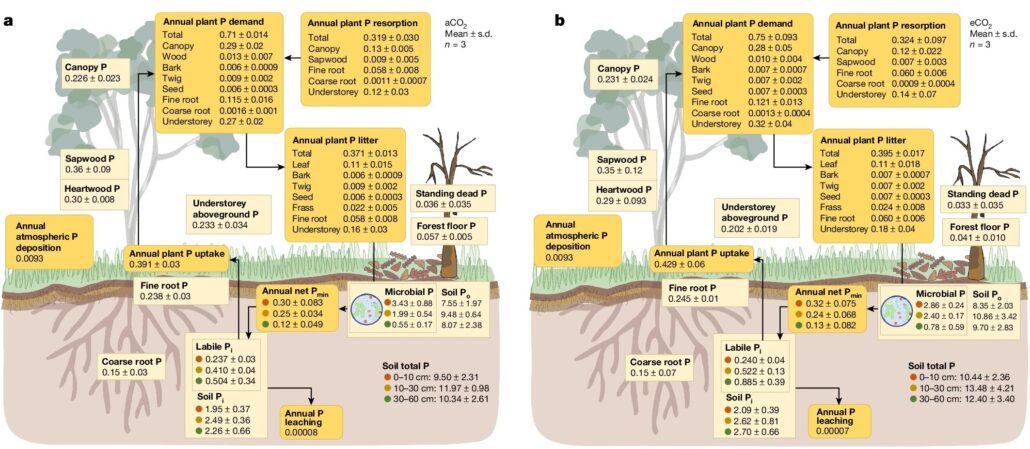
Phosphorus limitation limits carbon storage in CO2-enriched mature forests
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants fix carbon dioxide to generate biomass, and in many cases increasing the availability of CO2 enhances plant growth. However, some studies have shown that although yields of food crops such as rice might increase, their nutritional value decreases, due to limitations in availability of minerals…
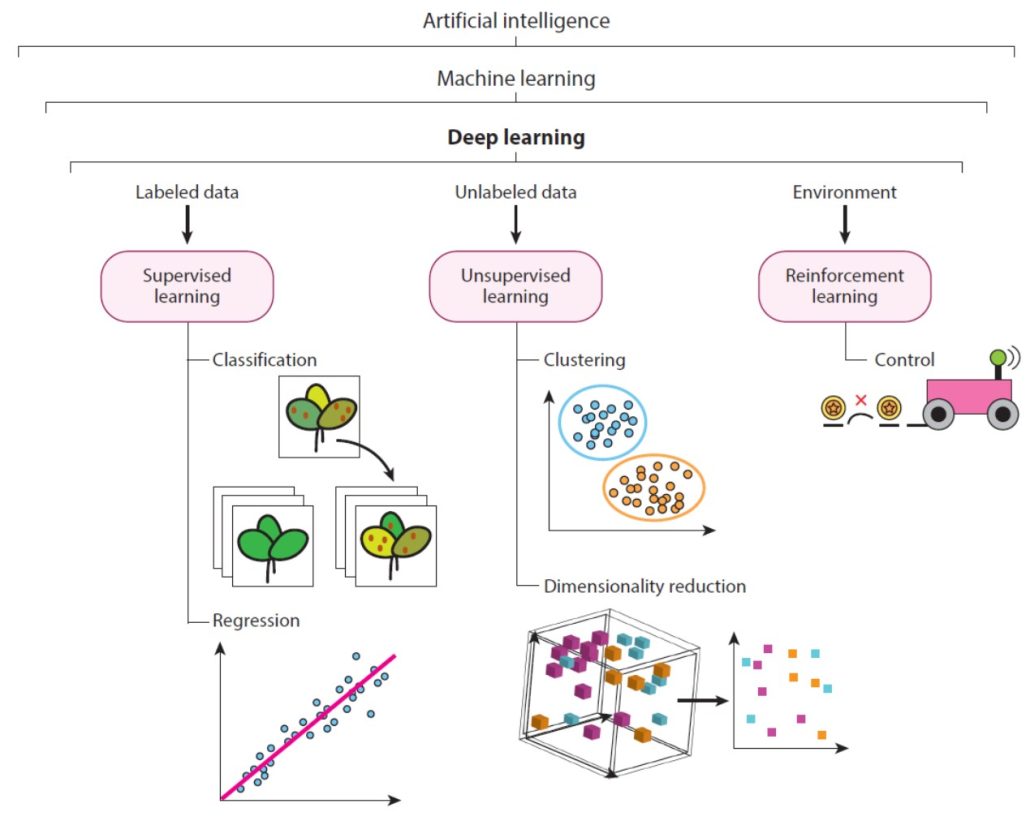
Review: Deep learning in image-based plant phenotyping
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs a writer and an editor, I am horrified by the idea that thinking can be replaced by artificial intelligence. But I do recognize that deep learning / machine learning / artificial intelligence can provide major opportunities for data analysis, as eloquently described in this review article by Murphy…
