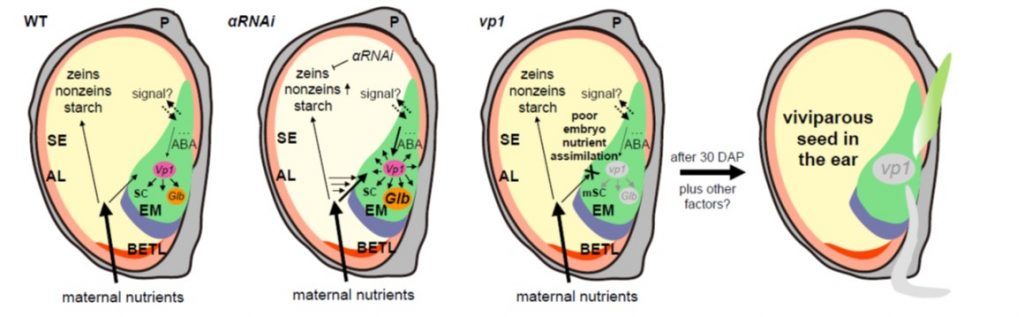
VP1 regulates intra-kernel protein reallocation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaize kernels have a triploid endosperm and a diploid embryo. Storage reserves move from the endosperm to the embryo as it grows. Mutants have been identified with abnormal embryos but normal endosperms, although usually a defective endosperm prevents normal embryo formation. Here Zheng and Li et al.…
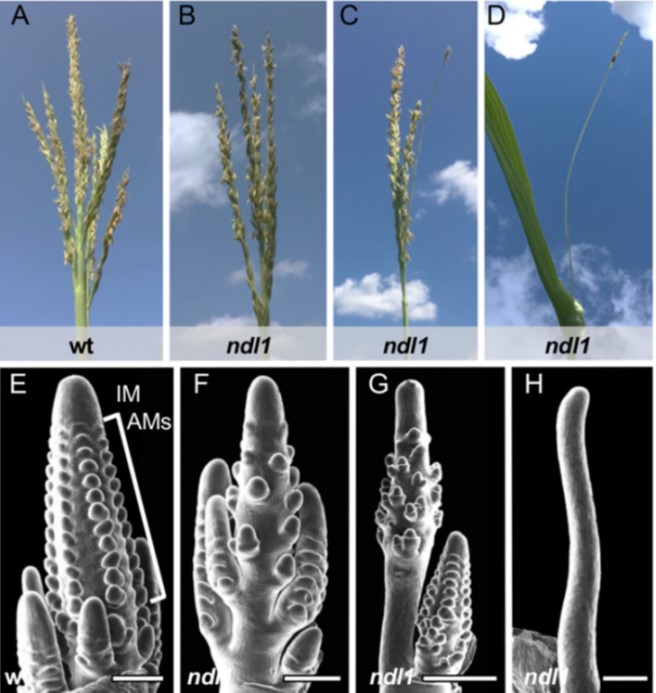

NEEDLE1 encodes a mitochondria localized ATP-dependent metalloprotease required for thermotolerant maize growth ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPreviously, the needle1 (ndl1) maize mutant was identified as showing a variable phenotype mainly affecting the tassel. Here, Liu et al. showed that this variability arises due to its temperature sensitivity, with strongest effects at warmer temperatures. In some cases, the plants arrest before reaching…
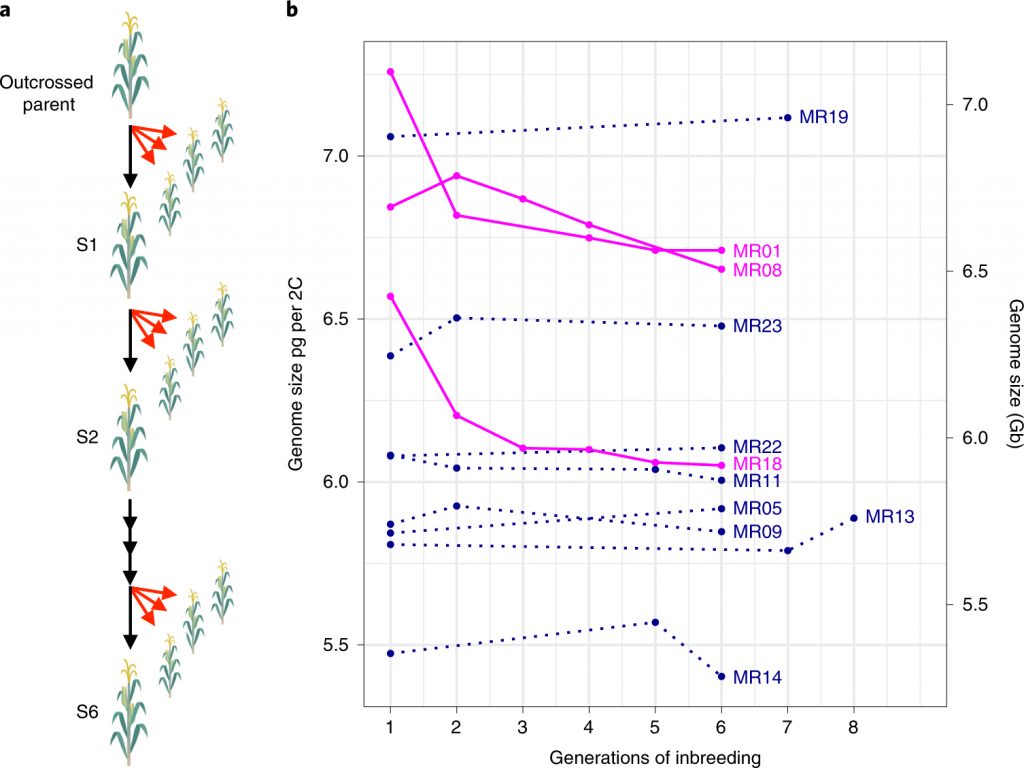
