
Branched chain amino acids accumulation contributes to drought tolerance in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe accumulation of metabolites such as proline as compatible osmolytes is a protective mechanism against drought stress in plants. Similarly, under drought conditions, there is an observable increase in the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), including the essential amino acids isoleucine,…
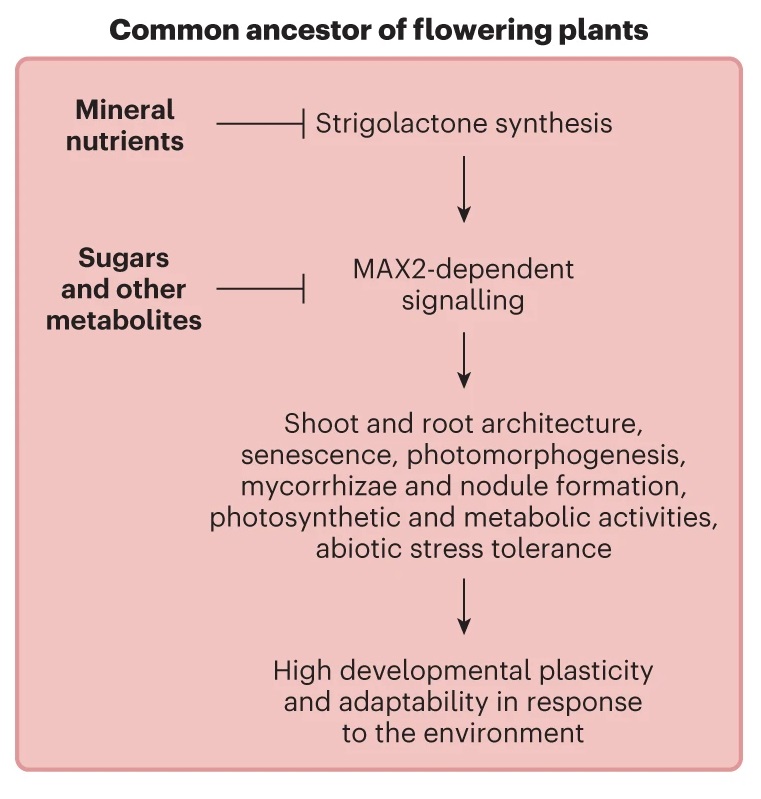
Review: Strigolactones integrate metabolic and nutritional signals
Plant Science Research WeeklyStrigolactones are a class of hormones first identified in the 1960s as components of root exudates that promote germination of parasitic Striga seeds, and later as a promoter of associations with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Strigolactones also have endogenous roles within plants, for example as regulators…
Shedding light on Arabidopsis seed oil biosynthesis
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDeslandes-Hérold et al. explore the integration of the PRK/Rubisco shunt into green embryo photosynthesis and metabolism.
Gabriel Deslandes-Hérold, Melanie R. Abt, and Samuel C. Zeeman, ETH Zurich
Background: Light promotes the accumulation of storage lipids during development of oilseeds with…
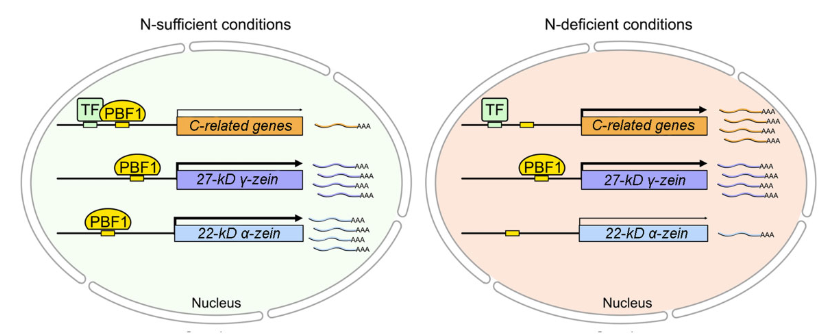
