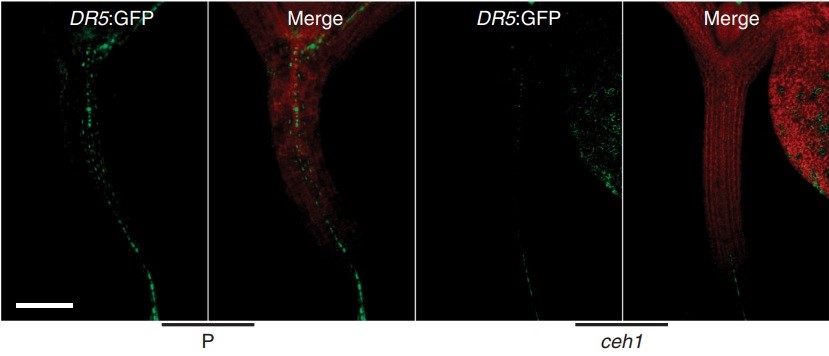
Interplay of auxin and MEcPP regulates adaptive growth (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMEcPP, methylerythritol cyclophosphate, is an essential bifunctional plastidial metabolite that serves as a precursor of isoprenoids and is produced by the plastidial methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. Jiang et al. demonstrated that MEcPP controls adaptive growth by regulating auxin responses…
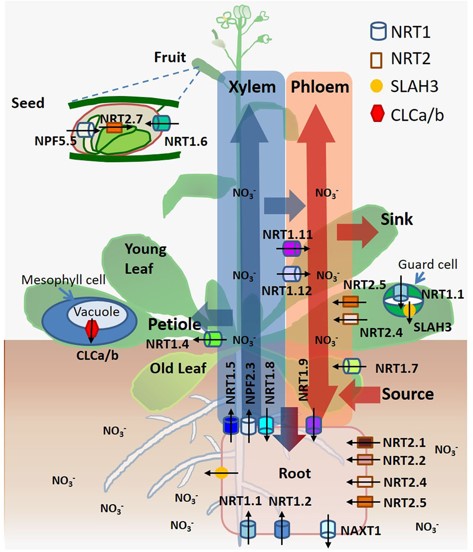
Dancing with hormones: A current perspective of nitrate signaling and regulation in Arabidopsis (Frontiers in Plant Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen (N) is a main constituent of amino acids and nucleotides and therefore plays a central role in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plants are able to take up nitrogen from the soil in two forms, nitrate and ammonium. Nitrate is the predominant form of nitrogen found in most crop…
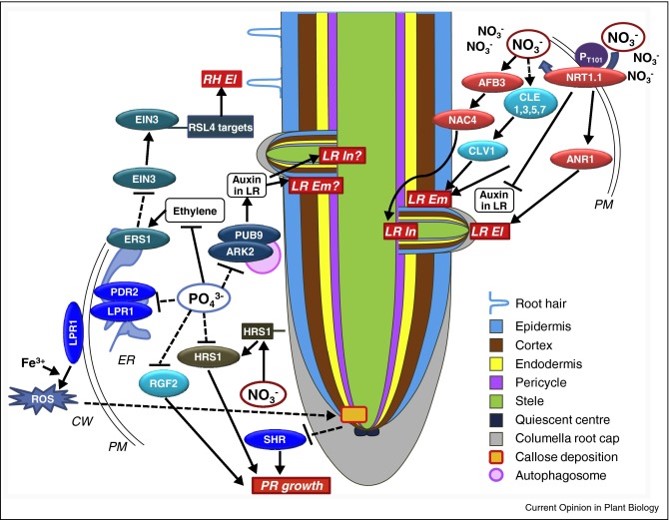
Food for thought: How nutrients regulate root system architecture (Current Opinion in Plant Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe arrangement of a plant’s root system in the soil (root system architecture, RSA) changes in response to nutrients through different signaling pathways. It is assumed that RSA adapts to optimize the uptake of nutrients from the environment, but strong evidence is still lacking. This review by Shahzad…
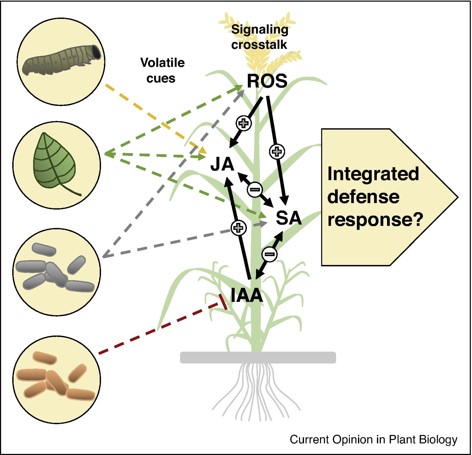
Volatiles as inducers and suppressors of plant defense and immunity — origins, specificity, perception and signaling (Current Opinion in Plant Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen plants are under attack by herbivores and microbes, running away is not an option. As a defence, plants produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that repel herbivores, attract enemies of the herbivores, or alarm surrounding plants; VOCs have mostly been viewed as positive regulators in the plant…
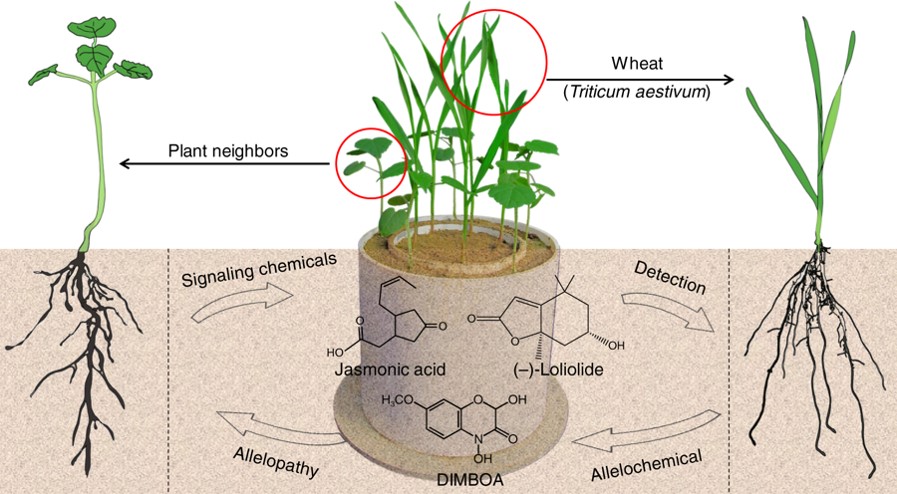
Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are not able to move out of their neighborhood if they are unhappy, but they are capable of recruiting and assembling a community in which they are able to thrive. Plants are also able to initiate defense when they sense that threats are near. To keep tabs on their neighbors, plants utilize both…
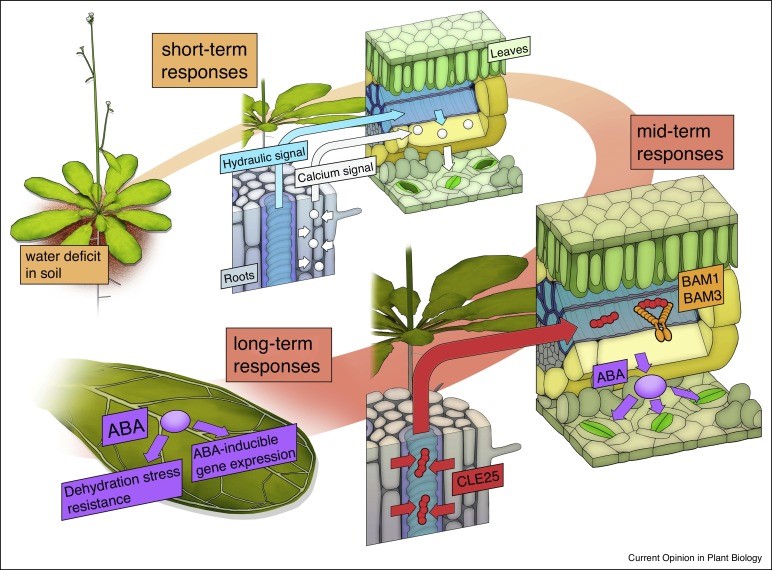
Review: Long distance signlaing in plant stress response (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo compensate for their lack of a nervous system, vascular plants have developed complex mechanisms to connect their organs and coordinate stress. Many different types of molecules are involved in long-distance signaling and must be integrated to maintain homeostasis. In this review, Takahashi and Shinozaki…
