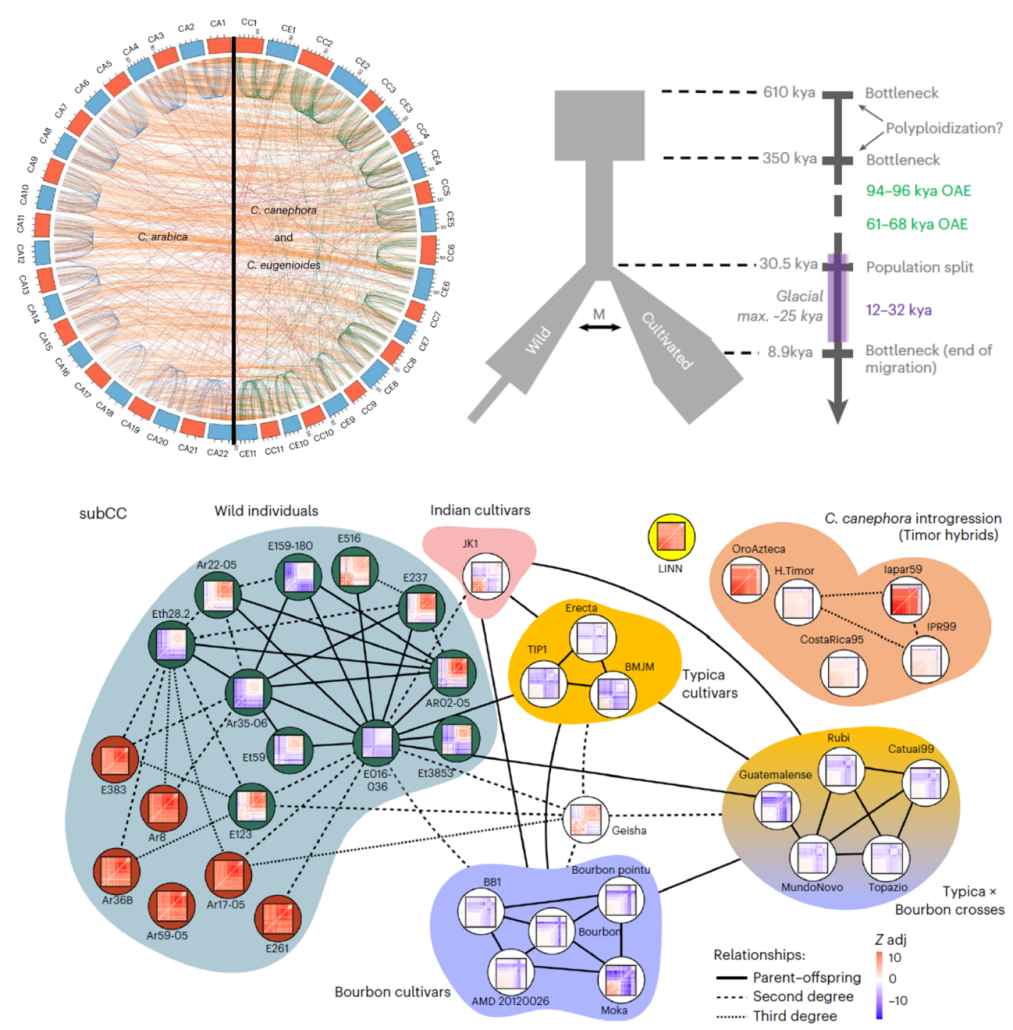
Genomics from bean to cup: New insights into the history of Arabica coffee diversification
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs one of the most traded commodities in the world, coffee has cultural and economic impact that spans continents. The main source of coffee beans, Coffea arabica (Arabica), is a polyploid species that resulted from the hybridization between diploid C. canephora (Robusta) and C. eugenioides (Eugenioides).…

Genetic gains underpinning a little-known strawberry Green Revolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe domestication of cultivated strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) traces back approximately 300 years, providing us with a relatively comprehensive