
Methylome robustness in plants is conferred by a methylation-sensitive system.
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDNA methylation is instrumental in promoting transcriptional silencing at repetitive elements, inhibiting illegitimate recombination and establishing genomic imprinting. In plants, DNA methylation profiles are stably inherited over generations through the activities of cytosine DNA methyltransferases…
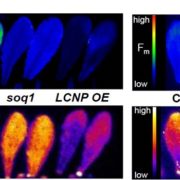
The plastid lipocalin LCNP is required for sustained photoprotective energy dissipation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants have several mechanisms to protect themselves from damage from excess light, including a set of reactions collectively described as non-photochemical quenching or NPQ. One of these is a sustained and slowly reversible form of NPQ, which the authors have named qH. How this sustained NPQ functions…

Cell density and airspace patterning in the leaf can be manipulated to increase leaf photosynthetic capacity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIncreasing photosynthetic conversion efficiency is an attractive target for improving crop yields. One way of affecting this is to alter the way CO2 is delivered to Rubisco, the carbon-fixing enzyme of photosynthesis. Lehmeier et al. aimed to change the pattern of air spaces within Arabidopsis leaves…
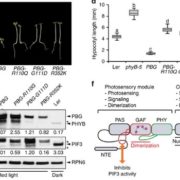
Role of C-terminal modules in phytochrome signaling
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPhytochromes are photoreceptors found in many organisms including bacteria, fungi and plants. Plant phytochromes regulate many aspects of plant growth and development, including germination, shade avoidance, defense against pests, and senescence. Phytochromes most likely transduce signals through the…
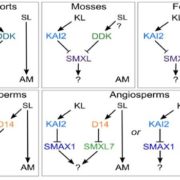
Reassessing the evolution of strigolactone synthesis and signaling
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMuch of our understanding of strigolactones (SLs) as developmental hormones and rhizosphere signals comes from studies of angiosperms. Understanding the ancestral role for strigolactones is complicated by the fact that some of the SL-related genes are closely related to those responsive to karrikins…
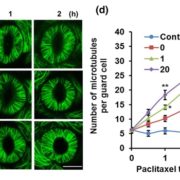
Microtubule involvement in stomatal dynamics
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogStomatal dynamics have been investigated in terms of ion exchange involvements, turgor pressure fluctuations, and transcriptional changes, particularly in response to environmental stresses. However, the involvement of the cytoskeleton during this process, particularly concerning the role of microtubules…
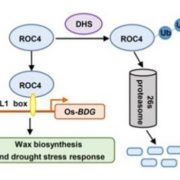
DROUGHT HYPERSENSITIVE negatively regulates cuticular wax biosynthesis by promoting the degradation of transcription factor ROC4 in rice
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWax covering the outer surface of the shoot (epicuticular wax) is crucial in the ability of the plant to conserve water. Wang et al. identified a drought hypersensitive plant that overexpresses an E3 ubiquitin ligase which they named DROUGHT HYPERSENSITIVE. In these overexpression plants, there was a…

Extremely flexible infection programs in a fungal plant pathogen
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFilamentous plant pathogens have developed an extra-ordinary level of dynamic genome architecture that adapts to changing host environment in the best possible way to promote infection. There are very limited studies describing the impact of this genome plasticity on phenotypic variation. Haueisen et…
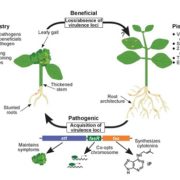
Evolutionary transitions between beneficial and phytopathogenic Rhodococcus
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRodococcus bacteria are often identified as causal agents in disease outbreaks. Savory et al. analyzed 60 isolates from diseased plants. By comparing these new isolates and previous isolates, they found that 64 of 66 pathogenic isolates carry a linear virulence plasmid, and that all but four carried…

