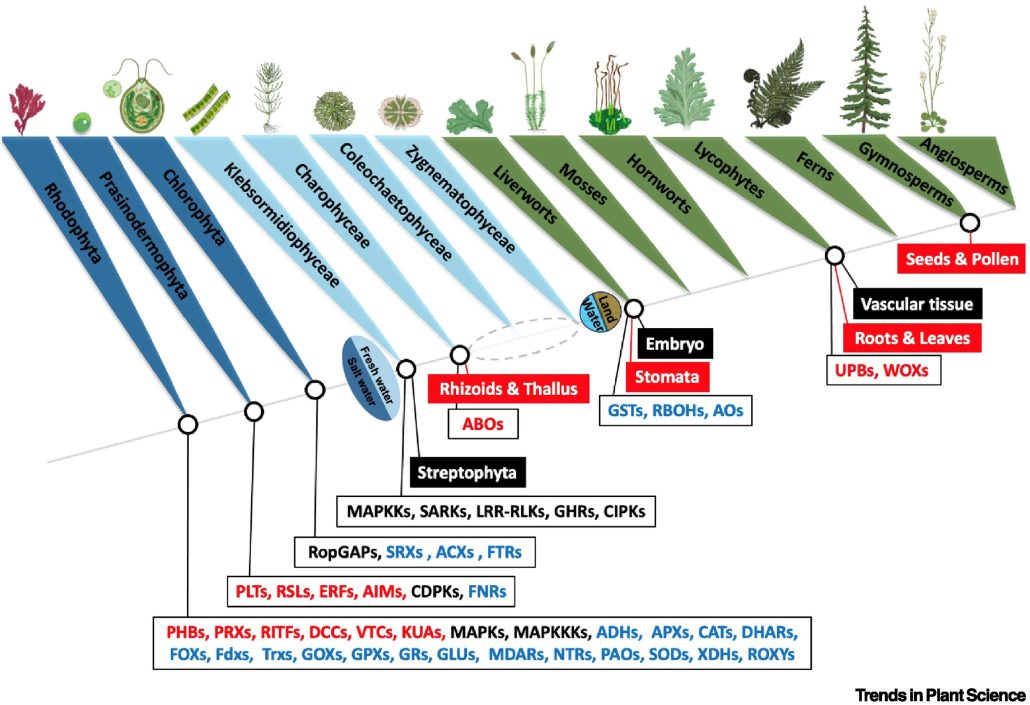
Review: Evolution of ROS targets for plant development
Plant Science Research WeeklyReactive oxygen species (ROS) are agents of damage but also potent signals. Here, Singh et al. review the cellular targets that support ROS signaling across the green kingdom. Many of the signaling roles for ROS have been uncovered in Arabidopsis and other angiosperms, so it is interesting to look at…
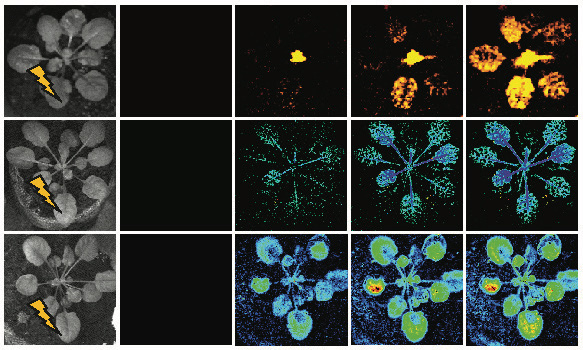
Identification of a plant receptor required for cell-to-cell reactive oxygen signaling
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFichman et al. identify a key player linking reactive oxygen species and calcium signals (but not electric signals) during responses to light stress. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac241
Yosef Fichman and Ron Mittler
Division of Plant Sciences and Technology, College of Agriculture Food and Natural…
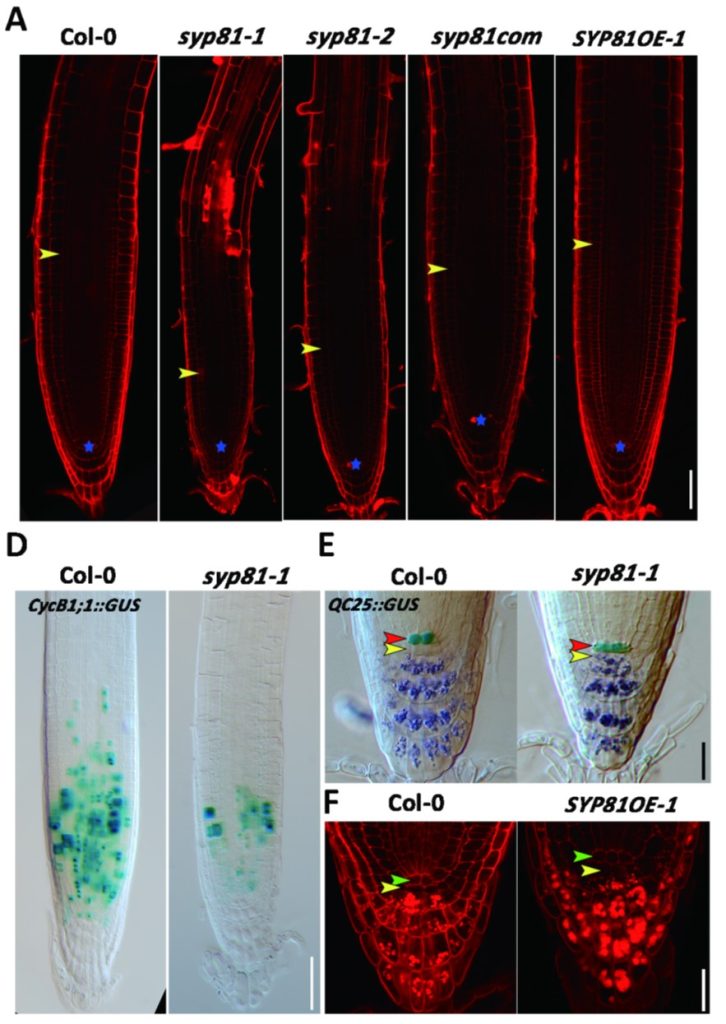
