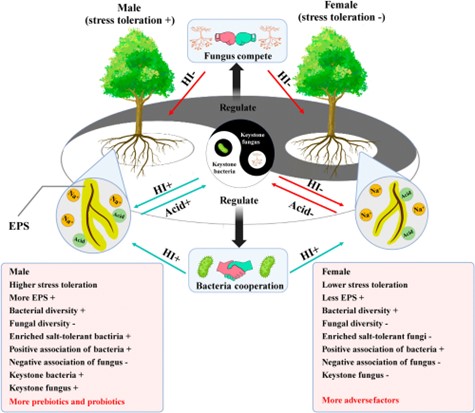
Dioecious dynamics: How male and female poplars shape microbial networks under stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants actively shape the microbial community in their rhizosphere to optimize nutrient acquisition and enhance resilience against environmental stresses. Interestingly, in dioecious plants, male and female individuals play distinct ecological roles and evolve different environmental adaptability. For…
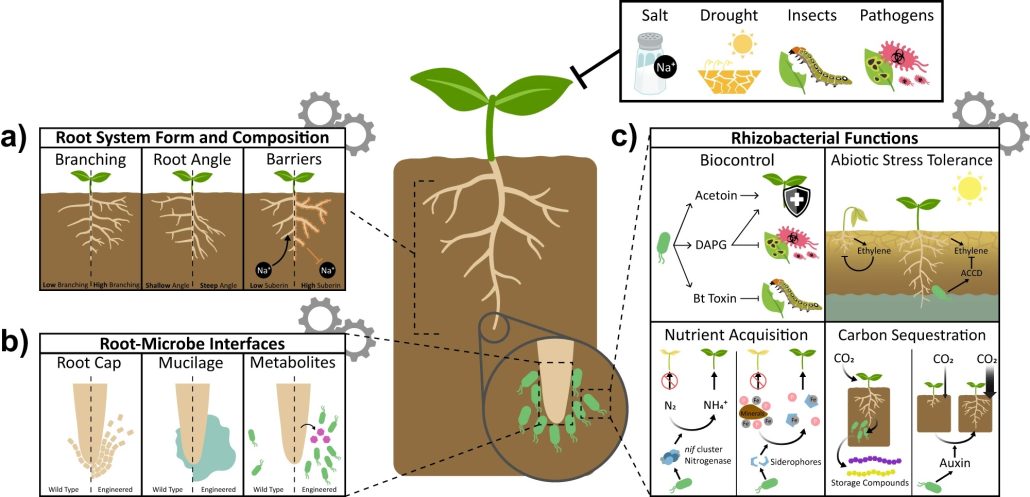
Review: SynBio takes on roots and the rhizosphere
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is an excellent introduction to how synthetic biology can be used to program plants for climate resilience by engineering them to respond predictably and in ways beyond those that evolution has explored, through the use of controllable synthetic gene circuits. Ragland et al. describe how precise…

Cross-enrichment of rhizobacteria improves iron nutrition during intercropping
Plant Science Research WeeklyIntercropping, the system of growing at least two crops simultaneously, increases crop productivity and ecological sustainability. An intercropping system of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and maize (Zea mays) has been previously found to improve the yield of peanut, specifically its iron nutrition and…

Silicate enhances rhizobacteria network complexity in sugarcane rhizosphere
Plant Science Research WeeklySilicon (Si) plays a significant role in helping plants to mitigate biotic and abiotic stress. Previous studies have shown that the application of Si also influences the microbial communities in the rhizosphere. However, the extent to which Si shapes the dynamics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria…
