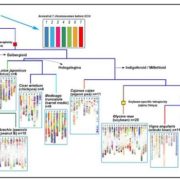
Hierarchically aligning 10 legume genomes establishes a family-level genomics platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Many legumes are important crops, and to date ten legume genomes have been sequenced, including soybean, common bean, mung bean, and two species of wild peanut. Wang et al. used hierarchical comparative genomics analysis of the ten legume genomes, which enabled them to detected gene colinearity between…
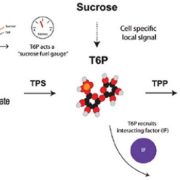
Opinion: Increasing crop yield and resilience with trehalose 6-phosphate ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTrehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) is a disaccharide formed from two glucose sugars, and more importantly is a signal of glucose availability and regulator of energy homeostasis. Acting via the protein kinase SnRK1, T6P controls the allocation of carbon, leading the plant down a “feast” (growth) or “famine”…
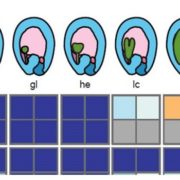
Commentary: Widespread contamination of Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchKnowing where a gene is expressed provides valuable information about its function, but that information is compromised if the RNA source is contaminated by other tissues. Schon and Nodine investigated the extent to which Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets are affected by tissue…

Decreasing readability in scientific papers over time
Education, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research“Reporting science clearly and accurately is a fundamental part of the scientific process, facilitating both the dissemination of knowledge and reproducibility of results.” In this way, Plavén-Sigray et al. introduce us to their preprint in which they analyzed readability in over 700,000 abstracts…
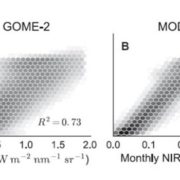
Canopy near-infrared reflectance and terrestrial photosynthesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA model is only as good as the data that go into it (garbage in, garbage out), so any effort to improve remote sensing data will contribute to better global models. Badgley et al. describe a new parameter, near-infrared reflectance of vegetation (NIRV), that more accurately quantifies photosynthesis…
Living on the edge: conservation genetics of seven thermophilous plant species in a high Arctic archipelago
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Arctic provides numerous opportunities to study how climate change and isolation affect plant populations. Birkeland et al. queried the genetic diversity within isolated populations of seven heat-loving (thermophilous) species in the high Arctic (74° – 81° N) Svalbard Archipelago, near the well-known…

Academic research in the 21st century: Maintaining scientific integrity in a climate of perverse incentives and hypercompetition
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn recent years it has become clear that misconduct in the scientific community is pervasive. In this recent publication by Edwards et al., the authors investigate the potential causes of this problem. Their conclusion is that due to decreased research funding from governments, development of quantitative…

Letter: Picking up the ball at the K/Pg boundary: Ancient polyploidies as a spandrel of asexuality
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRoughly 66 million years ago Earth was hit by a huge asteroid, resulting in climate changes that led to mass extinctions, most famously of the non-avian dinosaurs. This catastrophic event, which marks the boundary between the Cretaceous (K) and Paleogene (Pg) periods, also caused widespread mass extinctions…

Review: The evo-devo of plant speciation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSpeciation events result from a combination of molecular, environmental and stochastic (random) factors. Several models developed in the last 150 years help to explain how species emerge, but more recently evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) approaches give us tools to decipher plant speciation.…

