a connection between ammonium, a small RNA, and…
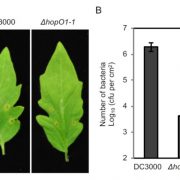
Pathogenic bacteria target plant plasmodesmata to colonize and invade surrounding tissues (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are regulated channels that connect adjacent cells, allowing movement of metabolites, RNA, proteins, and pathogens. Plants close their plasmodesmata as part of their immune response, but this closure can be interfered with by pathogens. Aung et al. examined the repertoire of effector proteins…

Resistant tomato restricts colonization and invasion by the pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum at four organismal levels (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRalstonia solanacearum is a pathogenic bacterium that infects many important crop species, including tomato. Following invasion into the roots, the bacteria move upwards into the shoot and cause dramatic wilting. Previous studies have identified moderately and highly resistant lines. Here, Planas-Marquès…

Medicago-Sinorhizobium-Ralstonia co-infection reveals legume nodules as pathogen confined infection sites developing weak defenses (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe pathogenic bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum enters roots through wounds and also at root tips. It can also infect legume nodules. Benezech et al. investigated how this infection occurs, and how it is affected by and affects nitrogen fixation. The authors found that nodules are as permissive of Ralstonia…