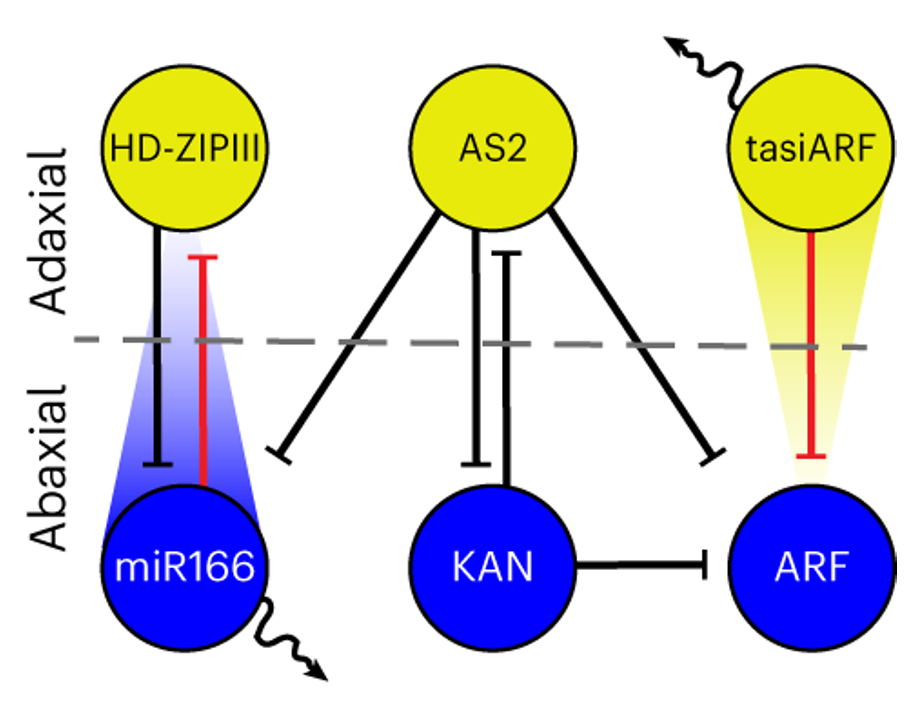
A diffusible small-RNA-based Turing system dynamically coordinates organ polarity
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe establishment of adaxial-abaxial polarity during the growth of the leaf primordium is a prerequisite for the formation of the flat, thin leaves observed in most (but not all) plants. The micro-RNAs tasiARF and miR165/6, which form concentration gradients within leaf primordia, are major contributors…
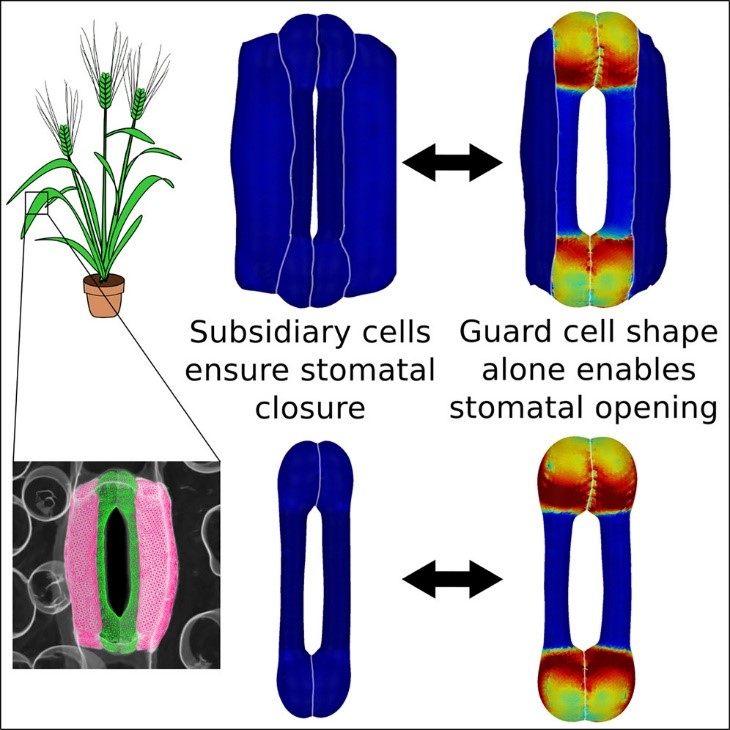
Grasses exploit geometry for improved guard cell dynamics
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata are pores on the surface of leaves essential for gas exchange. In grasses, stomatal aperture is controlled by pairs of dumbbell shaped guard