Nitrogen-dependent binding of the transcription factor PBF1 contributes to the balance of protein and carbohydrate storage in maize endosperm (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe majority of maize endosperm is made of starch (70%) and proteins (10%) and their biosynthesis is a complex process which involves many enzymes. N-containing compounds, such as enzymes, amino acids, and nucleotides are crucial for C metabolism. Thus, when N levels are altered, the storage of proteins…
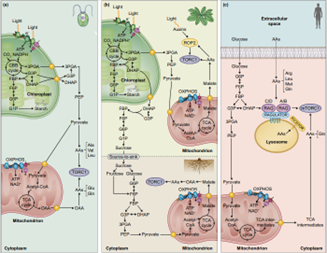
Tansley Insight: Analyzing the impact of autotrophic and heterotrophic metabolism on the nutrient regulation of TOR (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA protein kinase, target of rapamycin (TOR), controls cell growth and metabolism in all eukaryotes. The role of TOR in regulating synthesis and breakdown of organic compounds in response to nutrients, hormones and cellular energy to promote growth and development is universal in autotrophs and heterotrophs.…
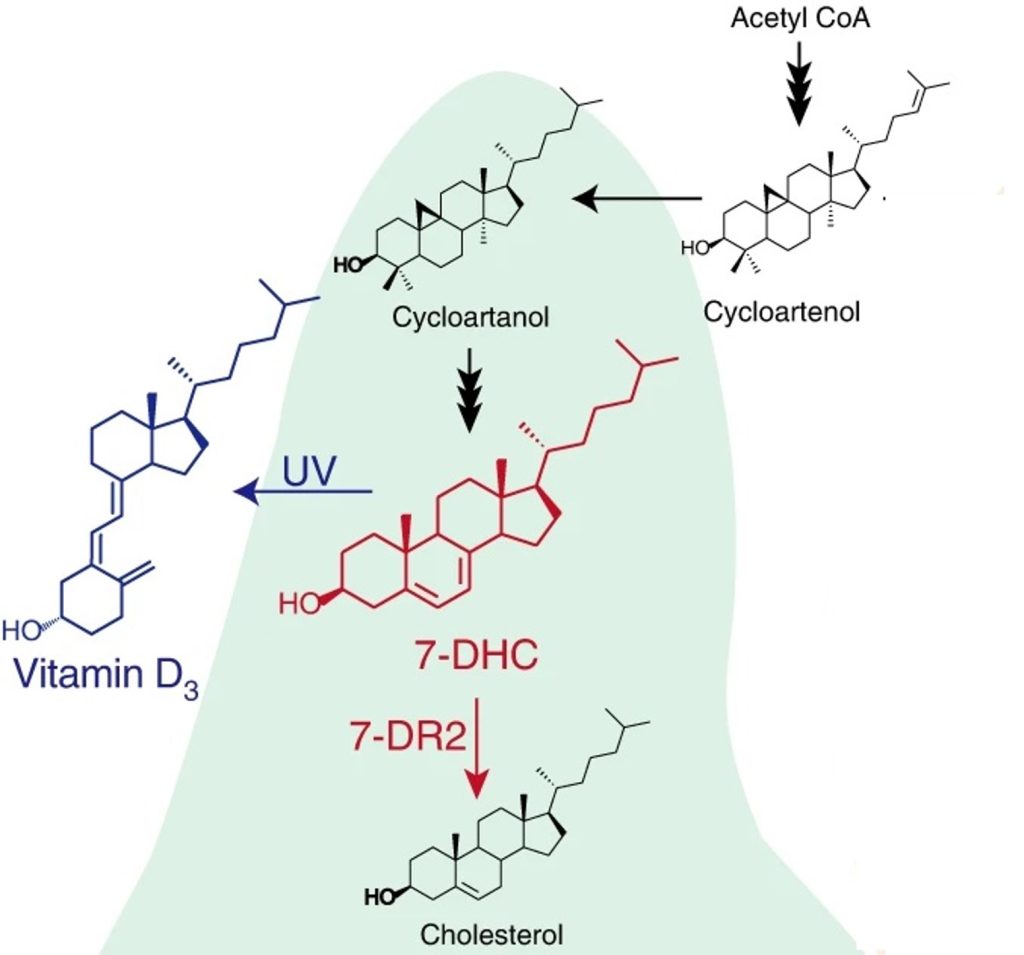
Biofortified tomatoes provide a new route to vitamin D sufficiency (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyVitamin D deficiency in humans is correlated with malfunction of the immune system and inflammation together with cancer, Parkinson disease, depression, neurocognitive decline, dementia, and severe COVID-19 infection. In humans, exposure of the skin to UV light promotes the production of Vitamin D from…
