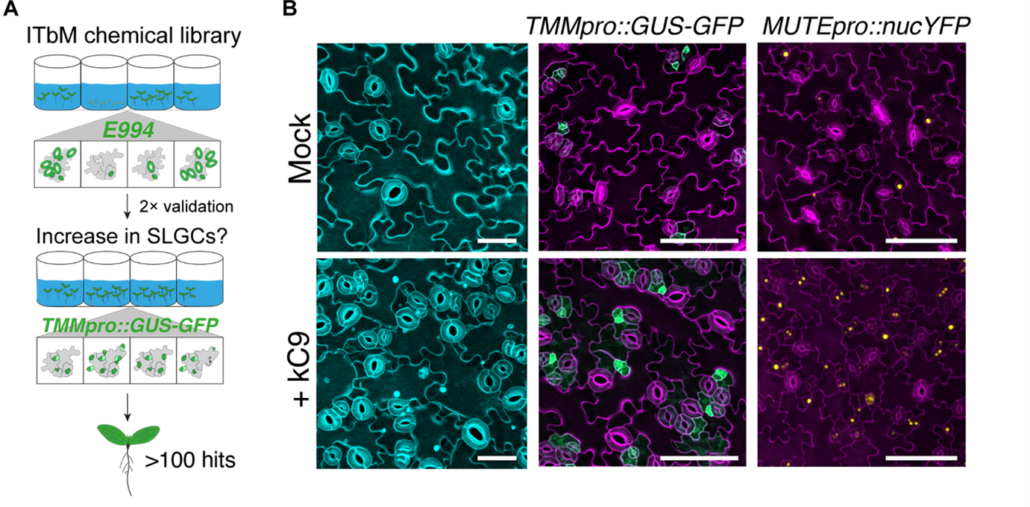
Finding balance: How plants achieve signal specificity in stomatal development and defense
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants need to develop and grow within their environment whilst defending themselves against potential external threats. There are limited resources for these energy-intensive processes and so cross-talk is common between the signalling pathways to find balance between growth and defence. Hermann et…
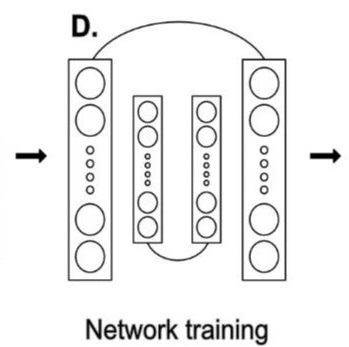
Review: Deep learning approaches to understanding stomatal function
Plant Science Research WeeklySydney Brenner famously said, “Progress in science depends on new techniques, new discoveries and new ideas, probably in that order.” Right now, we’re seeing how advancements and new techniques in artificial intelligence and deep learning are being applied in plant sciences, including in the analysis…
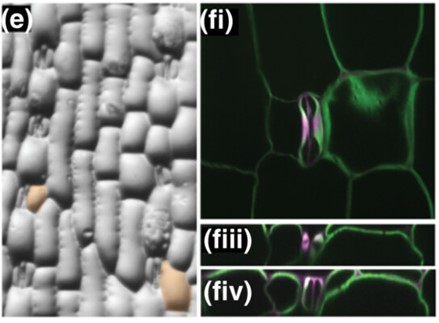
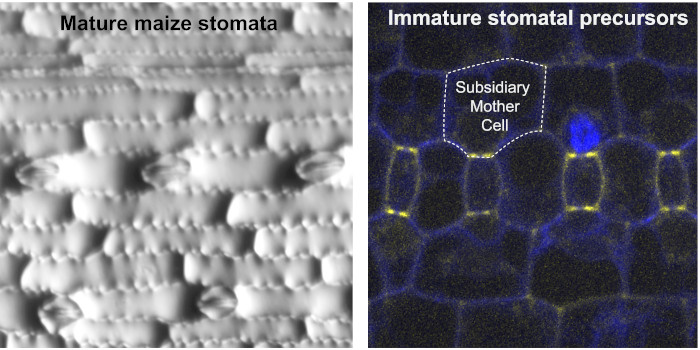
Subsidiary cells mediate stomatal closure in maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are pores on leaves which enable gas exchange. In grasses, stomata are surrounded by dumbbell-shaped guard cells that are flanked by subsidiary cells. However, the role of the subsidiary cells in stomatal closure is not fully understood. Here, Liu et al. investigated this using two maize (Zea…
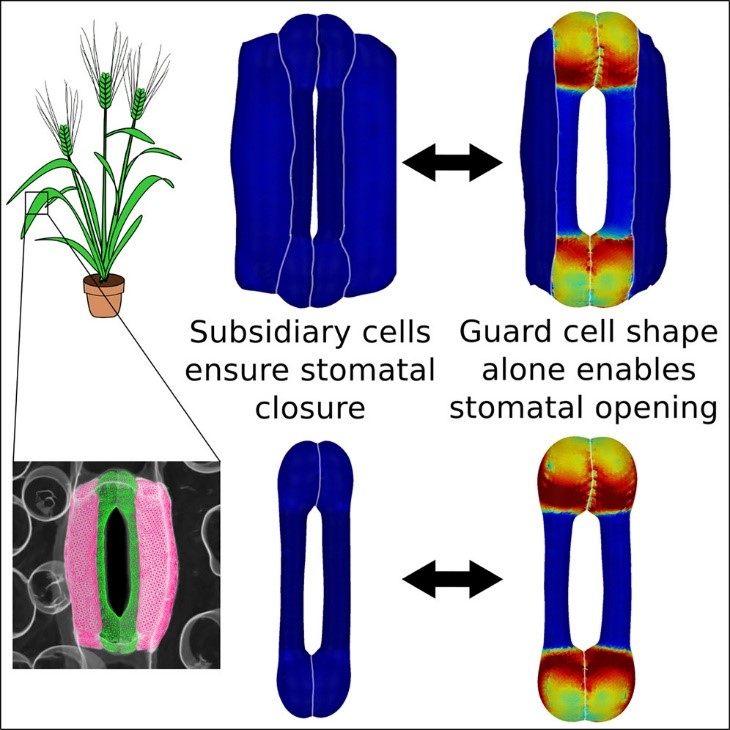
Grasses exploit geometry for improved guard cell dynamics
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are pores on the surface of leaves essential for gas exchange. In grasses, stomatal aperture is controlled by pairs of dumbbell shaped guard cells, with each guard cell surrounded by a subsidiary cell. Despite cell geometry being well described, it was unclear how it influences stomata function.…
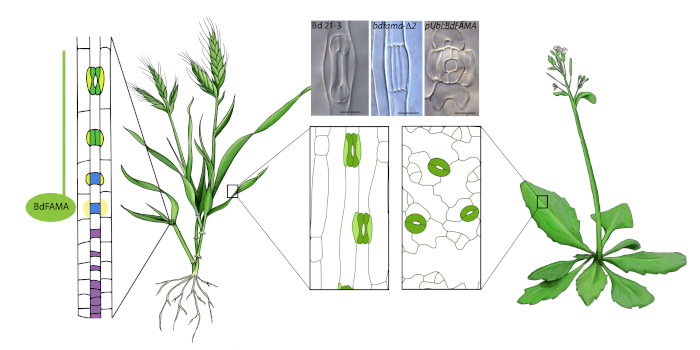
Helping out a neighbor: What FAMA tells us about specialization among stomatal genes across different species