cells, with each guard cell surrounded by a subsidiary cell. Despite cell geometry being well described, it was unclear how it influences stomata function.…
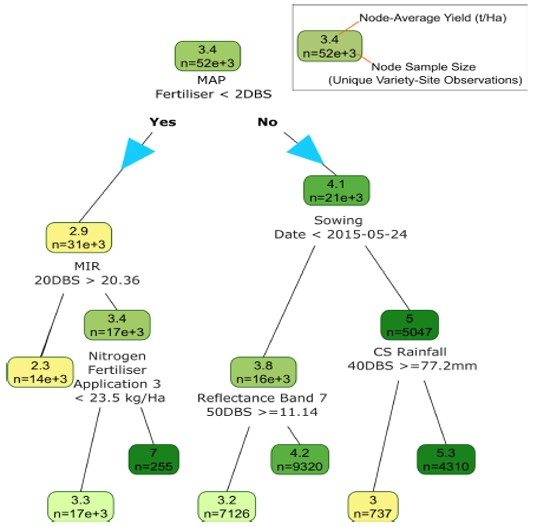
Using ‘Machine Learning’ to predict crop behaviour (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMachine Learning (ML) is described by Wikipedia as ‘the study of computer algorithms that can improve automatically through experience and by the use of data’. In agronomy, machine learning can predict important crop traits (including yield) by analysing the large datasets such as data generated…
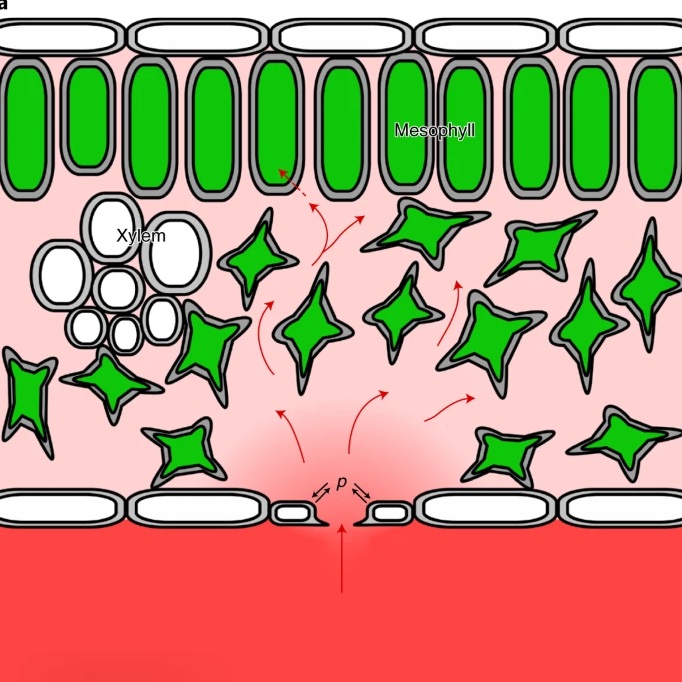
Guard cell endomembrane Ca2+-ATPases underpin a ‘carbon memory’ of photosynthetic assimilation that impacts on water-use efficiency (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomatal guard cells