Shade avoidance responses in Chinese white poplar rely on shared and unique roles of phytochrome-interacting factors
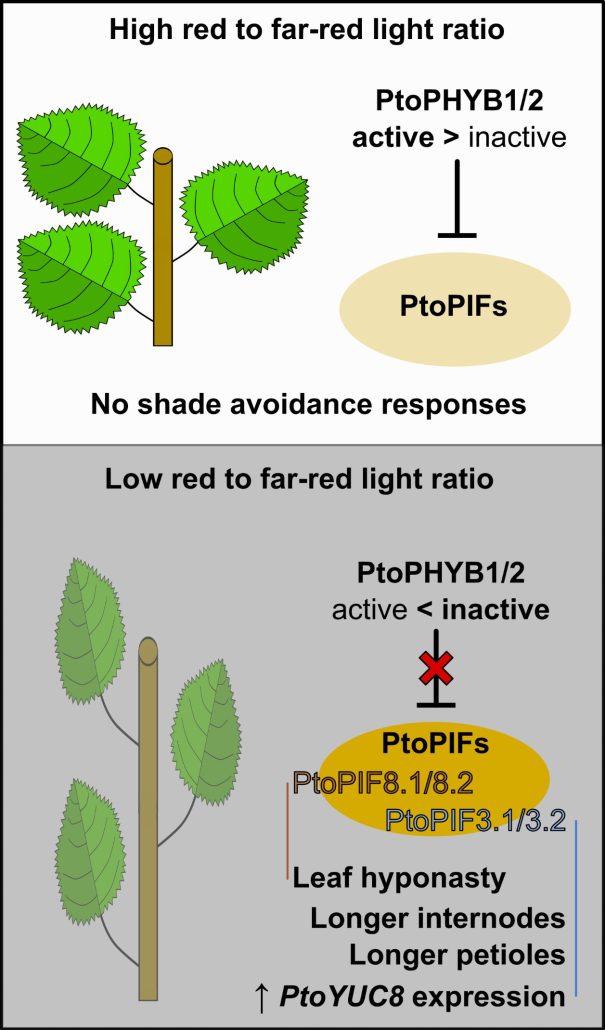
Plant Science Research WeeklyShade avoidance syndrome (SAS) is a set of adaptive growth responses to low red to far-red light ratios. SAS includes petiole and internode lengthening and upward bending of leaves (hyponasty). In Arabidopsis, PHYTOCHROME B (PHYB) and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) are implicated in these responses.…

