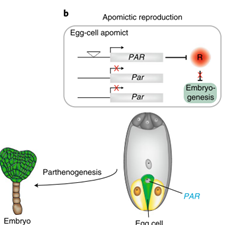
The PARTHENOGENESIS gene that contributes the clonal propagation through seeds in dicot dandelion (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants with sexual reproduction, the male contribution (two sperm cells) is necessary to fertilize two female cells, the egg cell that gives rise to the embryo and the central cell that gives rise to the endosperm. In contrast, apomictic plants (0.1% of flowering plants spread over 120 genera) don´t…
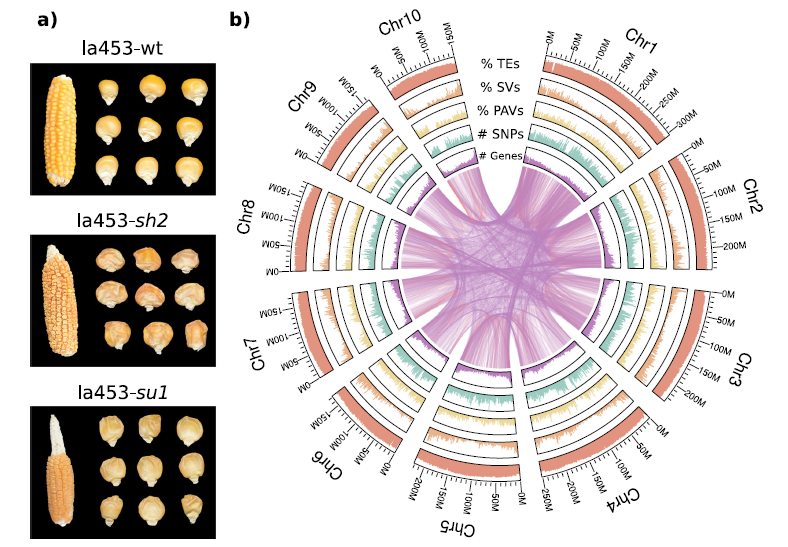
Genome assembly and population genomic analysis provide insights into the evolution of modern sweet corn (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn maize (Zea mays), loss of function mutations in genes involved in starch biosynthesis characterize sweet corn varieties that have increased sugar content in the kernel. Specifically, lines carrying the shrunken2 (sh2) allele revolutionized the corn industry in Northern America in the last 50 years…
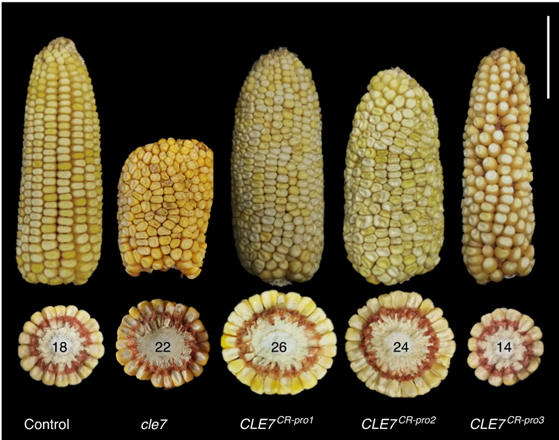
Enhancing grain-yield-related traits by CRISPR-Cas9 promoter editing of maize CLE genes (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring domestication of maize, one of the favorable traits was meristem size. Understanding the genetic circuit of maize meristem development and engineering for crop productivity are important from an agricultural perspective. In this article, Lie et al. used CRISPR-Cas9 to edit the promoter regions…
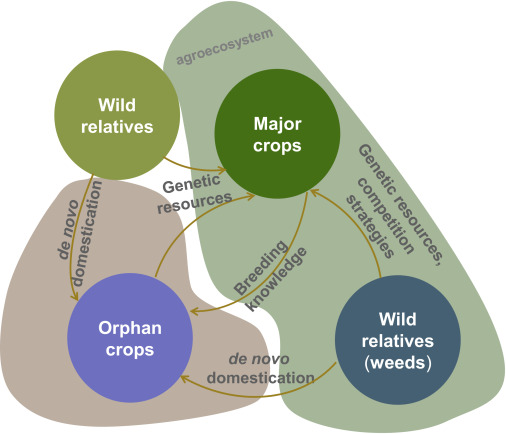
Review: Orphan crops and their wild relatives in the genomic era (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMore than half of human calories come from rice, wheat, and corn, although many other cereals have been domesticated as food crops. Several of these “orphan” cereal crops and their wild relatives are being studied with the goal of diversifying our food supply, which is particularly important due…
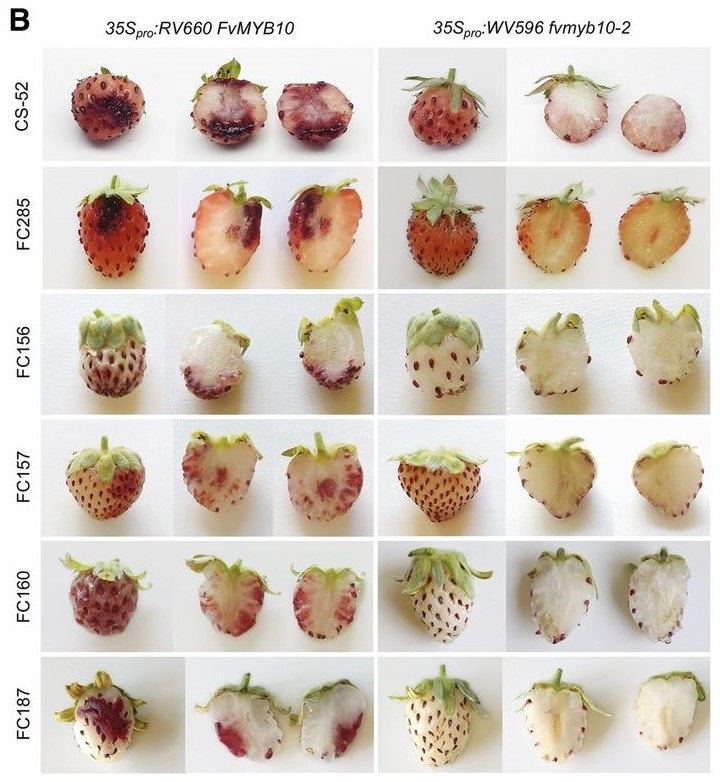