KonMari for Maize - keeping genomes clutter-free during selfing ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyJust like years of hoarding can end up cluttering our homes, years of self-fertilization or selfing can also accumulate harmful mutations in plant genomes. By removing such harmful alleles from the genome (i.e., purging) plants can reduce the mutational load and prevent fitness loss due to selfing. Roessler…
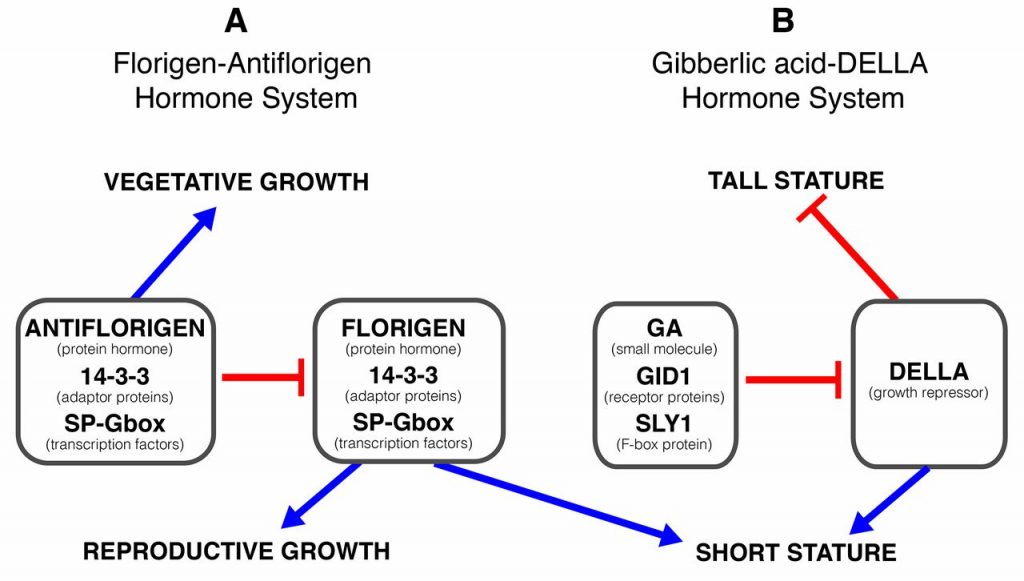
Review: Revolutions in agriculture chart a course for targeted breeding of old and new crops ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA few traits are associated with domestication across many species. Eshed and Lippman provide an overview of the changes to plant stature and flowering time that have been repeatedly selected by our ancestors. By comparing the molecular underpinnings of these traits across crops, it becomes clear that…
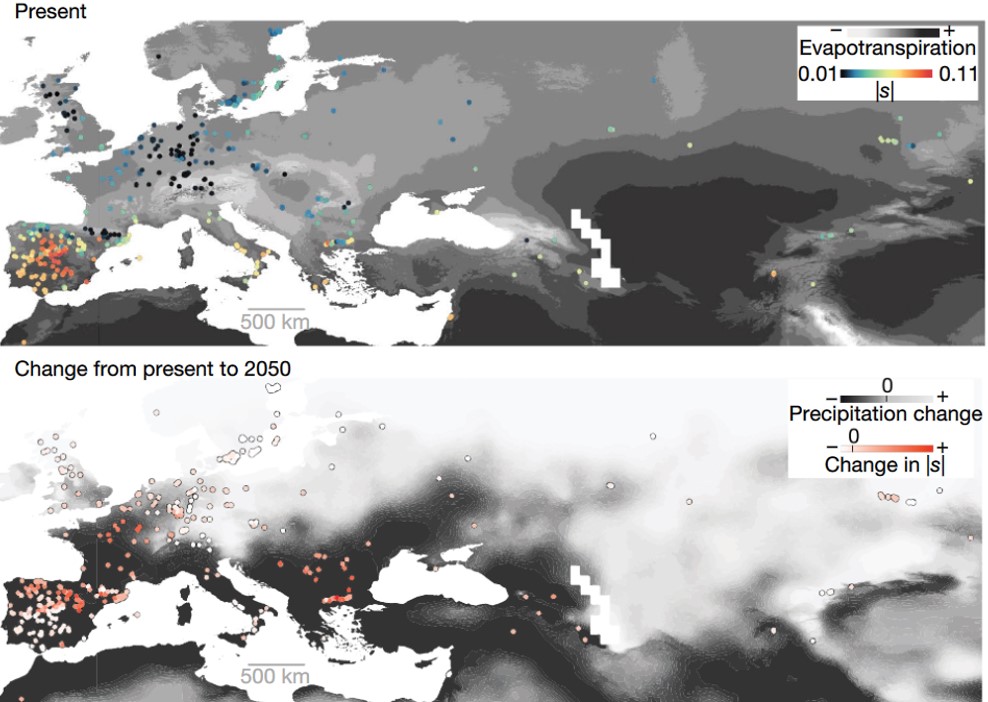
Natural selection on the Arabidopsis thaliana genome in present and future climates (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rapidly changing climate will