genealogy of this artificial hybrid species. Strawberry yield in the US has increased by 2,755% since the 1960’s, largely owing to the California strawberry…
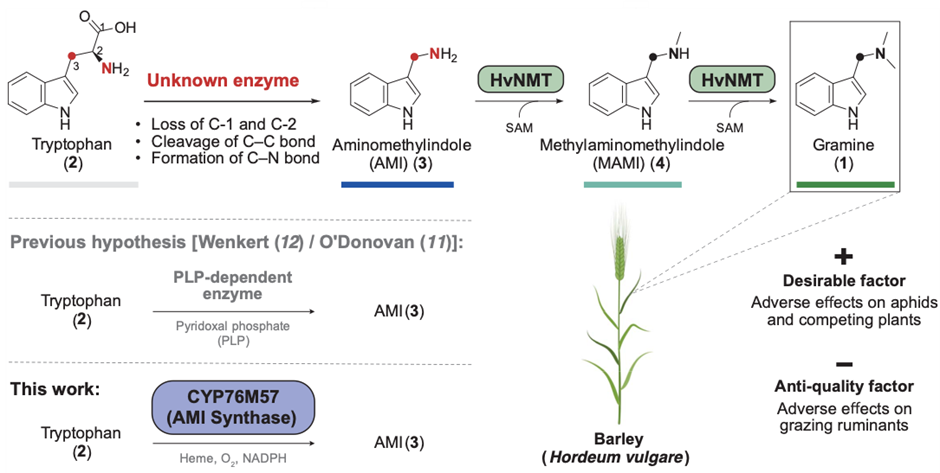
Unlocking nature’s arsenal: Engineering grasses for insect defense and livestock palatability
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe defensive alkaloid gramine, present in barley and other grass species, plays an important role in protecting the plant from insect damage but poses challenges for ruminant palatability. Breeding strategies balance these factors by maintaining the protective function and making the grain palatable…

Herbivore-deterring trichomes persist with the help of Woolly and Get02