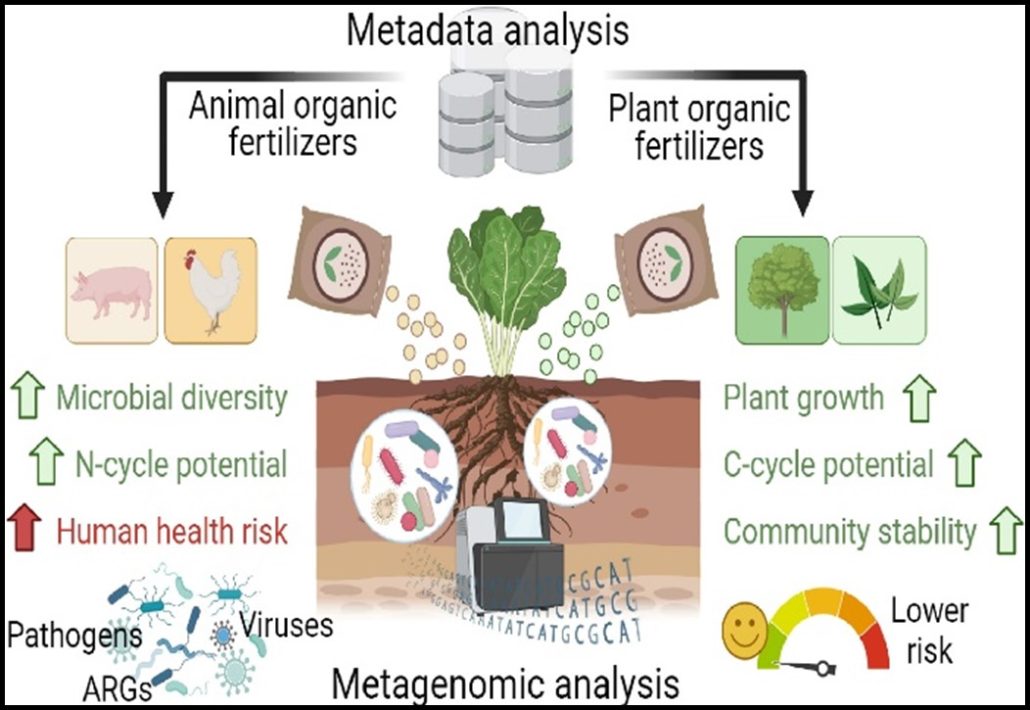
Effect of plant-derived versus animal-derived fertilizers on the rhizosphere microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklyYu et al. conducted a meta-analysis of published 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequenced soil samples to compare the effects of plant-based fertilizers (e.g. compost, seaweed fertilizer) versus animal-based fertilizers (e.g., dung, manure) versus control, unfertilized samples on soil microbial diversity and…
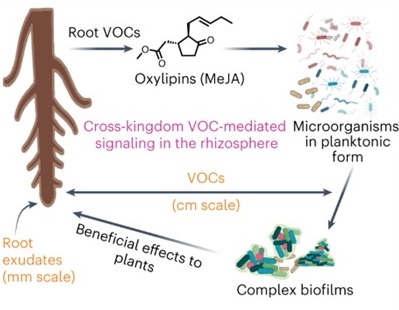
Volatile methyl jasmonate from roots triggers host-beneficial soil microbiome biofilms
Plant Science Research WeeklyVolatile molecules released from plant roots (root VOCs, rVOCs) can diffuse over long distances, thereby increasing the sphere of plant influence. However, their influence on complex soil microbial communities (or microbiomes) and ecological implications are poorly understood, mainly due to technical…
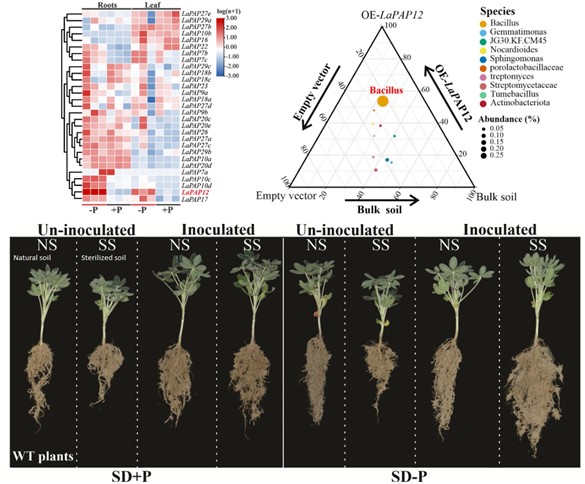
Root acid phosphatases and rhizobacteria synergistically enhance white lupin and rice phosphorus acquisition (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P, Pi in the form of inorganic orthophosphate) is crucial for plant homeostasis because it is a plant growth-limiting factor. White lupin is an excellent crop model to study Pi changes due to the development of cluster roots (CR). CR are composed of rootlets that allow a more efficient Pi…