control both carbon dioxide uptake and transpirational water loss. Guard cell control over the stomatal pore aperture is sensitive to water status (through ABA) as well as the amount of CO2 available within the leaf air space. Several studies have indicated that stomatal aperture…
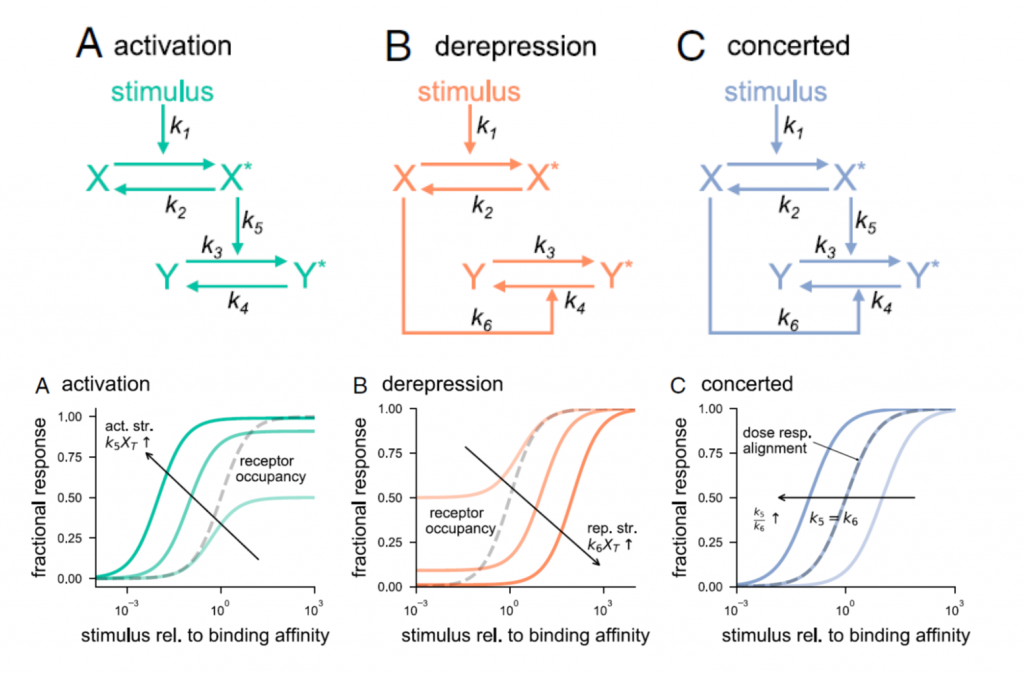
Molecular switch architecture determines response properties of signaling pathways (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenetic studies have provided us with countless examples of regulatory switches that transduce a signal into a response. Mutant analysis is usually sufficient to identify these controlling elements, but often in an all-or-nothing way. Here, Ghusinga et al. have taken a theoretical kinetic approach to…
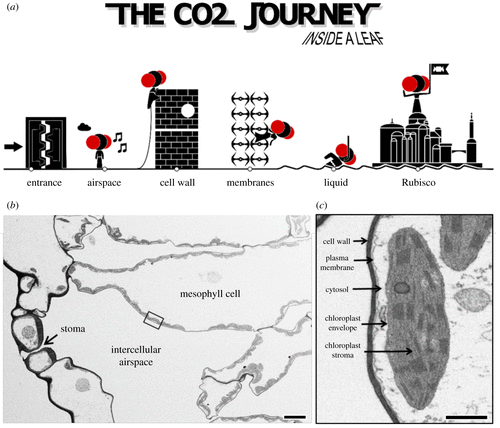