Plant Science Research WeeklyType-IV glandular trichomes, which produce acylsugars, are effective deterrents against herbivory in Solanum, but they only persist in the juvenile stage of the cultivated tomato (S. lycopersicum). Therefore, these trichomes serve as a marker for the transition from juvenile to adult phases in developmental…
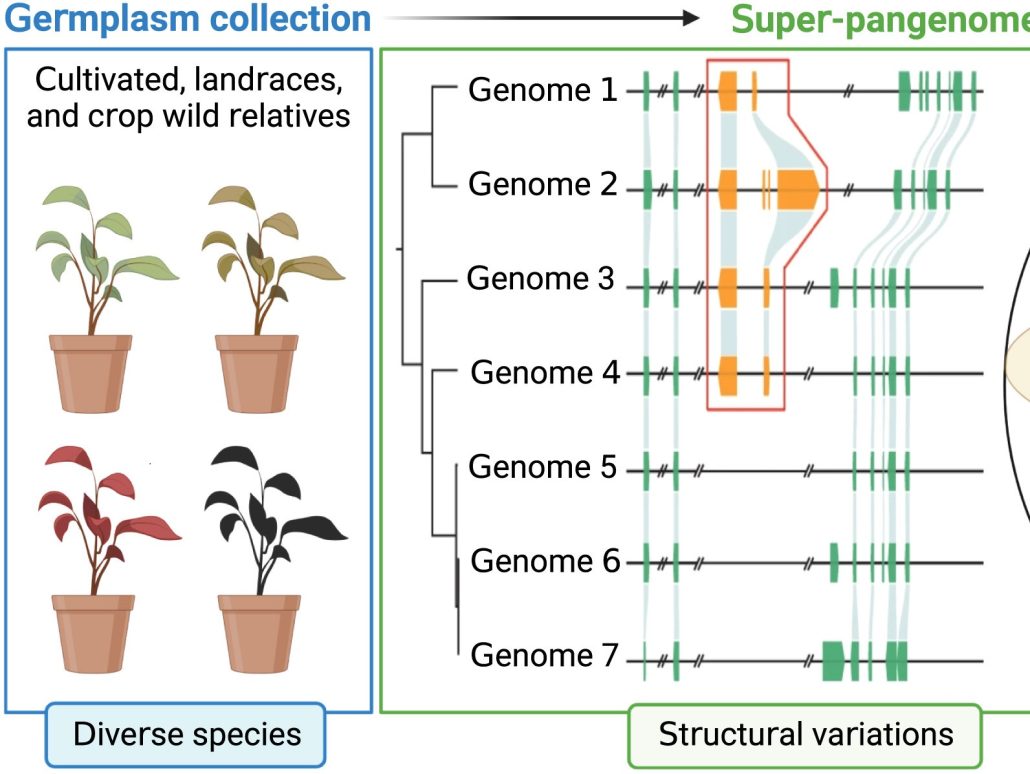
Spotlight: Super-pangenomes for improved breeding
Plant Science Research WeeklySometimes more really is better, and I think it’s safe to say that when it comes to genomic information, more is better. Here, Raza et al. highlight the great value of super-pangenomes. A pan-genome is defined as the entire set of genes within a species, created by combining sequences of many individuals.…
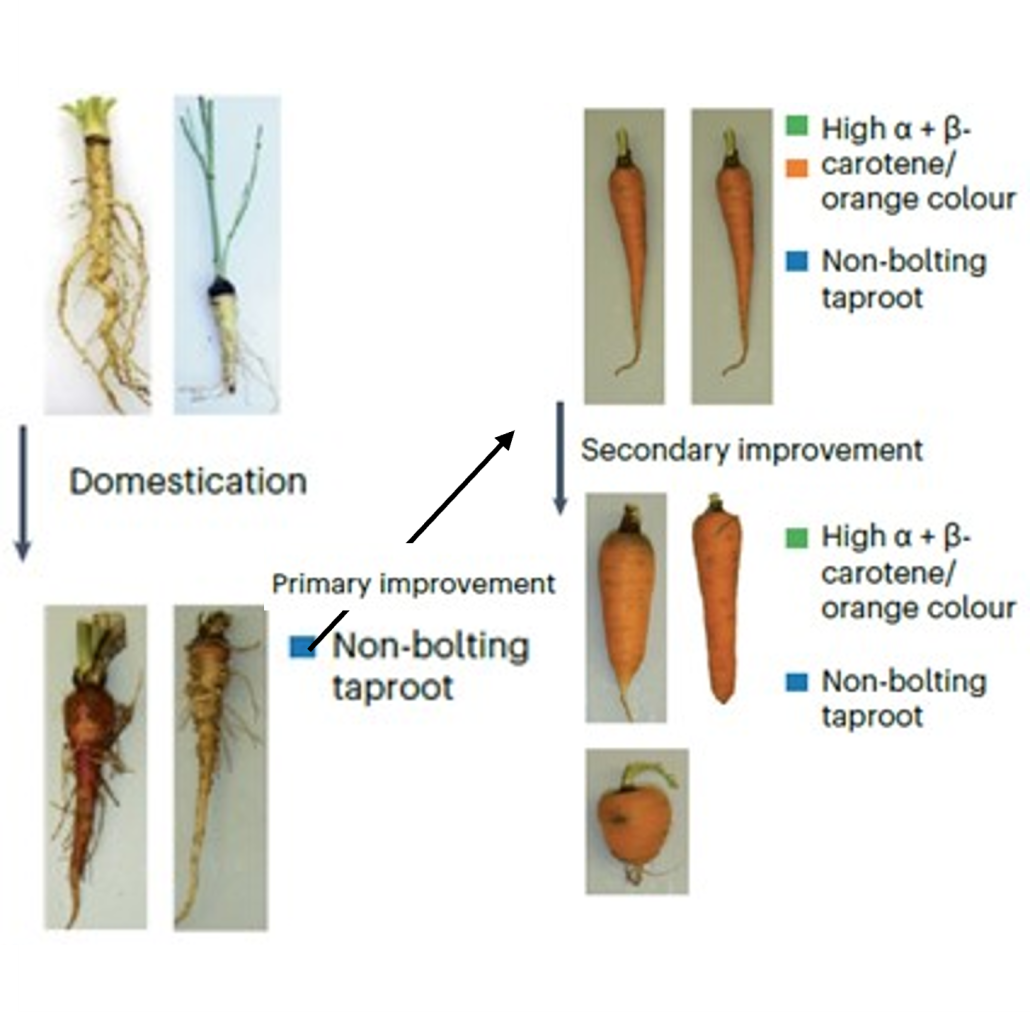
When and how did carrots turn orange?
