
Auxin response factor targeted by viruses (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin regulates various aspects of plant growth and development and it also contributes to plant defense. Auxin activates downstream signaling by promoting degradation of the repressor Aux/IAA proteins to liberate the key transcription factors ARFs (auxin response factors). Pathogens have been known…
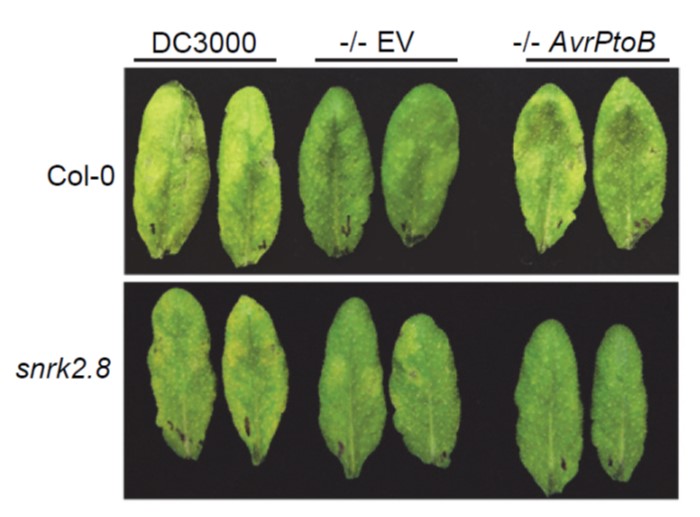
A plant kinase exploited by a bacterial effector (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved a suite of effector proteins that are secreted into plants and aid successful colonization. AvrPtoB is a well-conserved effector of pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae strains that targets multiple plant defense-related proteins and is required for pathogen virulence and bacterial…
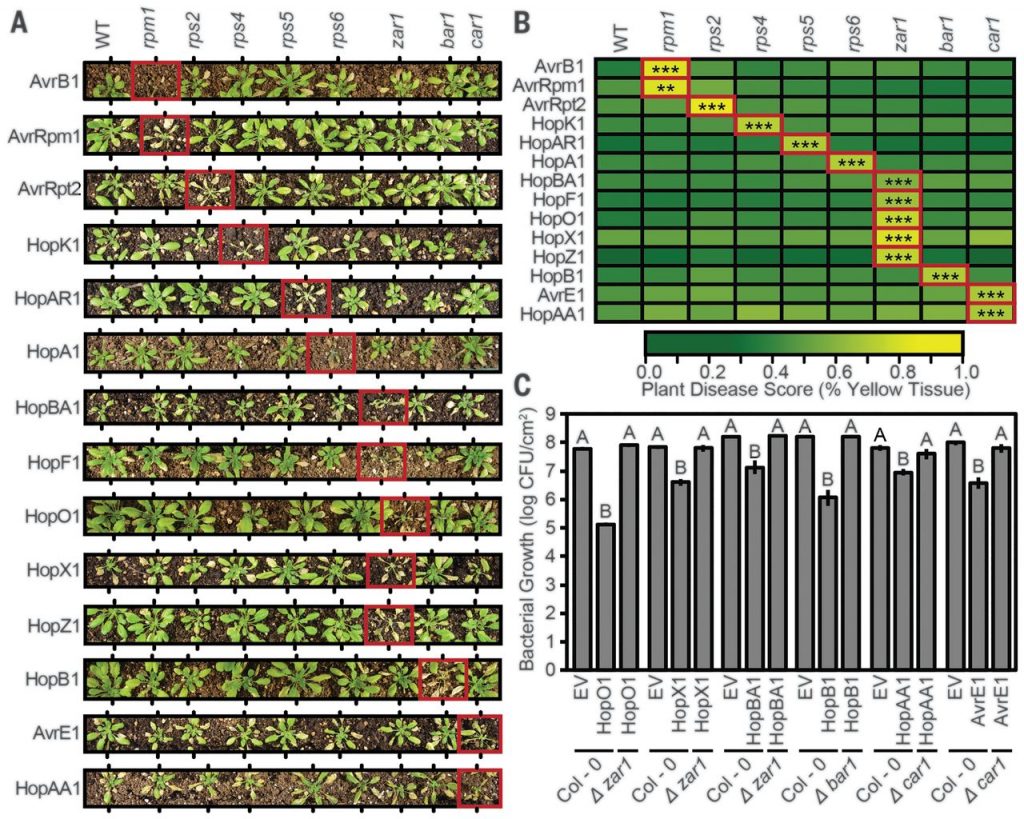
The pan-genome effector-triggered immunity landscape (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklySuccessful plant pathogens produce a suite of small molecules called effectors that are injected into plant cells and perturb plant defense. As a counter defense, plants have evolved intracellular receptors (called NLRs; nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat) that detect specific effectors and…
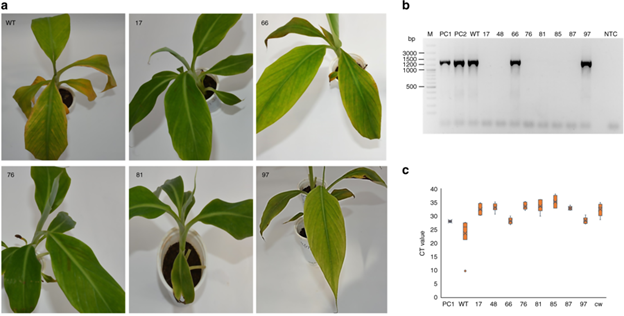
