The MICROTUBULE ORGANIZATION1–KATANIN1 interaction modulates microtubule dynamics
By Xiayan Liu and Fei Yu
Background: Microtubules (MTs) are highly dynamic cytoskeletal structures with essential functions in cell morphogenesis and cell division. Adapting to their sessile lifestyle, land plants have evolved unique MT arrays at different stages of the cell cycle. Diverse groups of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) directly bind to MTs and modulate the dynamic behavior of MTs. The MAP215 family MT polymerase/nucleation factor and the MT-severing enzyme katanin are two widely conserved MAPs. In Arabidopsis, the essential gene MOR1 encodes the homolog of MAP215 and KATANIN1 (KTN1) encodes the p60 catalytic subunit of katanin.
Question: MOR1 and KTN1 play critical roles in modulating MT dynamics. However, whether MOR1 and KTN1 coordinate to regulate MT dynamics remains unknown. In this work, we investigated the genetic, molecular, and functional interactions between MOR1 and KTN1 in Arabidopsis, taking advantage of a functional MOR1-GFP fusion protein.
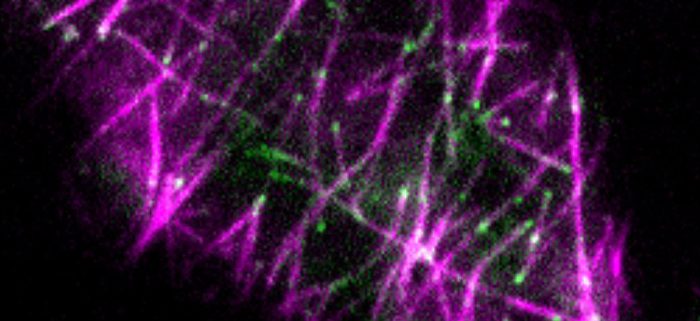
Findings: In living plant cells, MOR1 is associated with all types of mitotic MT arrays, predominantly tracks the growing plus-ends of cortical MTs, and is also found on MT lattices. In dividing cells, MOR1 is required for the proper formation of mitotic MT arrays and the positioning of the cell division plane. In interphase cells, MOR1 promotes MT plus-end dynamics and katanin-mediated MT severing. Genetically, MOR1 and KTN1 synergistically regulate cell division and cell expansion. Physically, MOR1 interacts with KTN1 and promotes the recruitment of KTN1 to MT severing sites. Our work identified an unexpected functional interaction between two widely conserved MAPs, MOR1 and KTN1, providing a glimpse into the functional interaction networks of plant MAPs.
Next step: In the future, it is essential to integrate genetics, cell biology, and biochemical tools to further uncover hidden treasures in the functional networks of plant MAPs.
Reference:
Yu Chen, Xiayan Liu, Wenjing Zhang, Jie Li, Haofeng Liu, Lan Yang, Pei Lei, Hongchang Zhang, Fei Yu (2022) MOR1/MAP215 acts synergistically with katanin to control cell division and anisotropic cell elongation in Arabidopsis. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac147