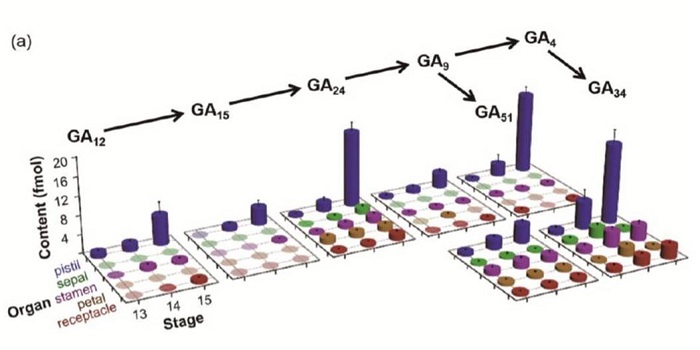
Technical Advance: Quantification of near attomole gibberellins in floral organs dissected froma single Arabidopsis flower ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
We all learned the series milli-, micro-, nano-, pico-, femto-, but I didn’t learn atto- (10-18), as it’s rarely used in biology, representing such a tiny number (FYI, atto- is followed by zepto- and yocto-). Li et al provide a method for quantifying gibberellin (GA) hormones at “near attomole”…
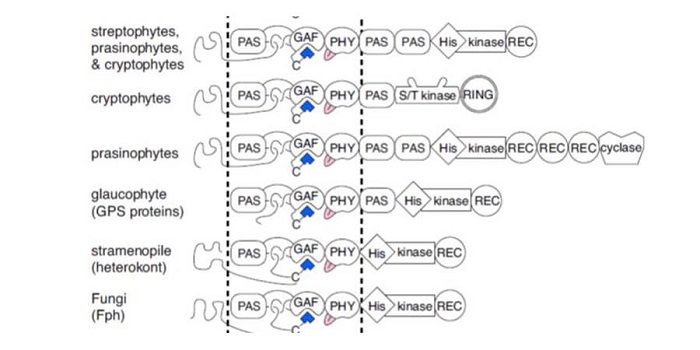
Review: Phytochrome diversification in cyanobacteria and eukaryotic algae ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhytochromes were first characterized in classic studies of plants, in which their contributions to seed germination and initiation of flowering were described. Subsequently, phytochromes were identified in cyanobacteria and in non-photosynthetic organisms including fungi. Rockwell and Lagarias review…
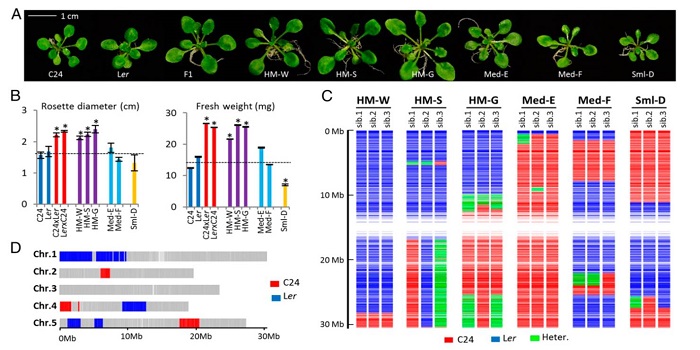
PIF4-controlled auxin pathway contributes to hybrid vigor in Arabidopsis thaliana
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHybrid vigor is a well-known but still poorly understood phenomenon in which the F1 hybrid progeny of a cross often show enhanced growth as compared to either parent. True-breeding lines that retain this enhanced growth, known as hybrid mimics, have been developed and are important tools for understanding…
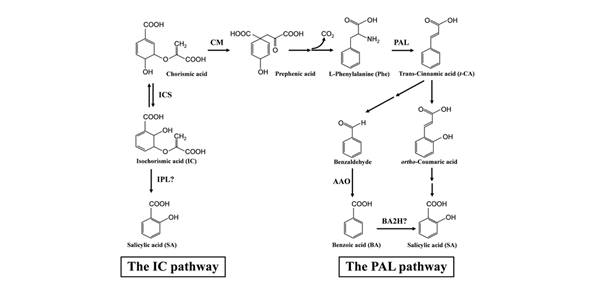
Review: How multifaceted salicylic acid combats disease in plants and humans
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe journal BMC Biology publishes occasional Question and Answer articles, including a series on plant signals. In the latest installment of this series, Dempsey and Klessig write about the hormone salicylic acid (SA) and how it combats disease in plants and humans. The article focuses on SA in plants…
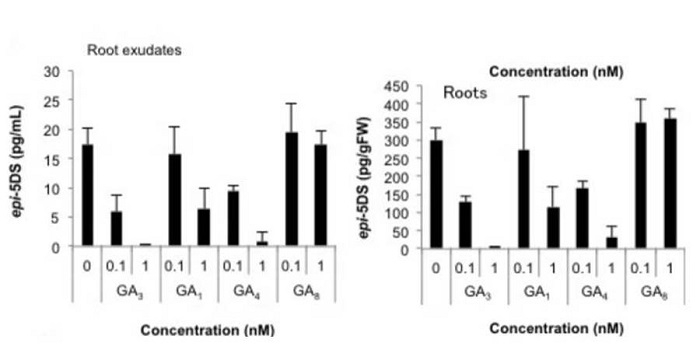
Regulation of strigolactone biosynthesis by gibberellin signaling
