
AT-hook transcription factors restrict petiole elongation by inhibiting PIF-activated genes (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe AT-hook motif nuclear localized (AHL) transcription factor family has one or two DNA-binding motifs to bind to AT rich DNA regions, and they also have a conserved PPC-DUF domain for protein-protein interactions. AHLs affect a wide range of biotic and abiotic responses but the mechanism of how they…
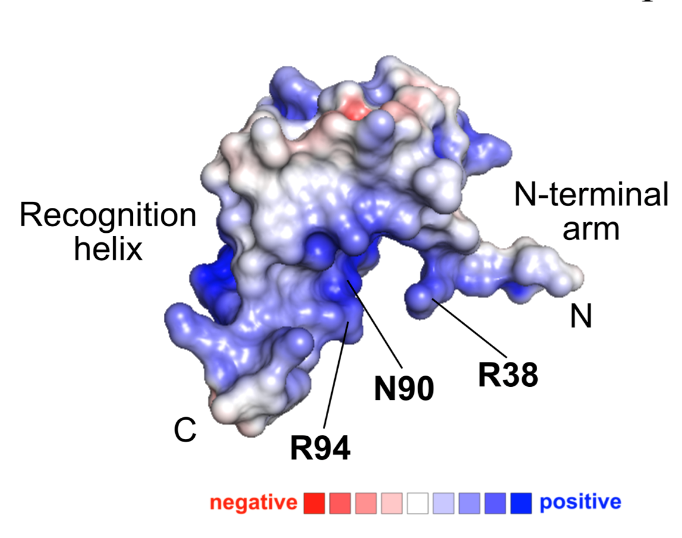
Structural basis for WUSCHEL binding (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transcription factor WUSCHEL (WUS) plays a central role in organization of the shoot meristem. The three-helix bundle homeodomain in WUS can bind to several distinct DNA sequence motifs in many target genes promoters, but a structural view of these binding events has been lacking. Here Sloan et al.…
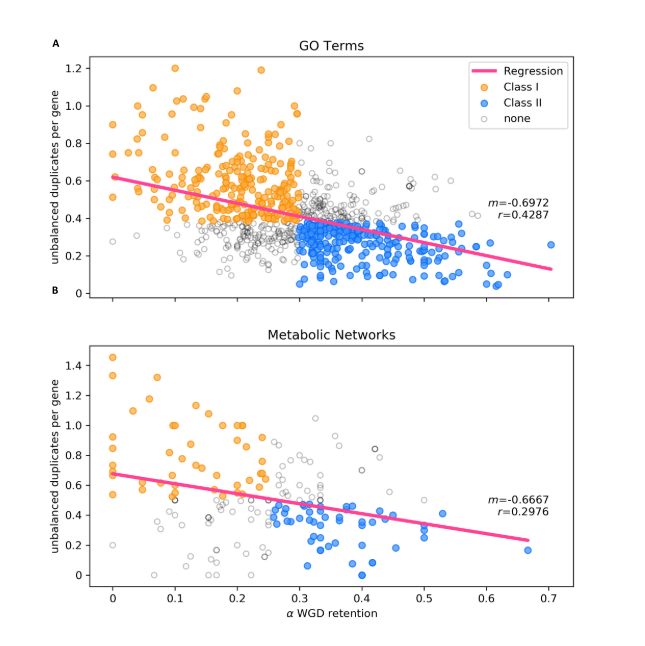
Gene balance predicts transcriptional responses immediately following ploidy change in Arabidopsis thaliana (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThroughout evolutionary time polyploidization events have occurred frequently, increasing the gene copy number (gene dosage) of multiple angiosperms. The gene balance hypothesis proposes that there is selection on gene copy number to maintain the stoichiometric balance between dosage-sensitive genes…