SYO81 regulates root meristem activity via ROS signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyLately, reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been recognized as signaling molecules that regulate plant cellular proliferation and differentiation in many areas of the plant, including root tips. Chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria are the main cellular compartments for ROS generation in cells.…
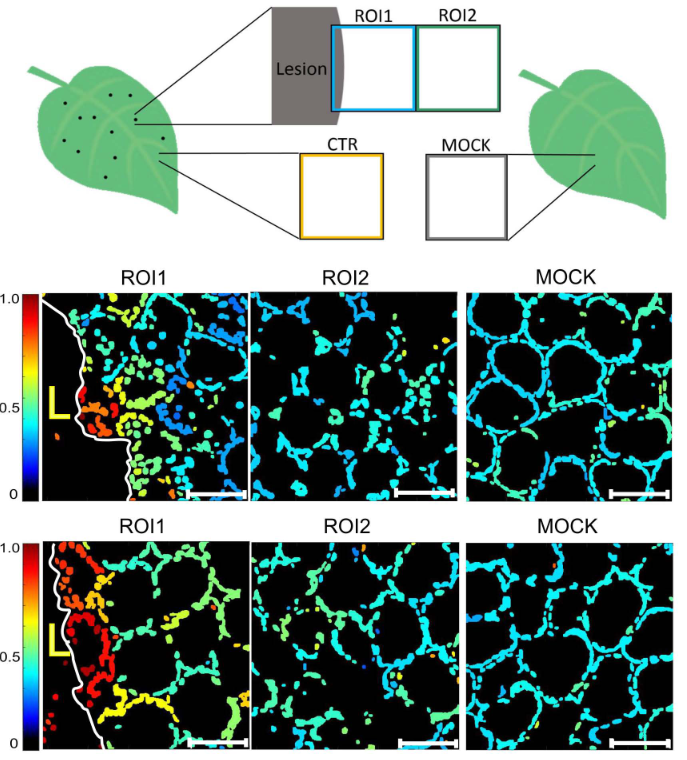
Chloroplast redox state changes mark cell-to-cell signalling in the hypersensitive response (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProgrammed cell death (PCD) plays roles in both developmental and environmental responses across plant species. During pathogen attack, the hypersensitive response can limit spread of infection by orchestrating an organised death of cells around the infection area. A recent study by Lukan et al. demonstrated…
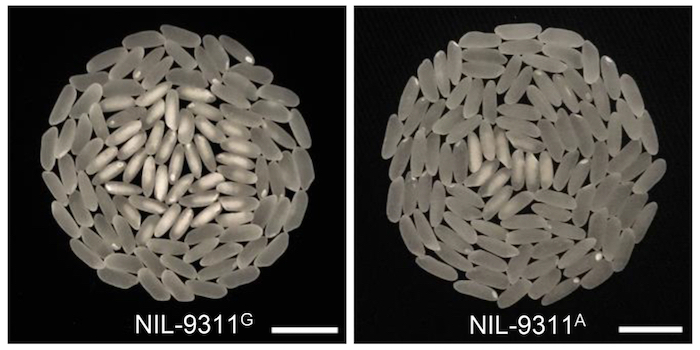
WHITE-CORE RATE 1 regulates grain chalkiness in rice
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWu et al. uncover a mechanism underlying chalkiness, an important grain quality trait in rice.
