
A Timer of Mr. Anther: Haste Makes Waste
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFang, Guo, Wang, et al. explore the molecular mechanism underlying anther dehiscence in rice.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae028
Yuxing Fang, State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, School of Life Sciences, Peking University.
Yi Wang, State Key Laboratory of Protein and…

Casparian strip formation at root endodermal and non-endodermal cell layers in rice
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. investigate the role of the OsCIF1/2–OsSGN3a/b signaling pathway in Casparian strip formation in rice.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad269
By Jixing Xia, of Life Science and Technology, Guangxi University, China.
Background: The Casparian strip (CS) is a belt-like lignin-based…

Cytokinin signaling determines rice panicle size
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellChun, Fang, Savelieva, Lomin et al. explore the mechanism by which cytokinin signaling influences the size of rice panicle.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad257
By Yan Chun (淳雁), and Xueyong Li (李学勇)
National Key Facility for Crop Gene Resources and Genetic Improvement, Institute…

Jasmonate-regulated gibberellin catabolism slows rice growth during herbivory
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellJin et al. identify a mechanism for rice growth suppression during herbivore attack.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad191
Gaochen Jin1, Jinfeng Qi2, Hongyue Zu1, Shuting Liu1, Jonathan Gershenzon3, Yonggen Lou1, Ian T. Baldwin4, Ran Li1,*
1State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology, Ministry of…
Epigenetic regulation during rice domestication and de-domestication
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCao et al. investigate the role of epigenetic variation in rice domestication and de-domestication. The Plant Cell (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad160
By Shuai Cao1,2 and Qingxin Song1
1 State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Germplasm Enhancement, Nanjing Agricultural University,…

Oryza glumaepatula: A wild relative to improve drought tolerance in cultivated rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen we speak about rice, we’re often referring to one of two domesticated species, Oryza japonica or Oryza indica. However, there are an additional 25 species in the genus Oryza. These so-called wild relatives harbor substantial genetic diversity that holds promise for crop improvement. Here, Prakash…

Residues required for polar localization of rice Si transporter
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKonishi et al. explore the mechanism underlying the polar localization of a silicon transporter.
By Noriyuki Konishi, Namiki Mitani-Ueno, Naoki Yamaji and Jian Feng Ma
Institute of Plant Science and Resources, Okayama University, Chuo 2-20-1, Kurashiki, 710-0046 Japan
Background: Silicon (Si)…
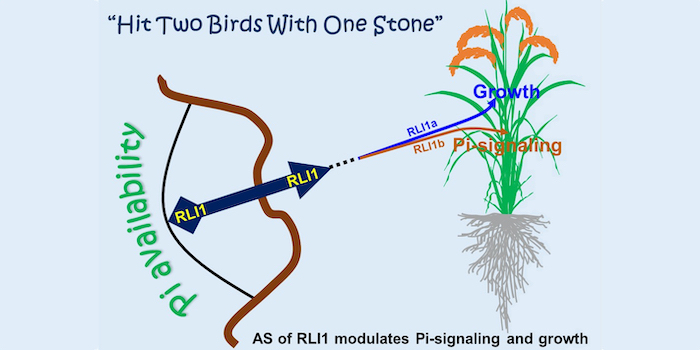
Alternative splicing orchestrates phosphate signaling and plant growth
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellGuo et al. demonstrate that alternative splicing of REGULATOR OF LEAF INCLINATION 1 modulates phosphate signaling and plant growth in the face of phosphate deficiency.
By Meina Guo, Wenyuan Ruan, and Keke Yi
Background: Phosphate (Pi) limitation represents a primary constraint on crop production.…

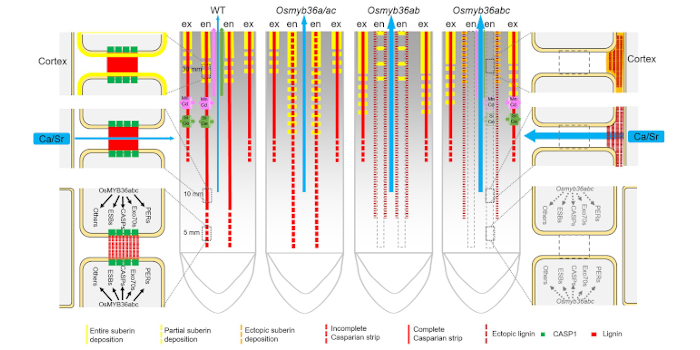
Casparian Strip formation at the root endodermis in rice
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. identify three OsMYB36s that redundantly regulate Casparian strip formation.
Jixing Xia; College of Life Science and Technology, Guangxi University, China
Background: The Casparian strip (CS) is a ring-like lignin-rich structure in the anticlinal cell wall between endodermal cells…