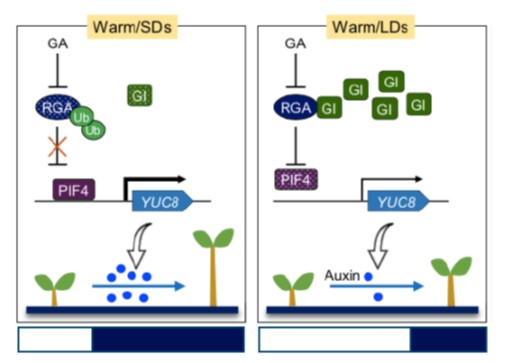
GIGANTEA shapes the photoperiodic rhythms of termomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants evolved molecular mechanisms to integrate seasonal changes with developmental programs. For example, warmer temperatures and increasing day-length mark the transition from winter to spring, and trigger flowering. Now, the synchronisation of ambient temperature and photoperiod is perturbed by global…
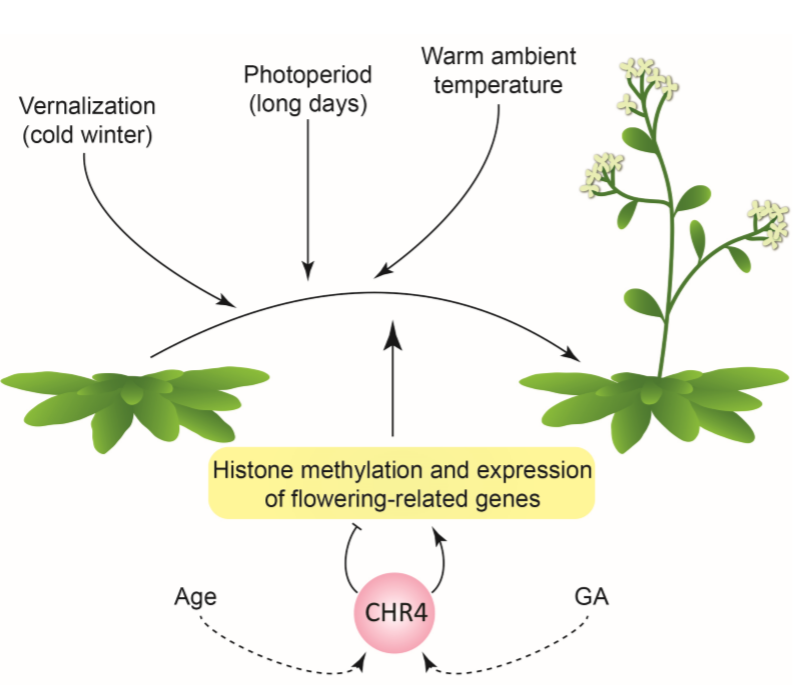
Roles for CHROMATIN REMODELING 4 in Arabidopsis floral transition (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe time at which flowers appear is critical for plant reproductive success. As such, the vegetative to reproductive growth transition is governed by several cues: environmental (photoperiod, temperature) and endogenous (gibberellins, age). Here, Sang et al. used an elegant forward-genetics approach…
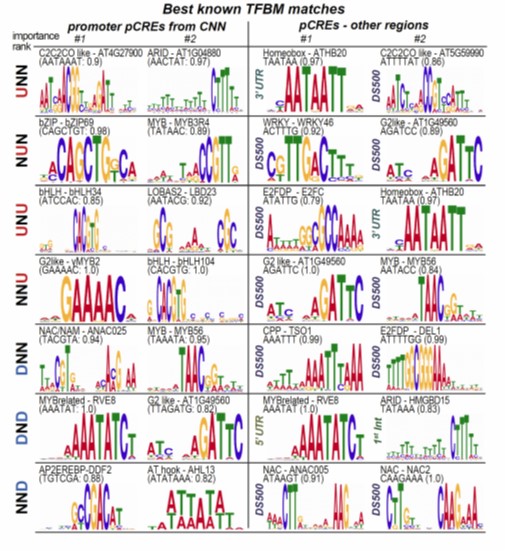
The cis-regulatory codes of response to combined heat and drought stress (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs sessile organisms, plants must not only respond to a single stress, but multiple stresses at the same time. To understand the DNA regulatory elements that mediate the transcriptional response to heat, drought and combined heat and drought stress, Azodi et al. utilized the known transcription factor…
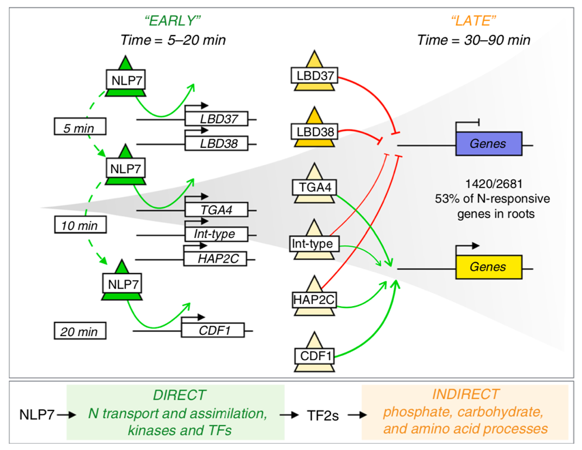
Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTranscription factors (TFs) and their genome-wide targets form gene regulatory networks that allow organisms to respond to stimuli. However, conventional biochemical assays only identify a subset of the TF-target interactions. In this paper, Alvarez et al. elucidate the genetic network of NIN-LIKE PROTEIN…
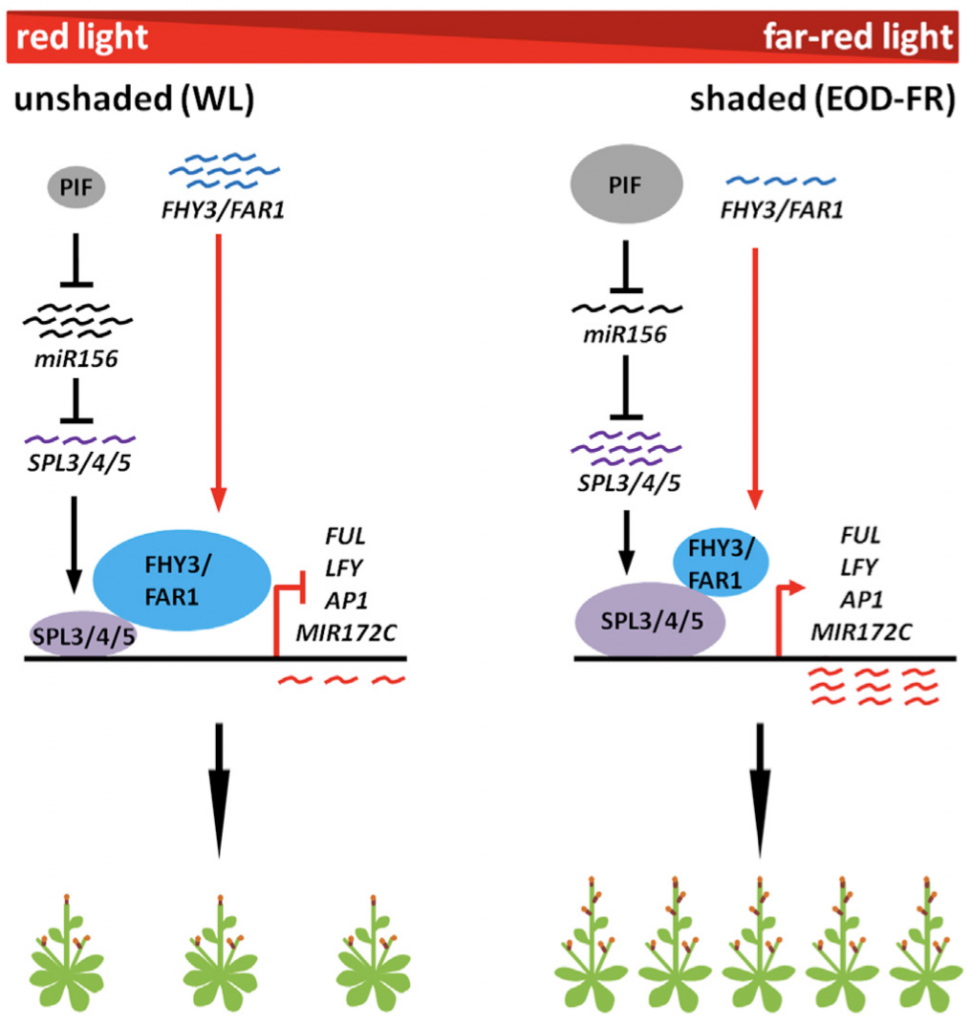
Integration of light signaling with endogenous developmental pathway to regulate flowering (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponse to changing environmental conditions is key for plant reproductive success. Previous studies have implicated FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL3 (FHY3) and FAR-RED IMPAIRED RESPONSE1 (FAR1) as inhibitors of flowering in phytochrome A signaling pathway. miR156-targeted SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN…
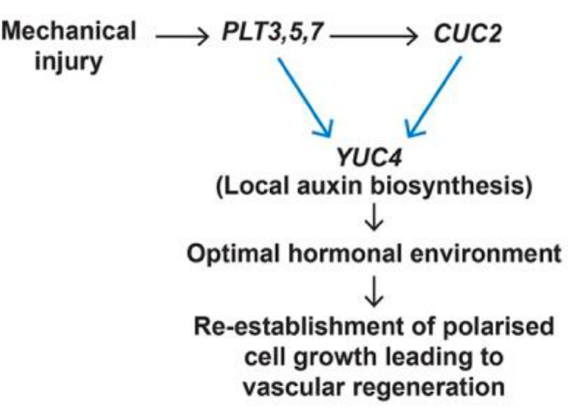
A feedforward loop controls vascular regeneration and tissue repair through local auxin biosynthesis (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are constantly exposed to biotic and biotic stresses that can cause tissue damage, and, as a response, plants have evolved remarkably plastic regenerative mechanisms in response to wounding. Although some genes required for regeneration have been identified in the Arabidopsis root context, most…