Background: With improved living standards, the demand for better grain quality has become a challenge in rice production areas. Rice chalkiness, i.e., endosperm containing opaque regions, seriously reduces…
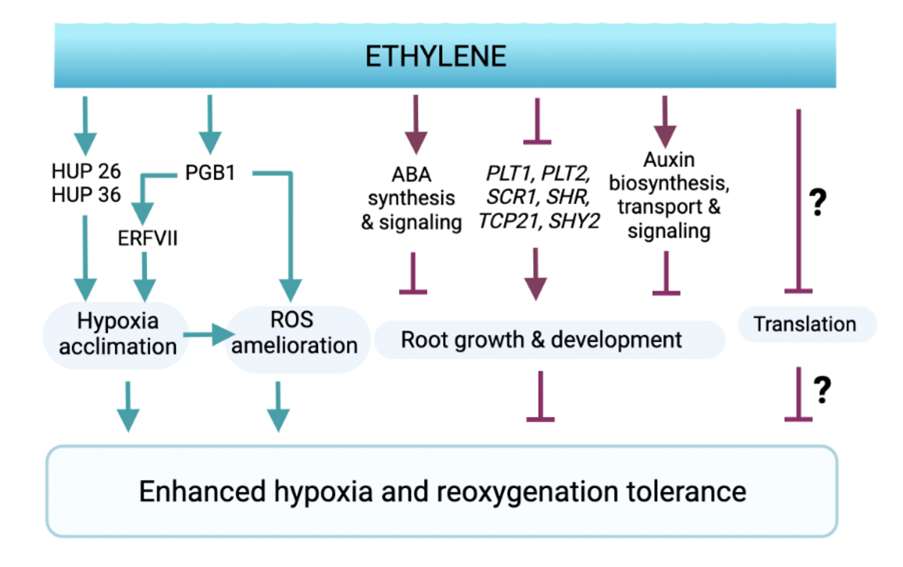
Ethylene augments root hypoxia tolerance through amelioration of reactive oxygen species and growth cessation (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlooding presents a dual threat to plants; not only is mitochondrial respiration supressed during the resulting hypoxic conditions, but once the floodwaters recede, the return to ambient oxygen levels triggers a cascade of harmful reaction oxygen species (ROS). One of the most well-studied responses…
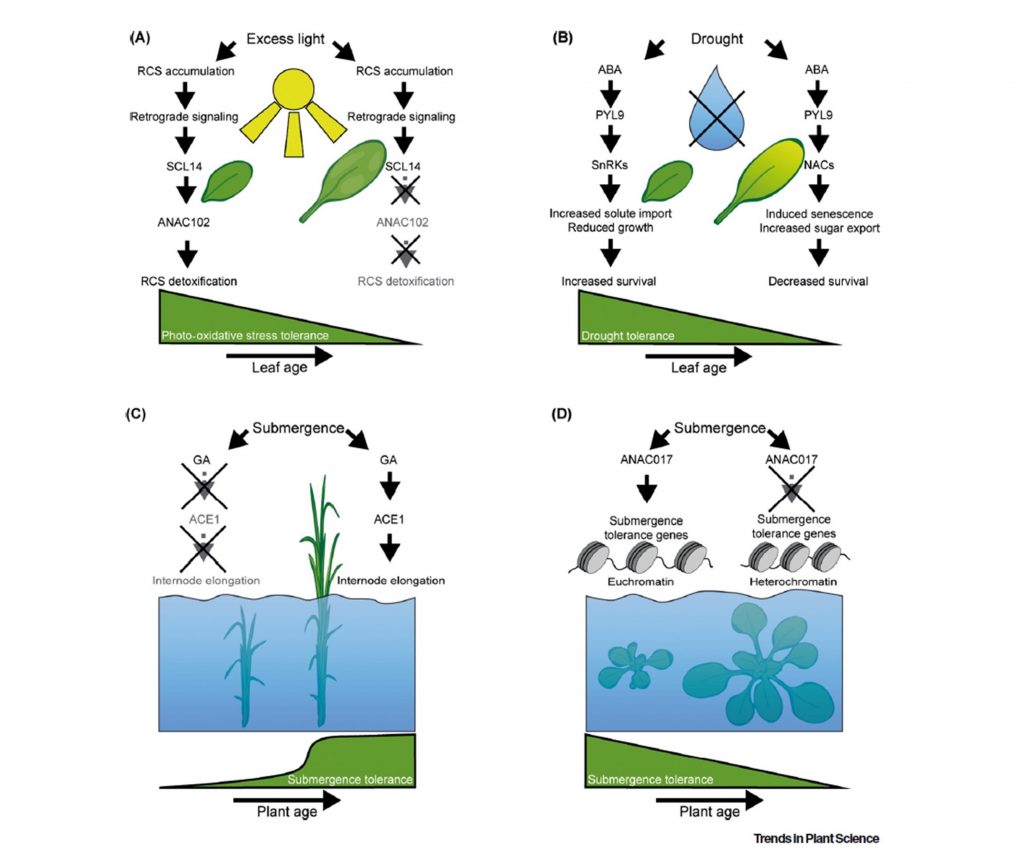
Review: Age is NOT just a number (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAging of plants is marked by the growth and differentiation of individual organs, as well as transitions of the whole plant through developmental phases: juvenile, vegetative adult, and reproductive phase. In their recent review, Rankenberg et al. discuss how abiotic stress responses vary in plants with…
