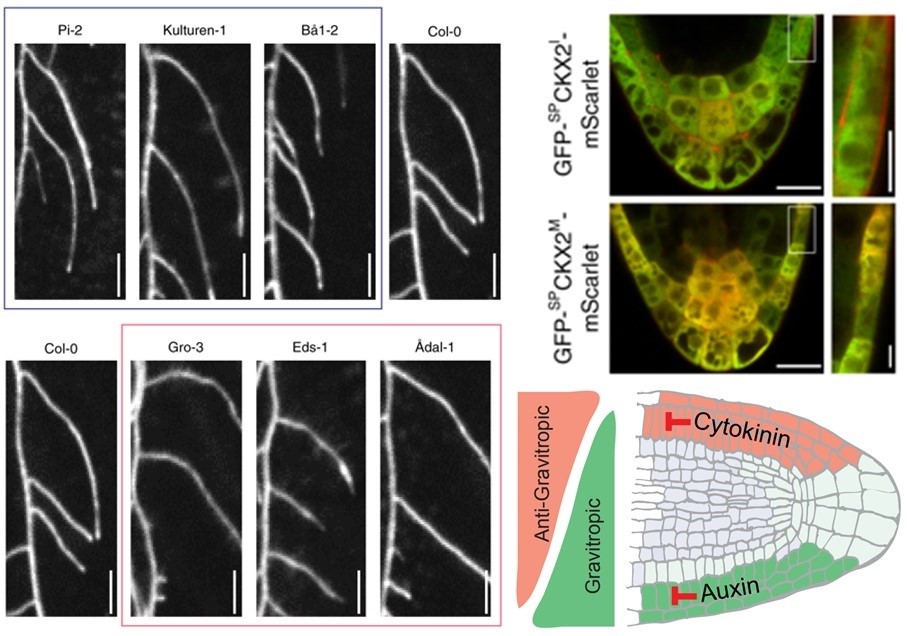
Cytokinin functions as an asymmetric and anti-gravitropic signal in lateral roots (Nature Comms)
Lateral roots help plants to explore the soil and environmental conditions. Waidmann et al. took advantage of natural variants to understand lateral growth angle by analyzing gravitropic set point angle (GSA). Using Col-0 as a reference, lines that over- or under-respond (steeper or shallower root angle)…

Review: Sulfated plant peptide hormones (J. Exp. Bot)
It’s hard to believe that when I was a student we were taught that “plants don’t have peptide hormones”. Since then we’ve discovered many diverse families of plant peptide hormones (see the Teaching Tool on peptide hormones for an excellent overview). Here, Kaufmann and Sauter review one family,…
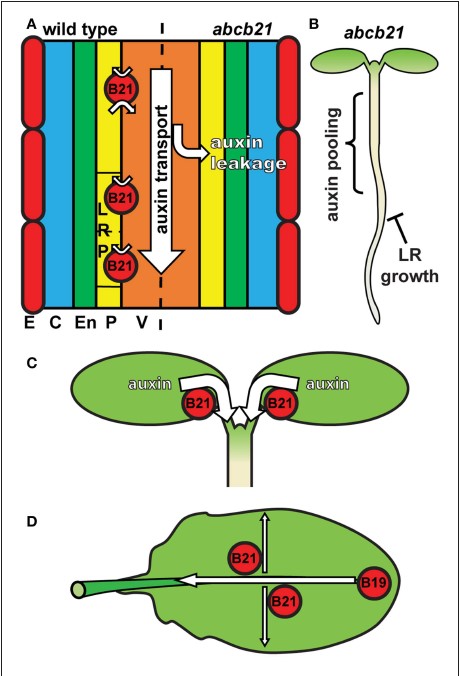
ABCB21 regulates auxin levels in cotyledons, pericycle and leaves (Frontiers Plant Science)