Using CRISPR/Cas9 editing to inactivate an endogenous virus impacting bananas (Commun. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBanana streak virus (BSV) is a plant pathogenic pararetrovirus that has integrated into the genome of banana Musa spp., reducing crop production. When BSV-infected banana plants become stressed, BSV reactivates to create functional infectious viruses that can cause lethal tissue necrosis. Tripathi et…
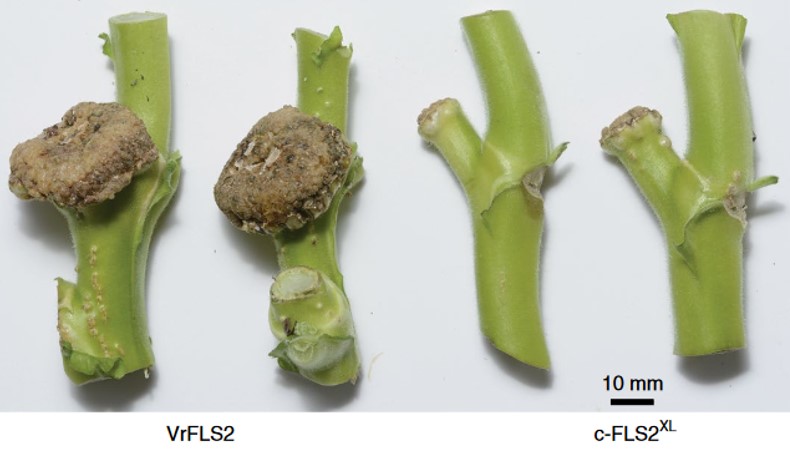

Perception of Agrobacterium tumefaciens flagellin by FLS2XL confers resistance to crown gall disease (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFLS2 is a well-characterized cell-surface receptor that recognizes a short epitope found on most bacterial flagellin proteins. The plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens, causative agent of crown gall disease, deviates strongly at this epitope region, and so is generally not recognized by FLS2 receptors,…
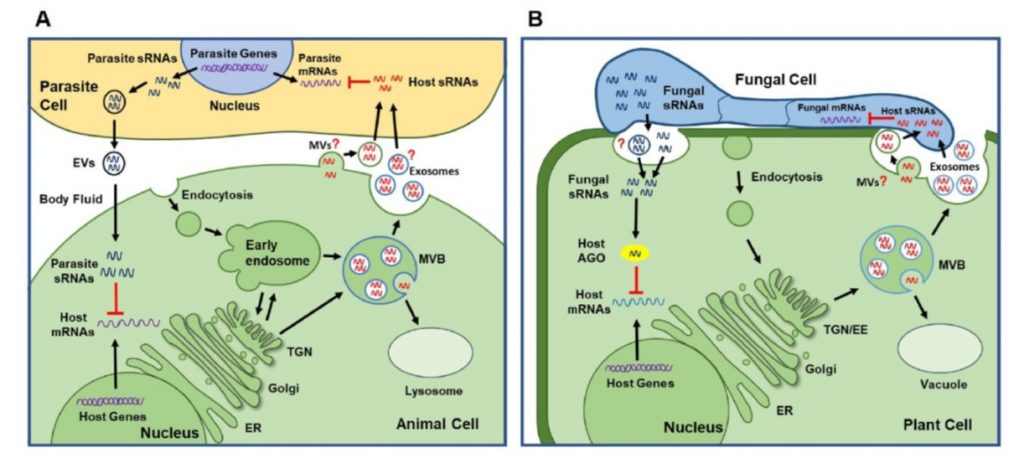
Review. Small RNAs and extracellular vesicles: New mechanisms of cross-species communication and innovative tools for disease control (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have only recently begun to appreciate the phenomenon of cross-species or cross-kingdom small RNA transfer, and its applications. Using examples from plants and animals, Cai et al. summarize how some pathogens have evolved the capacity to introduce small RNAs into their host to suppress host defense…
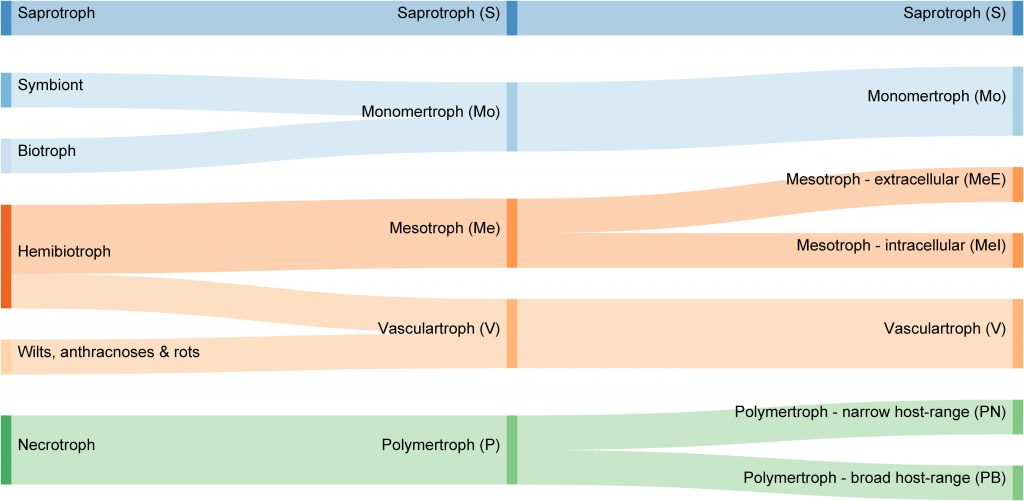
