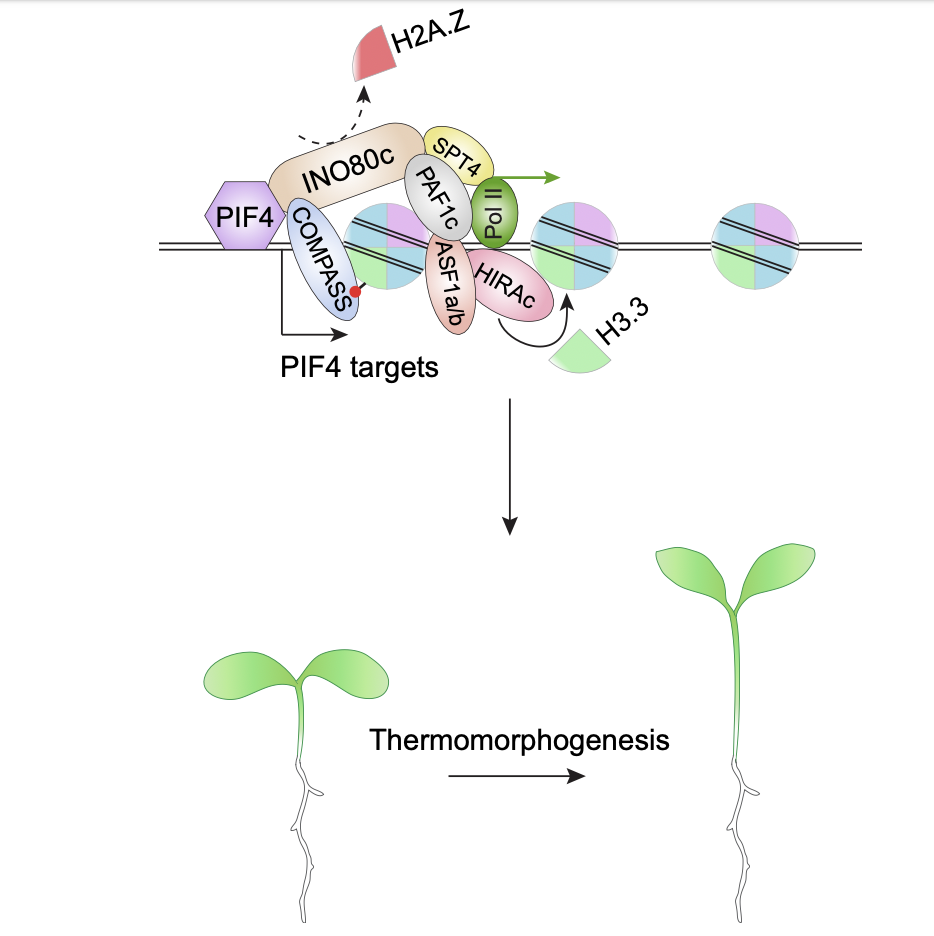
Coordinated histone variant H2A.Z eviction and H3.3 deposition control plant thermomorphogenesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe effect of temperature on plant morphology is known as thermomorphogenesis. The phytohormone auxin is important for thermo-induced cell elongation. In Arabidopsis thaliana, Phytochrome-Interacting Factor 4 (PIF4) forms the central hub of the thermal response pathway and directly regulates auxin synthesis…

PIF4 regulates microtubule organization to mediate high temperature–induced hypocotyl elongation
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant growth adaptation to heat stress (thermomorphogenesis) is regulated by changes in plant morphology such as petiole and hypocotyl elongation. One of the known players in this response is PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4), a central regulator of hypocotyl elongation. However, the mechanisms…
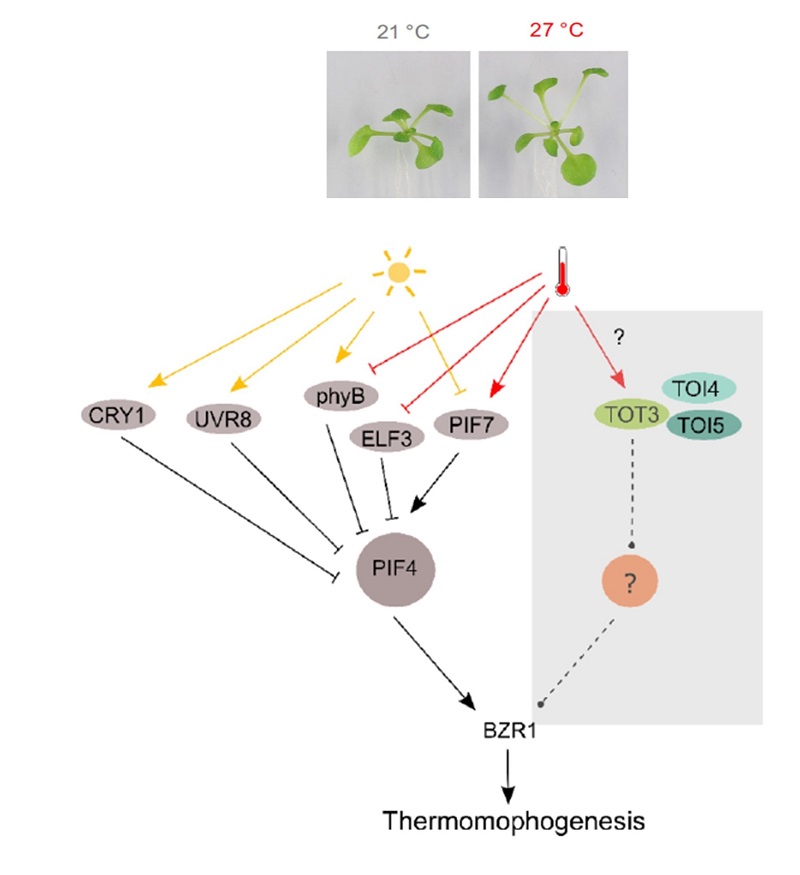
A TOTally new pathway regulating thermomorphogenesis (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIncrease in ambient temperature often causes remarkable changes in the shape and organization of plant body, including elongation of hypocotyl and petioles, early flowering, and reduction in stomatal index, collectively known as thermomorphogenesis. Virtually all the molecular pathways that are known…