Allelic variation of MYB10 controls natural variation in skin and flesh color in strawberry (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFew fruits have a more distinctive color than strawberry (Fragaria spp). Anthocyanins are responsible for strawberry’s characteristic red pigmentation with variations in receptacle color caused by altered anthocyanin levels. While the flavonoid synthesis pathway accountable for anthocyanin accumulation…

Leaf angle control across the sorghum canopy (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a rosette-forming plant like Arabidopsis, leaf radial angle is optimized to prevent self-shielding. By contrast, in a plant such as sorghum, leaf vertical angle affects self-shading. A “smart canopy” model has been proposed in which upper leaves have a more upright orientation to allow more light…
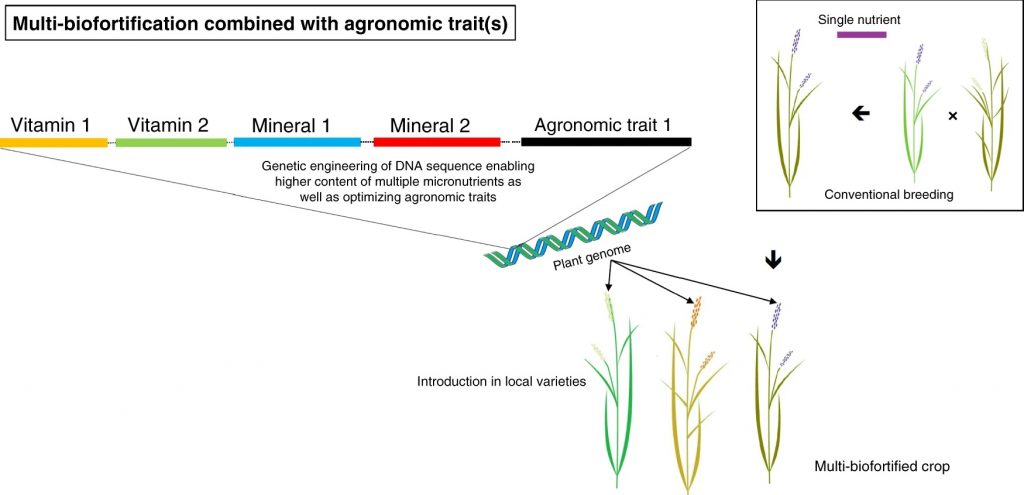
Perspective: Multiplying the efficiency and impact of biofortification through metabolic engineering (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
As heterotrophs, we are what we eat. One of the UN Sustainable Development Goals is to end all forms of hunger, including the “hidden hunger” that results from nutrient deficiencies. Van Der Straeten et al. provide an overview of biofortification strategies. They review current successes from…

Review: Applications of CRISPR–Cas in agriculture and plant biotechnology (Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis week’s announcement of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry being awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna “for the development of a method for genome editing” comes as no surprise to many. CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)– Cas (CRISPR-associated…
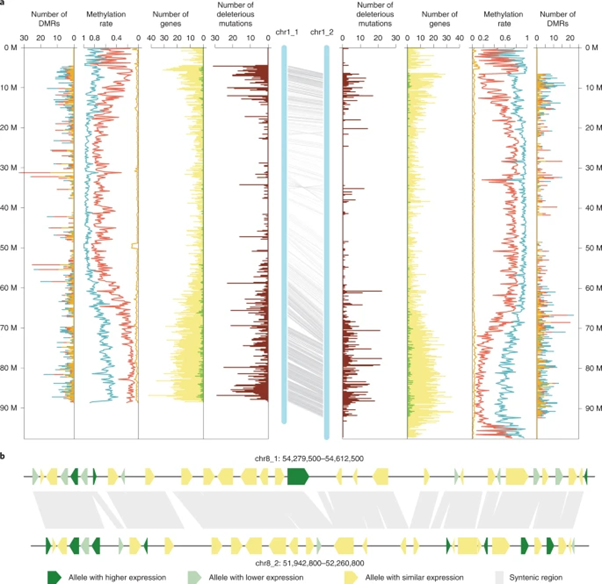
Haplotype-resolved genome analyses of a heterozygous diploid potato (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPotato (Solanum tuberosum) is the third most important food crop worldwide. It is also a clonally propagated tetraploid, making progress in breeding genetically improved cultivars extremely difficult. Therefore, there are ongoing efforts to redomesticate potato from a tetraploid, tuber-propagated crop…