Auxin activity is maintained through regulated biosynthesis, metabolism and transport. In this paper Jenness et al. characterized the physiological significance of a known IAA transporter, ABCB21 (ATP BINDING CASSETTE TRANSPORTER subfamily B member 21) in Arabidopsis. ABCB21 transports shoot derived…
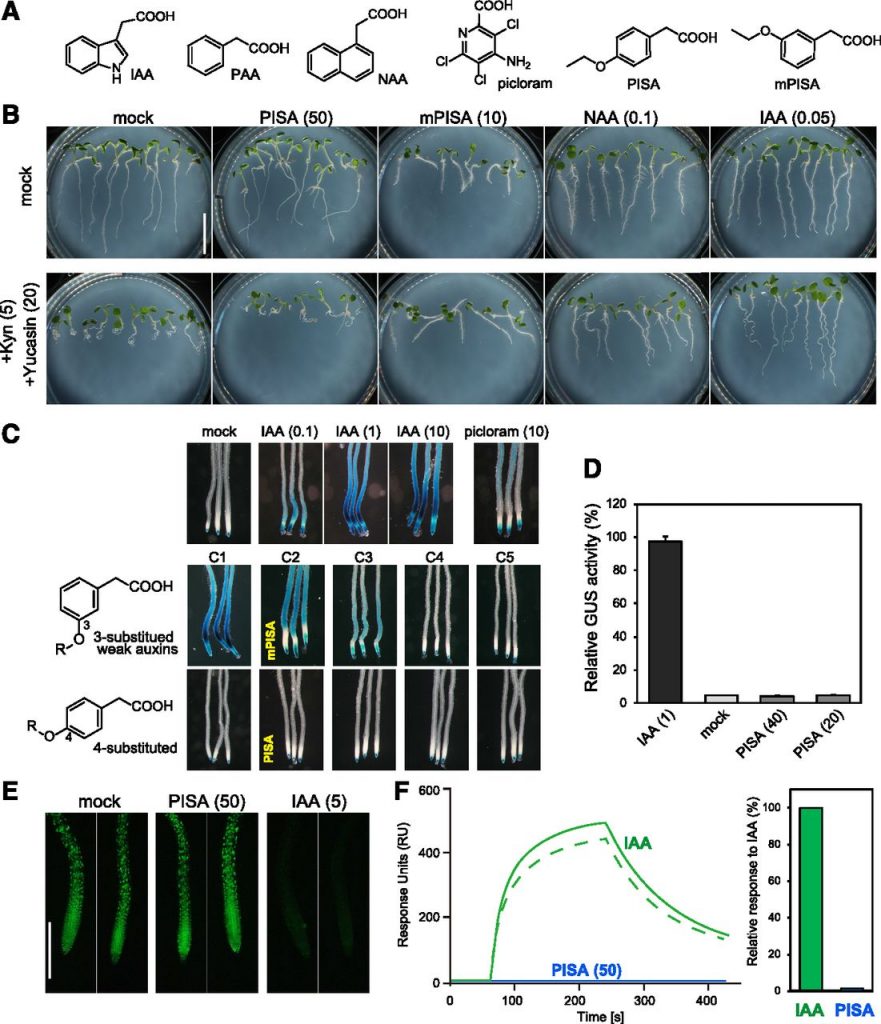
Pinstatic acid promoters auxin transport by inhibiting PIN internalization (Plant Physiol)
Auxin transport regulated by directional transporters such as PIN (PIN-FORMED) proteins ensures maintenance of proper auxin levels for growth and development. Plants modulate auxin flow by regulating the localization of PIN through exocytosis and endocytosis allowing recycling of PIN protein within a…
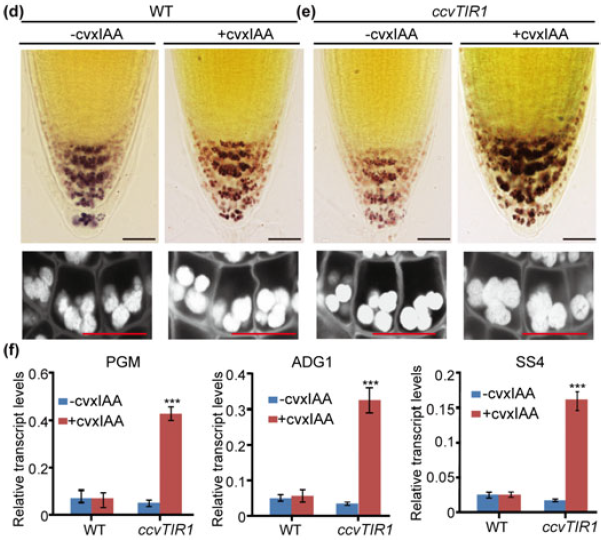
Auxin-mediated statolith production for root gravitropism (New Phytol)
