
Revealing the Invisible: A Synthetic Reporter for ABA
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsHow do you make the invisible visible? It’s a question that crops up again and again in molecular biology. Abscisic acid (ABA) is one of the most important hormones in plants and is essential for survival in suboptimal conditions. Despite this, we have only a basic understanding of where and when this…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Molly Perchlik
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesMolly Perchlik, first author of Leaf Amino Acid Supply Affects Photosynthetic and Plant Nitrogen Use Efficiency under Nitrogen Stress
Current Position: In search
Education: Ph.D. in Plant Biology, Washington State University. B.S. in Biology, Indiana University (Bloomington)
Non-scientific Interests: Travel,…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Linhui Yu
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesLinhui Yu, first author of Starch Deficiency Enhances Lipid Biosynthesis and Turnover in Leaves
Current Position: Postdoctoral fellow, Bioscience Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, New York, USA
Education: PhD in Plant Biology at the School of Life Science, University of Science and Technology…

Recognizing Plant Cell first authors: Fernanda A.L. Silva-Alvim
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Author ProfilesFernanda A.L. Silva-Alvim, first author of Predominant Golgi-residency of the plant K/HDEL receptor is essential for its function in mediating ER retention
Current Position: Visitor student, Centre for Plant Sciences, University of Leeds/UK
Education: BSc in Food Engineer, Master in Agroenergy,…

Review: MYBs drive novel consumer traits in fruits and vegetables (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe MYB transcription factors, specifically the R2R3 family of MYBs, are closely associated with the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. This easy-to-score trait made MYBs some of the earliest characterized plant transcription factors. Allan and Espley summarize the contributions of MYBs to pigmentation…
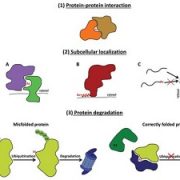
Roles of N-terminal acetylation and N-terminal acetyltransferases in plants (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN-terminal acetylation is a common protein modification completed by ribosome-associated N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs) or plastid-localized NATs. The recent discovery of the plastid-localized NATs upended the traditional model of static, co-translational imprinting of the plant proteome. These…
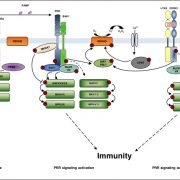
Review: Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling by phosphorylation and ubiquitination (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA key step in pathogen recognition occurs at the cell surface with the interaction between receptor-like kinases (pattern-recognition receptors) and their ligands. This event triggers a signal-transduction cascade that leads to the induction of defense responses. Mithoe and Menke review our current understanding…
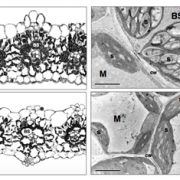
Diffusion of CO2 across the mesophyll-bundle sheath cell interface in a C4 plant with genetically reduced PEP carboxylase activity (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 photosynthesis relies on the transport of carbon (in the form of C4 acids) from the mesophyll into bundle sheath cells (BSCs). Subsequent decarboxylation of these C4 acids generates a high concentration of CO2 in the vicinity of Rubisco, helping to improve the catalytic efficiency of this enzyme. …
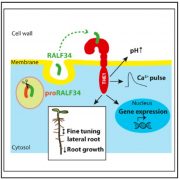
Receptor kinase THESEUS1 is a RALF 34 receptor with roles in lateral root development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRALF peptides were identified nearly 20 years ago, as small peptides that induce rapid alkalinisation of the culture medium when added to cell suspension cultures. Previously, members of the receptor-like kinase (RLK) family including FERONIA (FER) have been identified as RALF receptors. A related…

