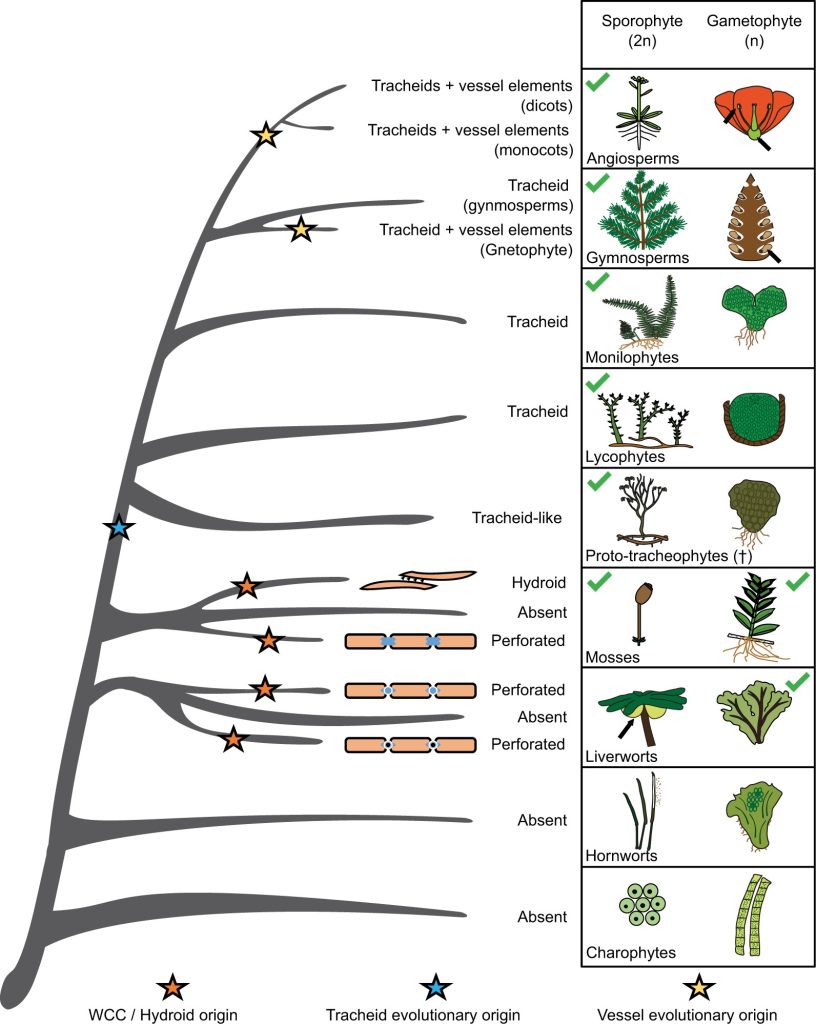
Review: Deep origin and gradual evolution of transporting tissues: Perspectives from across the land plants (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe development of vascular plants (tracheophytes) was a major innovation during the evolution of land plants. The classic view is that the evolution of transporting tissues is distinct to tracheophytes, but Woudenberg and Renema et al. discuss an alternative hypothesis where this was a gradual process…
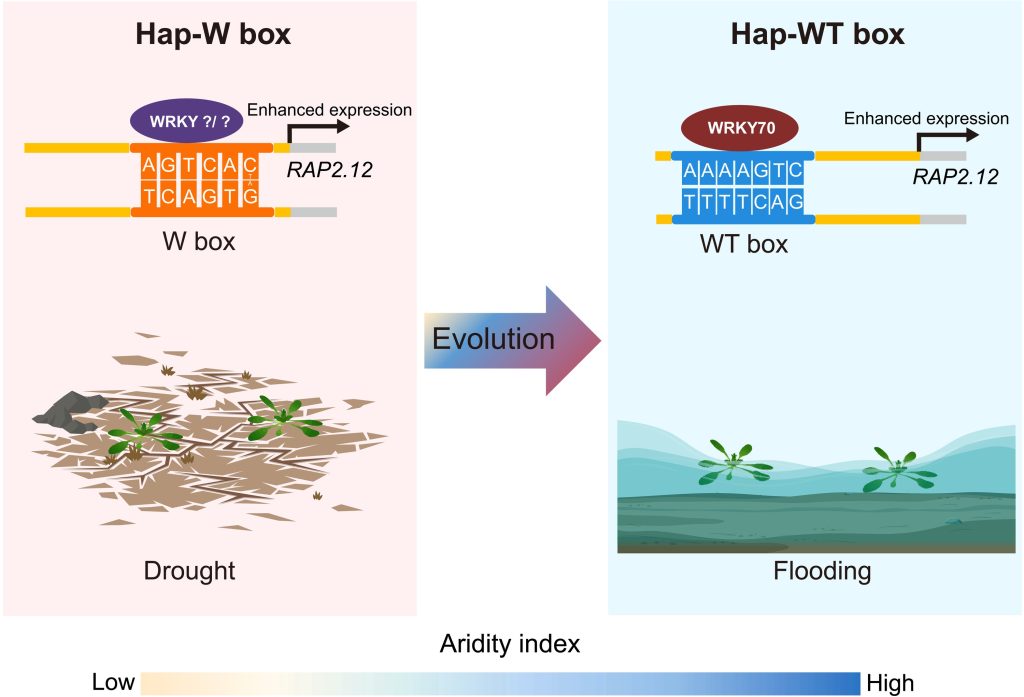
Allelic shift in cis-elements of the transcription factor gene RAP2.12 underlies adaptation associated with humidity in Arabidopsis thaliana (Science Adv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo better understand plant responses to different environments, Lou et al. compared Arabidopsis thaliana accessions derived from Sichuan (high precipitation/regular flooding) and Tibet (arid) to isolate genetic adaptations towards flooding stress. The two accessions showed divergent phenotypes: the Sichuan…
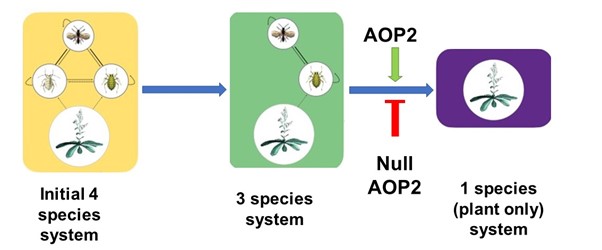
A plant gene that shapes its ecosystem (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKeystone species shape the structure of an entire ecosystem, but can a gene determine structure of the whole ecosystem? A recent study indicates yes, some genes can, and such genes are called keystone genes. Barbour et al. set up a small ecosystem containing two herbivore aphids, one predator of these…
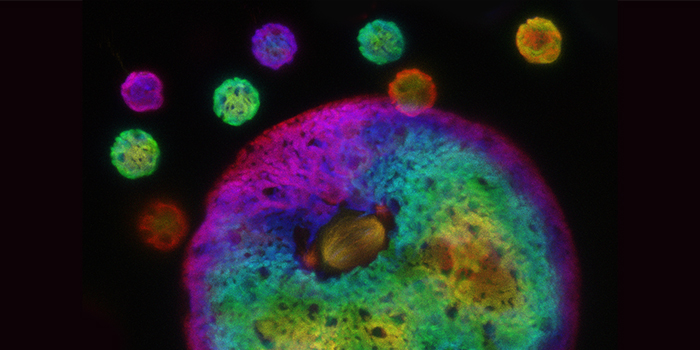
Make two from one: How embryonic algal cells divide in an orchestrated flow of subcellular structures
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellVon der Heyde and Hallmann uncover the enormous dynamics of early cell divisions in Volvox embryos. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac004
Eva Laura von der Heyde and Armin Hallmann