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAuthor et al. explore the genes involved in making stomata in a temperate grass.
Katelyn Hansen-McKown and Dominique Bergmann, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford University and Howard Hughes Medical Institution.
Background: Plants are essential players in global carbon and water…
Microtubule control during stomatal movement
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. investigate the function of SPR1 in ABA-induced stomatal closure
By Pan Wang and Sijia Qi
State Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry; Department of Plant Sciences, College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China
Background: Drought…
At the right time and in the right place: WPRs functions in maize stomatal development
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellNan et al. examine the localization of key factors in maize stomatal development.
Qiong Nan and Michelle Facette
Department of Biology, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, 01003, USA
Background: Stomata are small pores on the plant surface that open and close to allow gas exchange––allowing…
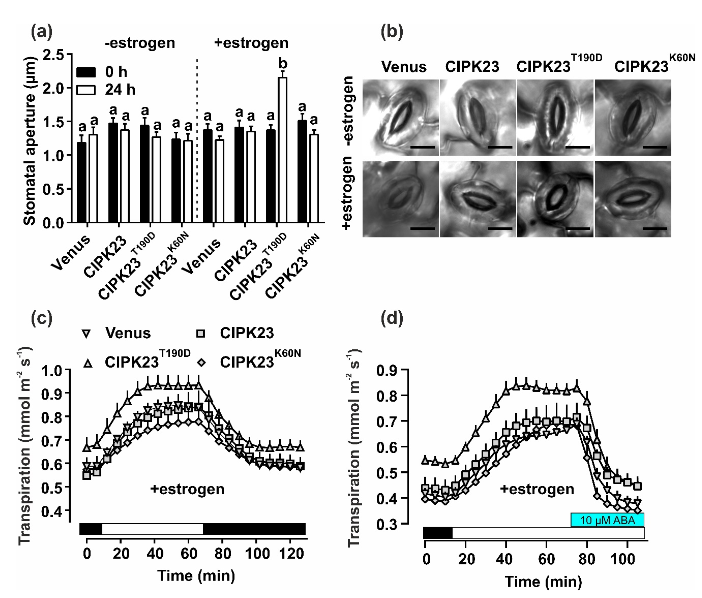
Control of guard cell aperture by protein kinase CIPK23
Plant Science Research WeeklyGuard cells are responsible for the opening and closing of stomata through changes in osmotic content and turgor pressure. These changes occur in response to activation or inactivation of ion transport proteins that are in turn regulated by protein kinase and phosphatase networks. The kinase network…

Improving water use efficiency in maize
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBlankenagel et al. discover a major link between variation in water use efficiency and carbon isotope discrimination
By Sonja Blankenagel, Stella Eggels, and Viktoriya Avramova
Plant Breeding, TUM School of Life Sciences, Technical University of Munich
Background: Growing crops with high…

