Type one protein phosphatase regulates fixed-carbon starvation-induced autophagy in Arabidopsis
Wang et al. demonstrate that TOPP regulates autophagy through ATG1a-ATG13a complex. The Plant Cell (2022). https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac251
By Qiuling Wang, Qianqian Qin, Meifei Su, Na li, Jing Zhang, Yang Liu, Longfeng Yan, and Suiwen Hou
Key Laboratory of Cell Activities and Stress Adaptations, Ministry of Education, School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, People’s Republic of China
Background: Autophagy is a conserved, essential degradation process in eukaryotes. This process is mainly driven by numerous autophagy-related (ATG) proteins. Among these components, the ATG1-ATG13 complex plays an essential role in initiating autophagy and the core subunit ATG13 recruits downstream ATG proteins to the ATG1-ATG13 complex. Arabidopsis ATG13 is hyperphosphorylated under nutrient-rich conditions but is dephosphorylated immediately after nutrient starvation.
Questions: Which phosphatase dephosphorylates ATG13? Which components in the autophagy pathway are regulated by TYPE ONE PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE (TOPP)? What is the key phosphorylation site of ATG13a? How does ATG13a phosphorylation regulate autophagy?
Findings: Using T-DNA insertional and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis, we generated septuple (topp-7m) and octuple (topp-8m) mutants of TOPP and demonstrated that these mutants showed a significant autophagy-deficient phenotype upon fixed-carbon starvation. ATG13a was a substrate of TOPP and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry–mass spectrometry identified 18 phosphorylation sites in ATG13a. Moreover, dephosphorylation of ATG13a by TOPP facilitated ATG1a-ATG13a complex formation to promote autophagy and increase plant tolerance to fixed-carbon starvation.
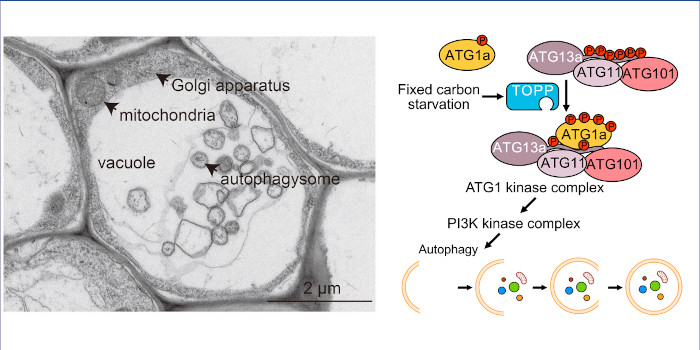 Next steps: After fixed-carbon starvation, TOPP is activated to dephosphorylate ATG13a. However, how TOPP is activated remains to be determined. In addition, ATG13a contains more than the eighteen phosphorylation sites we identified; how these phosphorylation sites respond to different environmental conditions and nutrient deficiencies requires further study.
Next steps: After fixed-carbon starvation, TOPP is activated to dephosphorylate ATG13a. However, how TOPP is activated remains to be determined. In addition, ATG13a contains more than the eighteen phosphorylation sites we identified; how these phosphorylation sites respond to different environmental conditions and nutrient deficiencies requires further study.
Reference:
Qiuling Wang, Qianqian Qin, Meifei Su, Na li, Jing Zhang, Yang Liu, Longfeng Yan, and Suiwen Hou (2022). Type one protein phosphatase regulates fixed-carbon starvation-induced autophagy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac251



