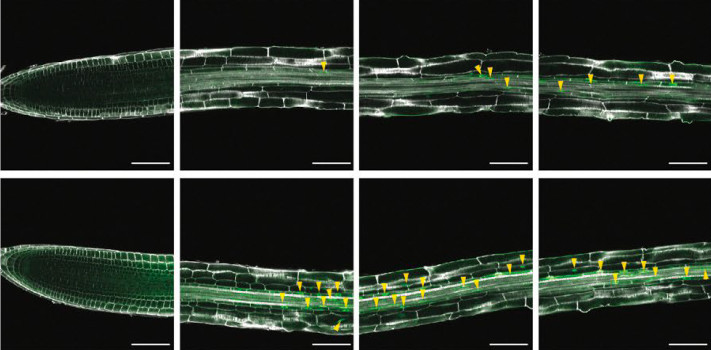
Rooting in salt: It’s not all about auxin
Yanxia Zhang1,2
1 Laboratory of Plant Physiology, Wageningen University & Research, The Netherlands
2 College of Agriculture, South China Agricultural University, China
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad317
Background: Soil salinity causes crop yield losses world-wide. Adjusting plant…
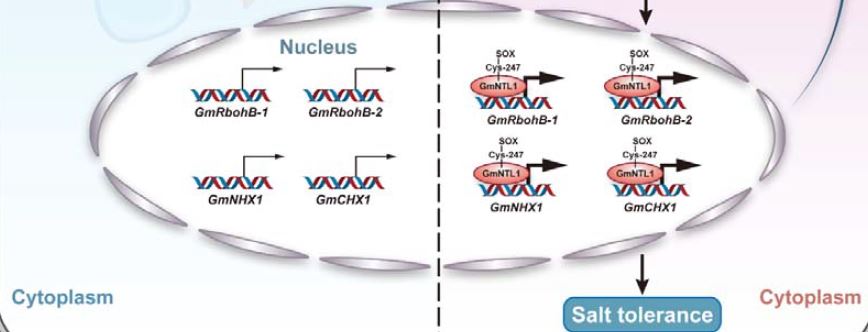
The Membrane-bound Transcription Factor GmNTL1 Promotes Salt Tolerance in Soybean
Zhang et al. identified a membrane-bound NAC transcription factor GmNTL that can be oxidized and released from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus, thereby regulating downstream target genes to promote salt tolerance in soybean.
Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad250
Wenxiao Zhang,…
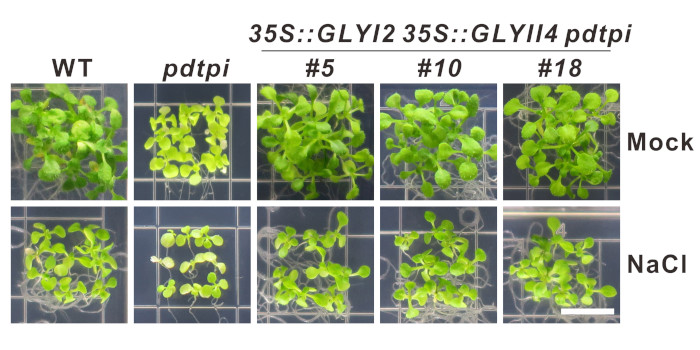
Salt stress disturbs sugar metabolism
Fu et al. examine how salt stress affects sugar metabolism via the reactive oxygen species hydrogen peroxide.