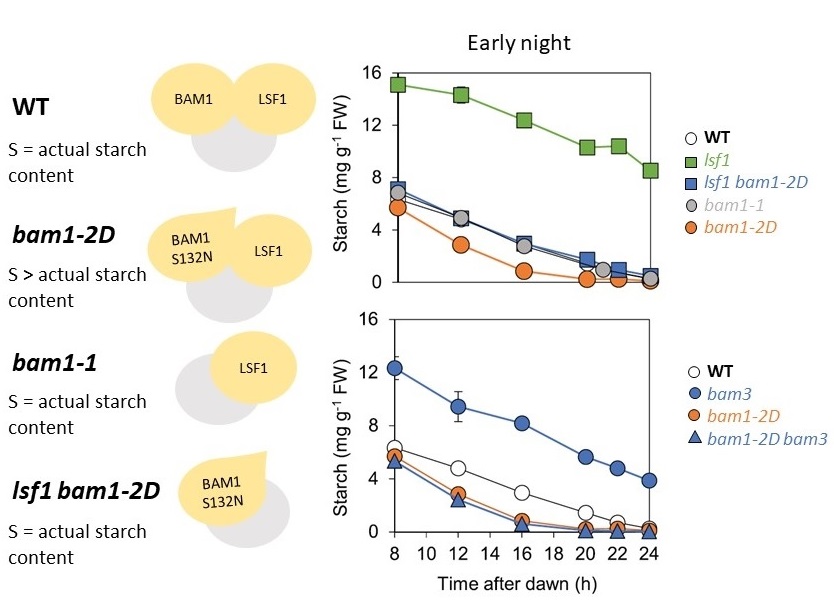
A dominant mutation in β-AMYLASE1 disrupts nighttime control of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants use starch in leaf chloroplasts to fuel their growth and metabolism during the night. In Arabidopsis, nighttime starch degradation is tightly regulated; the degradation rate is linear and adjusts to both the availability of starch and length of night, so that most but not all the starch is used…
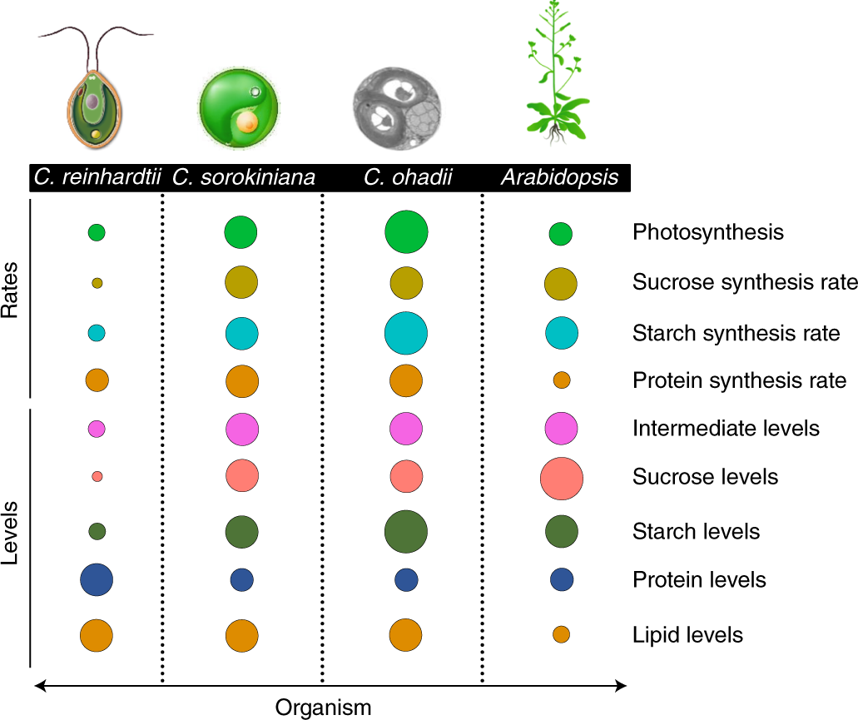
Carbon flux through photosynthesis and central carbon metabolism show distinct patterns between algae, C3, and C4 plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is an attractive target for improving crop yields, and tailoring downstream photosynthesis-associated metabolism is a relatively unexplored path for achieving this. Chlorella ohadii is the fastest growing photosynthetic organism identified, has high photosynthetic rates, and can survive…
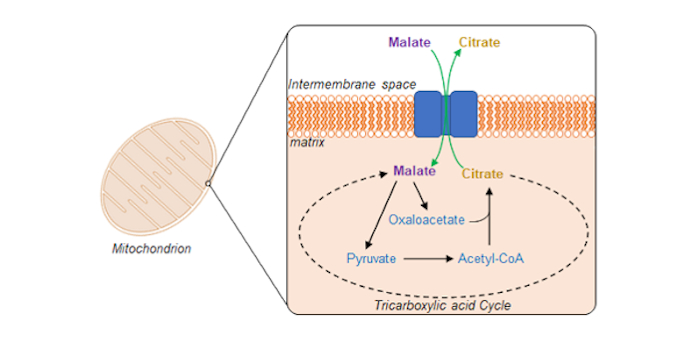
Swapping citrate for malate by plant mitochondria
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLee et al. unravel a mitochondrial transporter responsible for selectively exporting citrate in exchange for malate. Plant Cell (2021)
By Chun Pong Leea, Marlene Elsässerb, Philippe Fuchsb,c, Ricarda Fenskea, Markus Schwarzländerb, A. Harvey Millara
aARC Centre of Excellence in Plant Energy Biology,…