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn a screen for chemicals that regulate strigolactone (SL) levels in rice, Ito et al. found that gibberellins suppress SL biosynthesis. This effect depends on the gibberellin signaling module, and involve a decrease in expression level of SL-biosynthetic genes. Furthermore, GA treated rice exuded less…
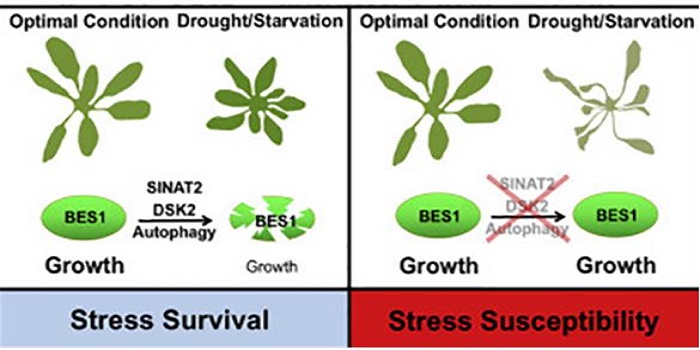
Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBrassinosteroid (BR) signaling promotes growth and development by regulating gene expression through the BES1 and BZR1 transcription factors. Nolan et al. show how plants balance growth and stress tolerance by cross-talk between the BR and autophagy pathways. Under environmental stresses, BES1 is targeted…
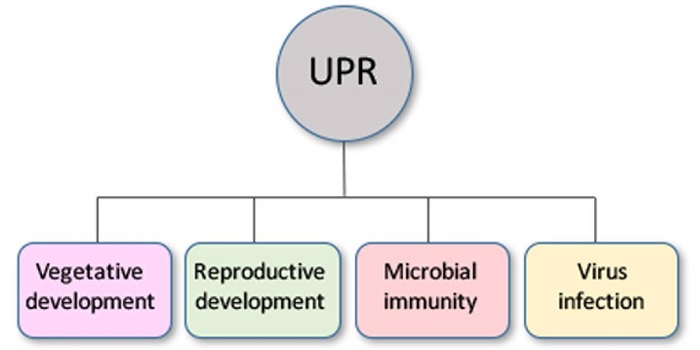
Review: The unfolded protein response in development, defense, and stress
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe unfolded protein response (UPR) is a eukaryote-wide signalling pathway in which unfolded proteins in the ER (often caused by abiotic stress) initiate signals transduced to the nucleus that lead to the expression of stress-response genes. Bao and Howell review the UPR in plants. They describe two…
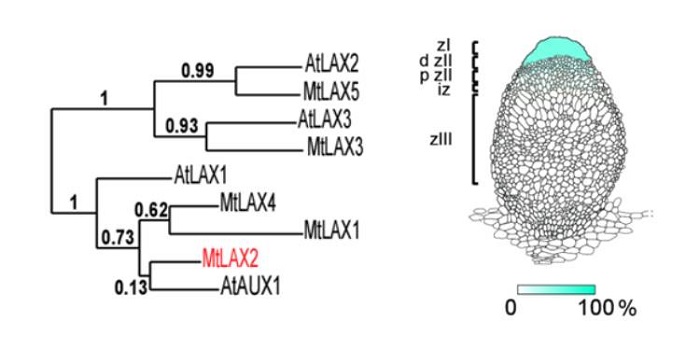
MtLAX2, a functional homologue of the auxin influx transporter AUX1, is required for nodule organogenesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNodules are specialized structures that form symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing associations with rhizobia on some plants including Medicago truncatula. Previous work has shown that auxin signalling is involved in nodule formation. Roy et al. extend this knowledge through the identification of a Medicago gene…
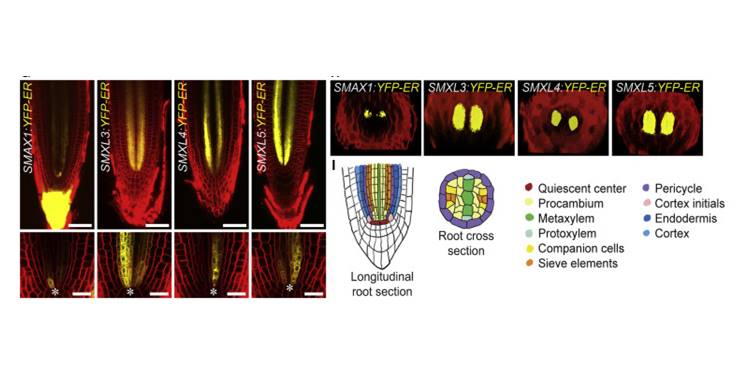
Strigolactone- and karrikin-independent SMXL proteins are central regulators of phloem formation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSMAX1 (SUPPRESSOR OF MAX2 1) was identified genetically as a suppressor of the enhanced seed dormancy phenotype of the max2 mutant, which is affected in both strigolactone (SL) and karrikin (KAR) responses (karrikins are smoke-derived germination promoters). SMAX1 is the founding member of an eight-member…