Zheng-Wei Fu (State Key Laboratory of Hybrid Rice, College of Life Sciences, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China)
Background: Soil salinization is a serious…
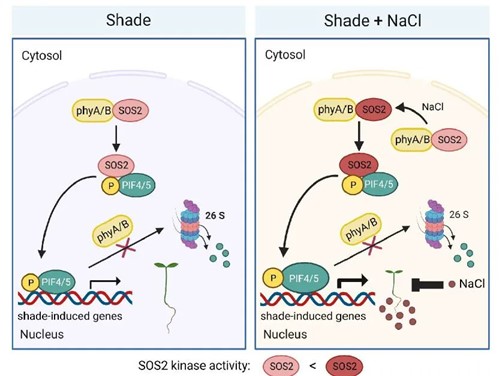
Shade finds a salty connection
Light acts as a crucial signal for plant growth and development and is perceived by several types of photoreceptors including phytochromes (phys). Sun-loving plants often exhibit shade avoidance syndrome (SAS), like longer hypocotyl, lesser branching, and earlier flowering to outcompete their neighbors…
Flowering Under Stress
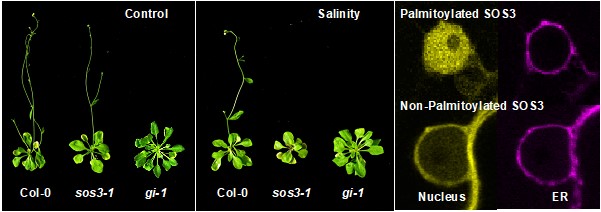
Park H.J., Gamez-Arjona F., et al. show how plants reset the time of flowering under salinity stress. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac289
Background: For plants, extremes in the cardinal conditions of light, temperature, nutrients and water availability are major drivers of natural selection.…

Hormone distribution via hydraulic flux determines root branching
Climate change affects rain patterns and hydrological cycles all over the world, exacerbating water scarcity issues. Root branching is altered by local spatial differences in soil moisture. Indeed, when root tips temporarily lose contact with moisture, root branching stops until the appropriate moisture…
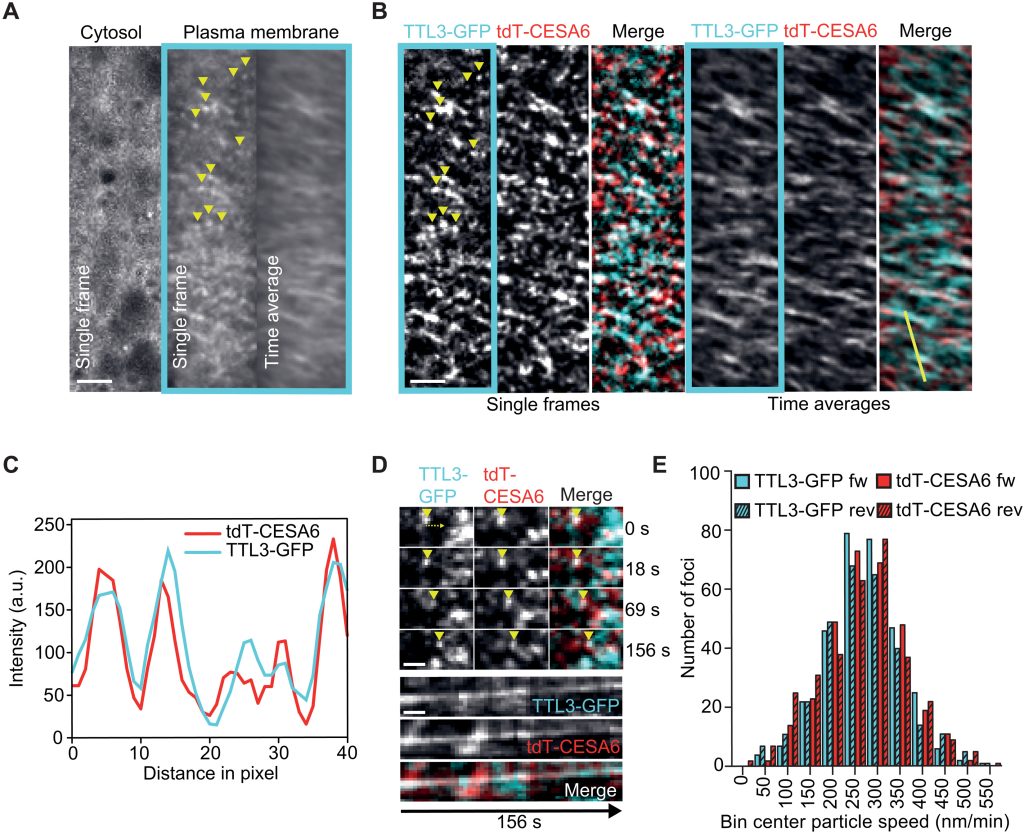
TTL bridges microtubules and cellulose synthase complexes
Cellulose synthase (CESA) complexes (CSCs) synthesize the main polysaccharide component of plant primary cell wall, cellulose. The trafficking and dynamics of CSC are tightly regulated. Kesten et al. identified a new family of CSC- and microtubule-interacting proteins, named TETRATRICOPEPTIDE THIOREDOXIN-LIKE…

Tobacco leaf tissue rapidly detoxifies direct salt loads without activation of calcium and SOS signaling (New Phytol)
Salinity stress is one of the primary abiotic causes of crop loss worldwide. In roots, the early response to high salt levels is coordinated largely via the well characterized salt-overly sensitive (SOS) pathway, which is dependent on Ca2+ signaling. However, how plants cope with elevated salt levels…