have profound effects on Earth’s ecosystems, but as yet it is difficult to determine exactly what these effects will be. Exposito-Alonso et al. have set up a large experiment to try to identify how a population’s genetic diversity will enable it to survive a future…
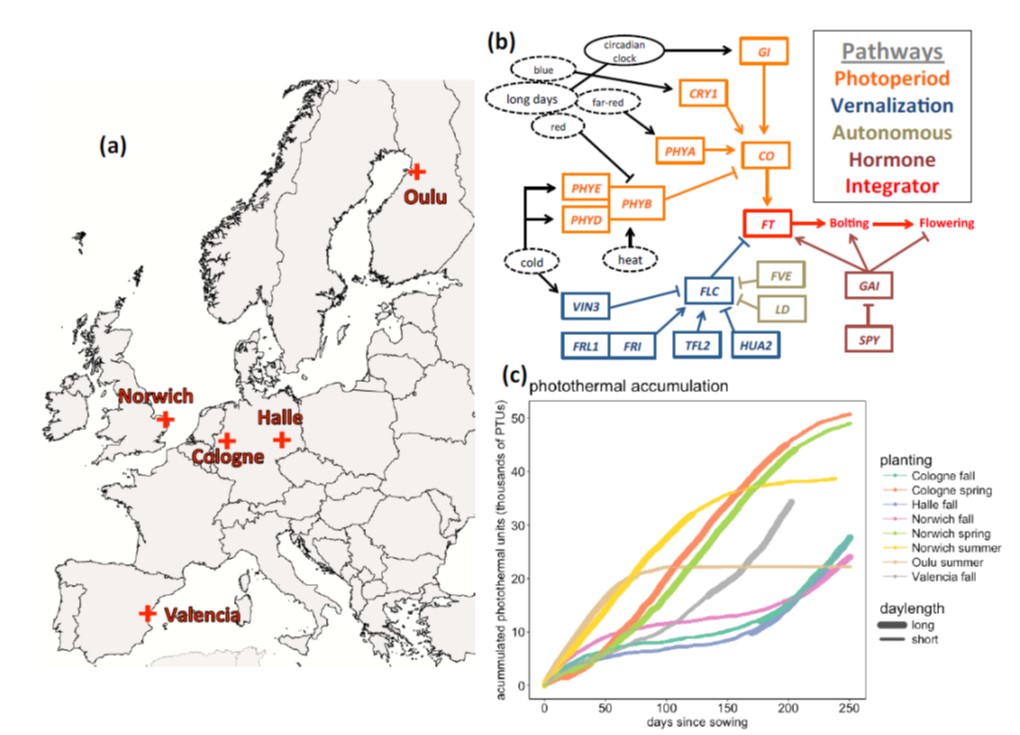
Large-effect flowering time mutations reveal conditionally adaptive paths through fitness landscapes in Arabidopsis thaliana (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have a tendency to think of genes carrying mutations as having a negative impact on fitness, which raises the question of why they might persist in a population. Taylor et al. tested whether large-effect mutations that affect flowering time might not be detrimental in all conditions, by comparing…

Update. GMO-free RNAi: exogenous application of RNA molecules in plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCriticism of transgenic plants and GMOs motivates research into effective GMO-free RNA delivery methods. In this review, Dalakouras et al. discuss different strategies for exogenous application of RNA molecules (dsRNAs, siRNAs) into plants to trigger RNA interference (RNAi) against various targets, such…