Plant Science Research WeeklyCarrots were not always orange, and a new paper by Coe, Bostan, Rolling et al. sheds new light into the history of carrot domestication and improvement, i.e., how we went from white, knotty carrots to the orange, smooth ones that are now consumed all over the world. The authors published a new version…

Commentary: Time to fight the over-hype
Plant Science Research WeeklyA year ago, graduate student Merritt Khaipho-Burch Tweeted a reaction to an article about a gene described as enhancing yield, which led to lively on-line and in-the-lunchroom discussions about how to realistically measure yield, and, maybe more importantly, where to draw the line between potential and…

Plant Physiology Focus Issue: Fruit Crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyJuly brings delicious fruit harvests in the Northern Hemisphere, and a very special focus issue of Plant Physiology. I particularly like this issue because of the wide variety of species covered, starting with apple, banana, blueberry, cherry, citrus, and so on. It’s a nice departure from our usual…
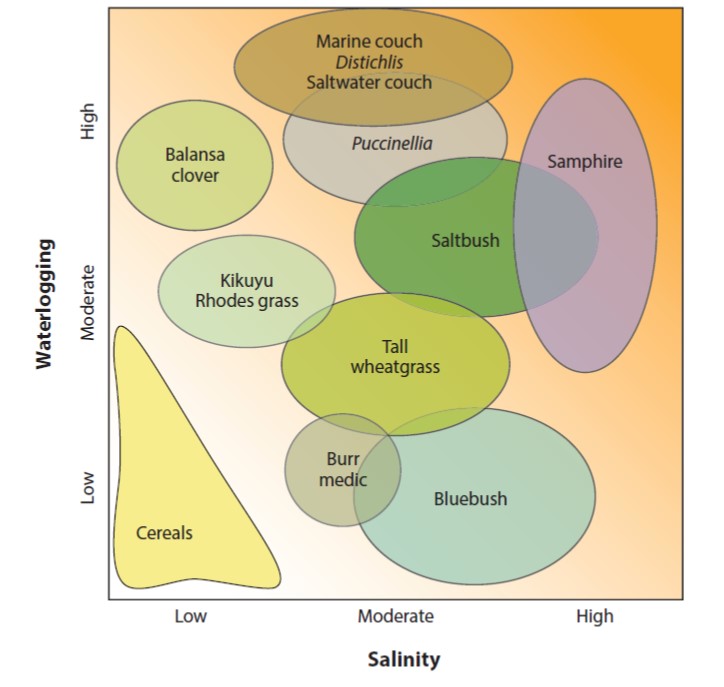
Review: Salt-tolerant crops: Time to deliver
Plant Science Research WeeklyFew topics are as inherently interesting from both fundamental and applied perspectives as salt tolerance in crop plants. From the basic science side, cells have several strategies that they use to keep Na+ levels low in their cytosol in spite of what can be a very steep concentration gradient from out…