Plants have evolved the ability to perceive and respond to gravity, one of the most persistent external cues. This response process, termed gravitropism, has been extensively studied for its importance in plant development and its potential to improve agronomic traits of crops. The gravitropic response…
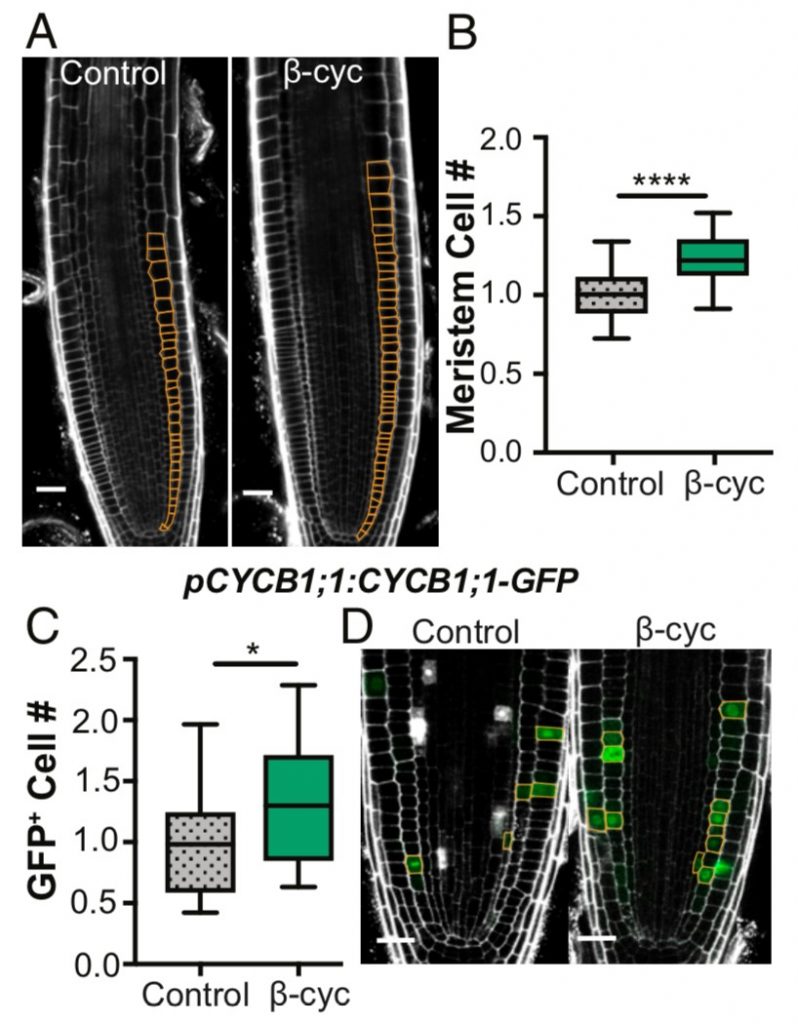
β-cyclocitral, a novel regulator of root growth ($) (PNAS)
Root growth and branching have essential roles in nutrient and water uptake, and are common targets in crop improvement. Dickinson et al. looked for novel apocarotenoids involved in root development and found that dihydroactinidiolide (DHAD) and β-cyclocitral increase lateral root (LR) branching in…

Reflections on Classics: Plant Cell‘s 30th anniversary
“The 1980s were an exciting and revolutionary time for biology, and plant molecular biology in particular,” begins an editorial by Bob Goldberg, Brian Larkins, and Ralph Quatrano, the three Founding Editors of The Plant Cell. They describe why the American Society of Plant Physiologists (ASPP; later,…