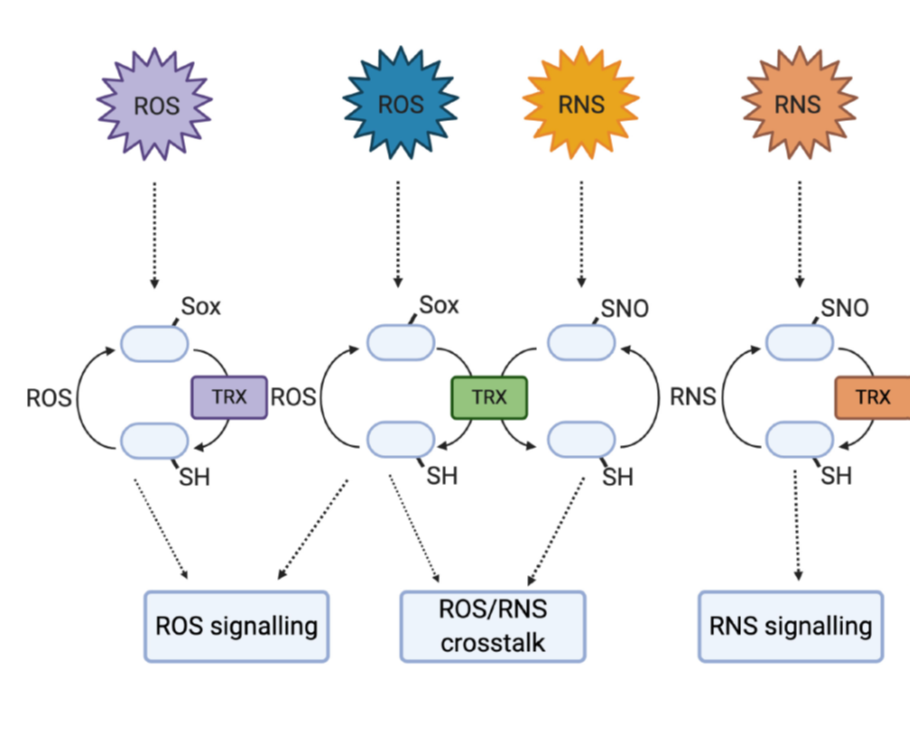
Review: Selective redox signaling shapes plant-pathogen interactions (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyReactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are often presented as something of enigmas. They are damaging by-products of metabolism and stress, but also intentionally produced as a signal and defense response to pathogens. This excellent Update by Bleau and Spoel synthesizes new…
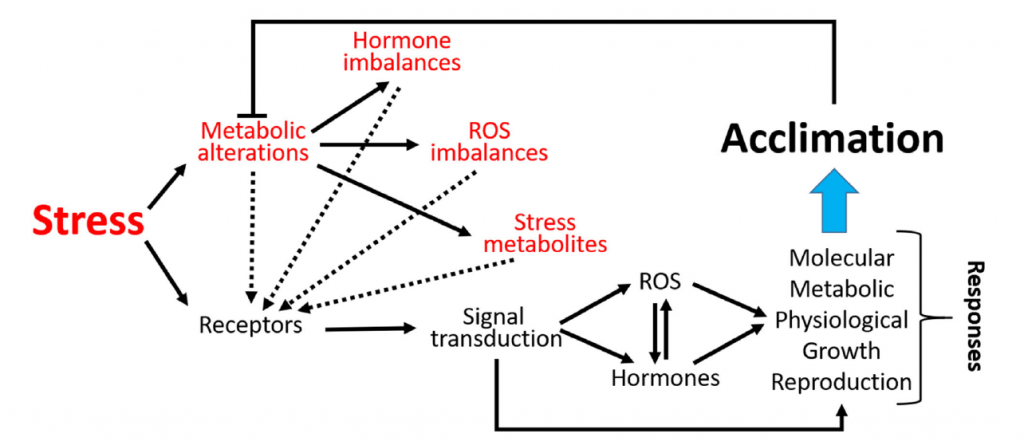
Review: Integration of reactive oxygen species and hormone signaling during abiotic stress (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
During its life cycle, a plant experiences many types of abiotic stress including drought. While waiting for the next drops of water, a thirsty plant acclimates by initiating a series of tolerance responses. Stress perception is followed by stress-induced signaling which can include reactive oxygen…