A proposed new classification scheme for fungal and oomycete pathogens based on carbohydrate-active enzymes (Front. Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFilamentous pathogens (fungi and oomycetes) use a variety of tactics to obtain nutrients from plants. Classically, they have been categorized as biotrophic ("eating" living tissues), nectrotrophic (eating dead tissues) or hemibiotrophic (biotrophic followed by heterotrophic). Hane et al. point out that…
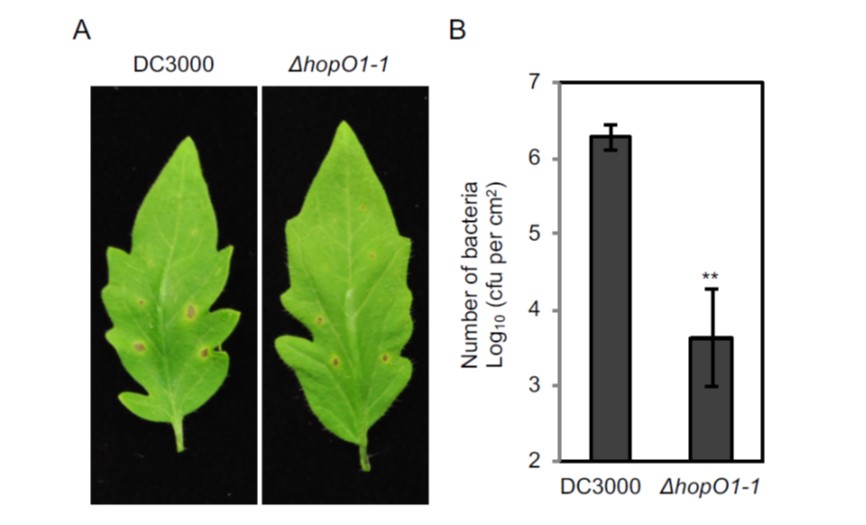
Pathogenic bacteria target plant plasmodesmata to colonize and invade surrounding tissues (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are regulated channels that connect adjacent cells, allowing movement of metabolites, RNA, proteins, and pathogens. Plants close their plasmodesmata as part of their immune response, but this closure can be interfered with by pathogens. Aung et al. examined the repertoire of effector proteins…

Resistant tomato restricts colonization and invasion by the pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum at four organismal levels (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRalstonia solanacearum is a pathogenic bacterium that infects many important crop species, including tomato. Following invasion into the roots, the bacteria move upwards into the shoot and cause dramatic wilting. Previous studies have identified moderately and highly resistant lines. Here, Planas-Marquès…