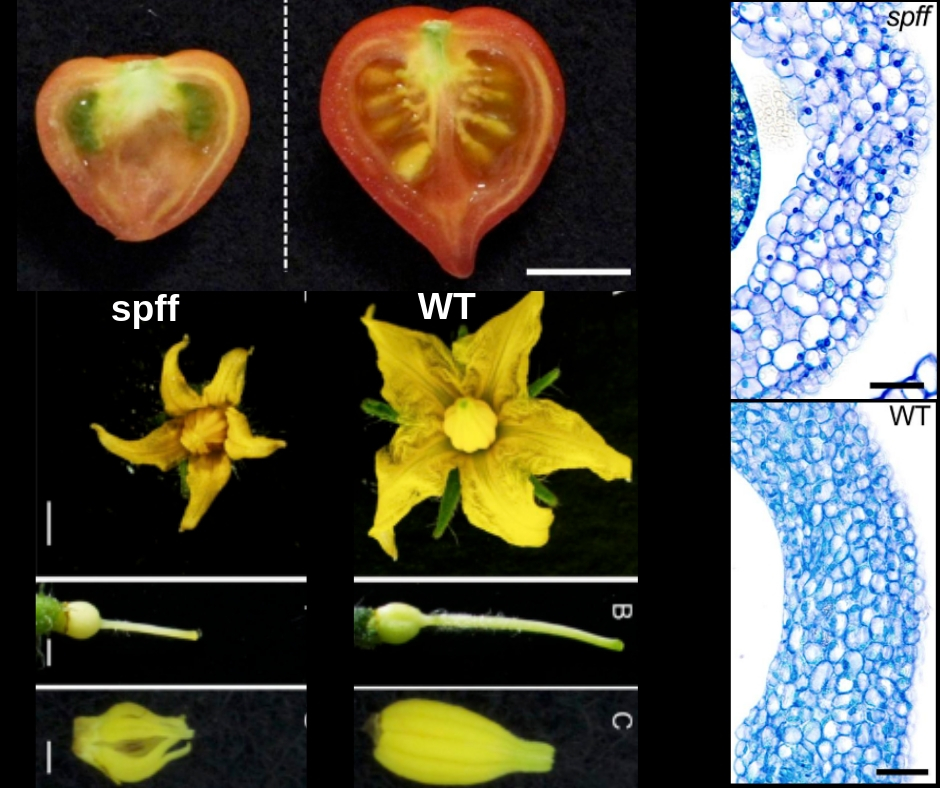
Loss-of-function of a tomato receptor-like kinase impairs male fertility and induces parthenocarpic fruit set (Front Plant Sci)
The flower-to-fruit transition (fruit set) and parthenocarpy, the pollination-independent development of seedless fruits, are controlled by complex hormone networks. Takei et al. identified a tomato gamma-ray induced mutant named small parthenocarpic fruit and flower (spff) with small fruits and flowers,…
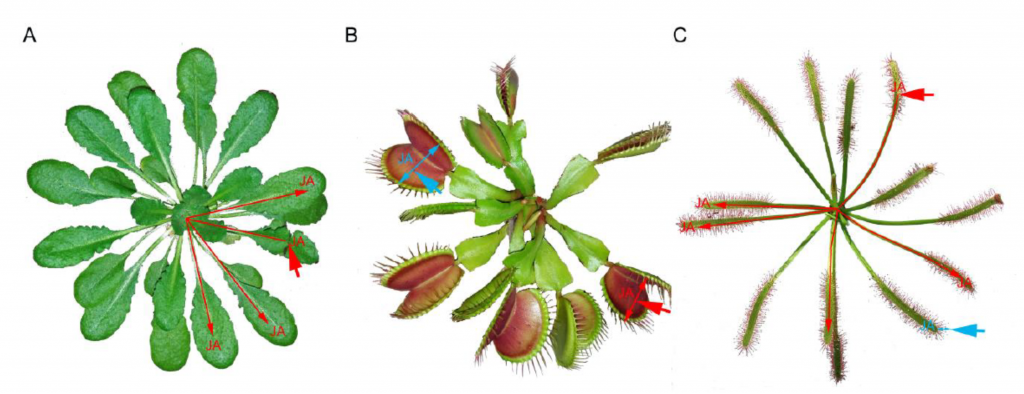
Review: Jasmonate signalling in carnivorous plants: Copycat of plant defence mechanisms (J Exp Bot)
Carnivorous plants are one of the easiest ways to demonstrate to children that “plants are cool too”. In their new review, Pavlovič and Mithöfer show that carnivorous plants can also be a gateway to introduce the subject of how plants defend themselves against herbivory, by drawing links between…