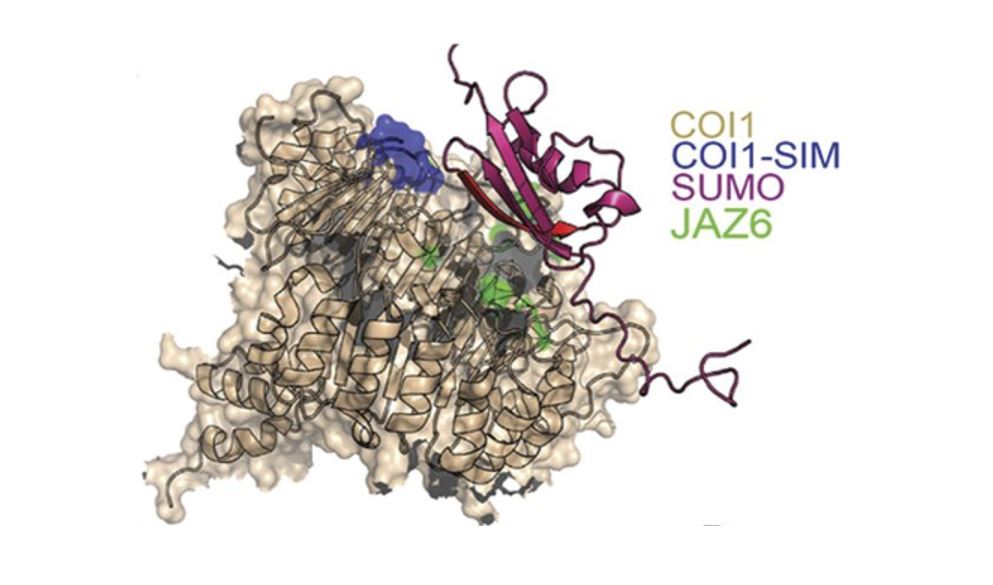
SUMO Aids Rapid Regulation of Hormone Responses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSrivastava et al. identify a mechanism for rapid regulation of jasmonic acid signaling. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00036
Background: The sessile nature of plants dictates that growth must be integrated with changes in the natural environment. Modulation of hormone signalling pathways…
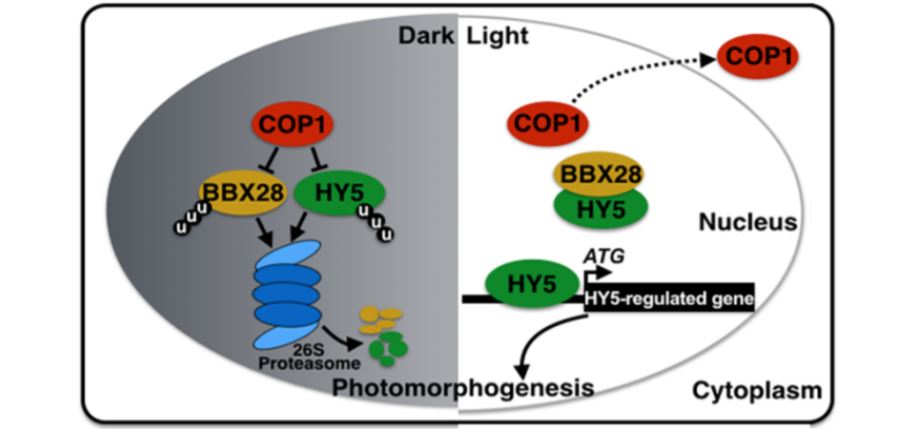
BBX28 Negatively Regulates Photomorphogenesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLin et al. show that B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN28 plays a role in regulating plant development in response to light signals. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00226.
By Dongqing Xu and Xing Wang Deng
Background: Sunlight is one of the key environmental cues influencing plant growth and development.…
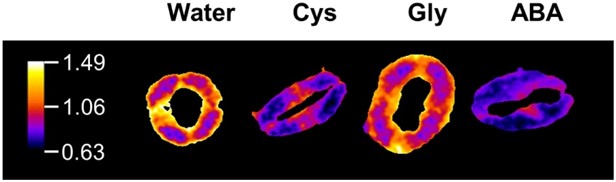
Uncovering the Steps Before: Sulfate Induces ABA Biosynthesis and Stomatal Closure
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant stomatal aperture regulation via guard cells is an example of how plants dynamically process environmental signals to induce a physiological response. The drought stress hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is a well-characterized signal that induces stomatal closure, preventing water loss. ABA acts via…