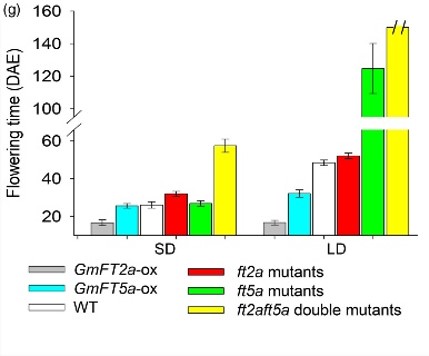
GmFT2a and GmFT5a collectively controls flowering of soybean (Plant Biotech. J)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] is a globally important high-protein crop, whose breeding is an ongoing, important objective for plant biologists. Since soybean is a short-day plant, controlling flowering time is a key step to influence its adaptation to diverse latitudes and farming system. Recently,…
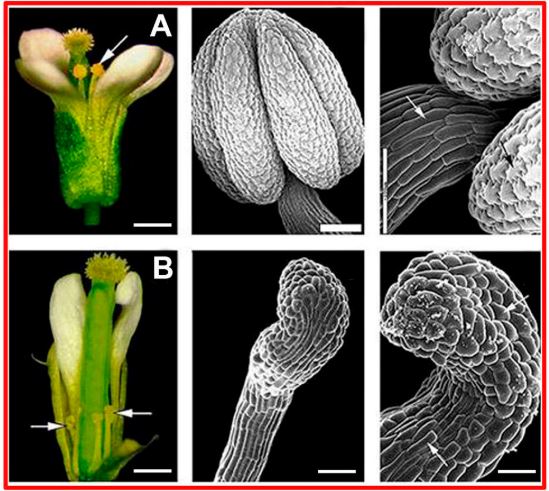
Review: Engineered male sterility by early anther ablation (Frontiers Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMale sterility in seed production could be used to increase crop yields, eliminate pollen allergies or avoid gene flow between genetically modified plants and other species. Here, Roque et al. developed a system to produce engineered nuclear male sterile plants using the pea Pisum sativum ENDOTHECIUM…