CO2 diffusion in tobacco: a link between mesophyll conductance and leaf anatomy (Interface Focus)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThree key factors affect a plant’s ability to fix carbon: enzymatic activity of Rubisco, stomatal conductance, and the journey from sub-stomatal cavity to Rubisco, also known as mesophyll conductance (gm). This latter is the focus of this new work by Clarke et al. They delightfully compare this journey…
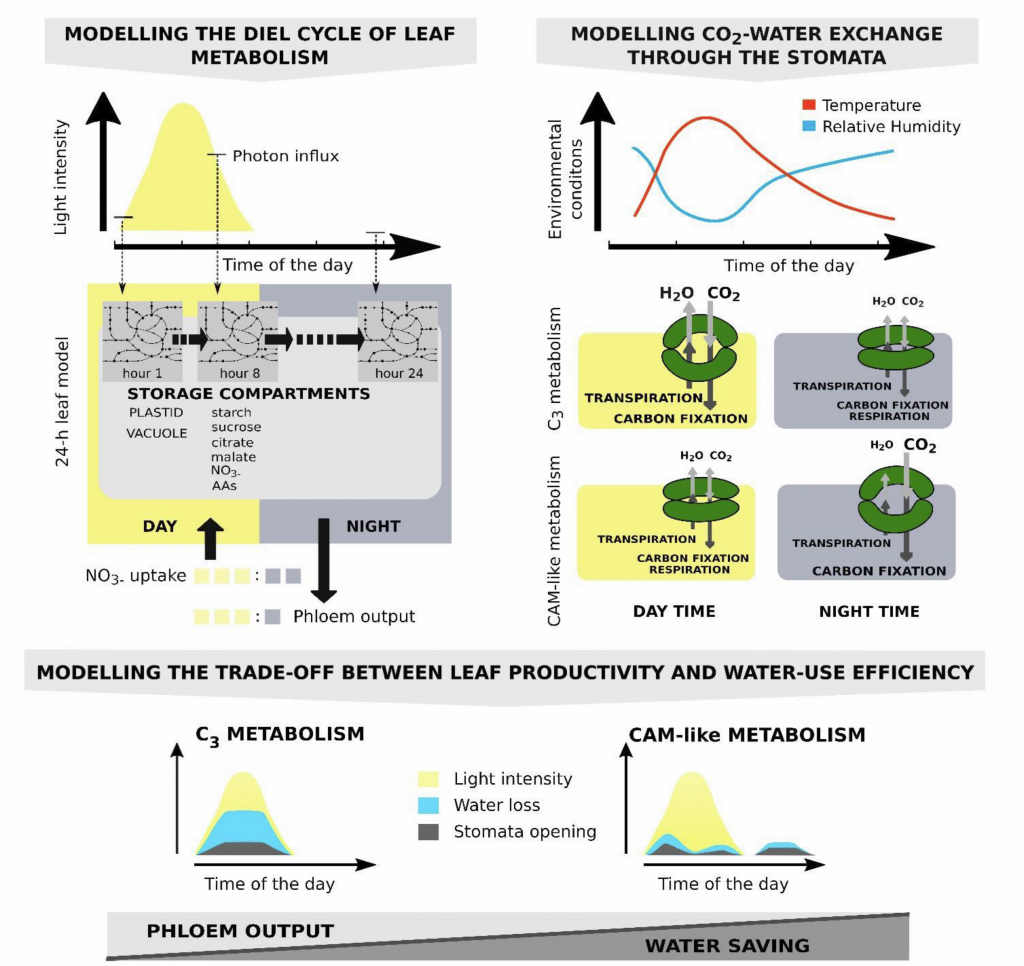
Alternative CAM and water-saving flux modes into C3 leaf metabolic model (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a photosynthetic adaptation pathway in arid environments to minimize water loss by opening the stomata at night, when the temperature and therefore water loss due to transpiration is lower. Carbon dioxide is initially fixed at night and stored in the vacuole. Engineering…