Department of Cellular and Developmental Biology of Plants, University of Bielefeld, Universitätsstr. 25, 33615…

Special issue: Sex determination and sex chromosome evolution in land plants (Philosophical Transactions B)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAt some point, most biology students learn the term “dioecy” (two houses), which refers to the separation of male and female function into different individuals, a characteristic that is common in animals but less so in flowering plants. About 6% of angiosperms and 65% of gymnosperms are dioecious,…
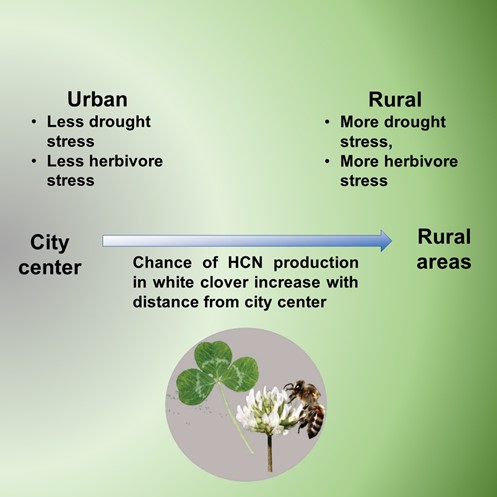
The urban environment led to unintended adaptive evolution in plants (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenerally, evolution is driven by natural selection, but not always. Human activities lead to the creation of unique niches, and other organisms must adapt accordingly. Cities are unique niches that are significantly different from rural areas and natural conditions. The urban habitat provides plants…
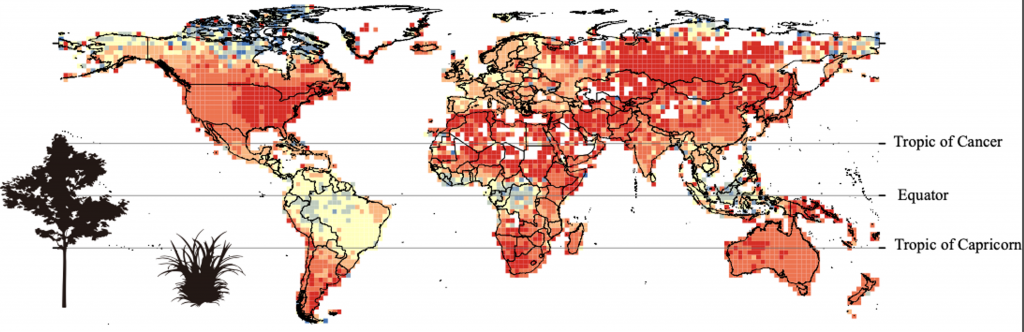
Seed dormancy in space and time: global distribution, paleo- and present climatic drivers and evolutionary adaptations ($) (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed dormancy is widely recognized as a key mechanism to ensure that germination takes place under the most suitable conditions. Such is its importance that multiple studies have described the morphological, physiological, and genetic mechanisms behind it, yet its global distribution and the past and…

A species-specific partial duplicate gene in Arabidopsis thaliana evolved novel morphological effects
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHuang, Chen and colleagues take advantage of a partial duplicated gene to compare the functions of the partial duplicate and its parental copy.
By Yuan Huang, Jiahui Chen, Shengqian Xia and Manyuan Long, Department of Ecology and Evolution, The University of Chicago, Chicago, USA
Background:…
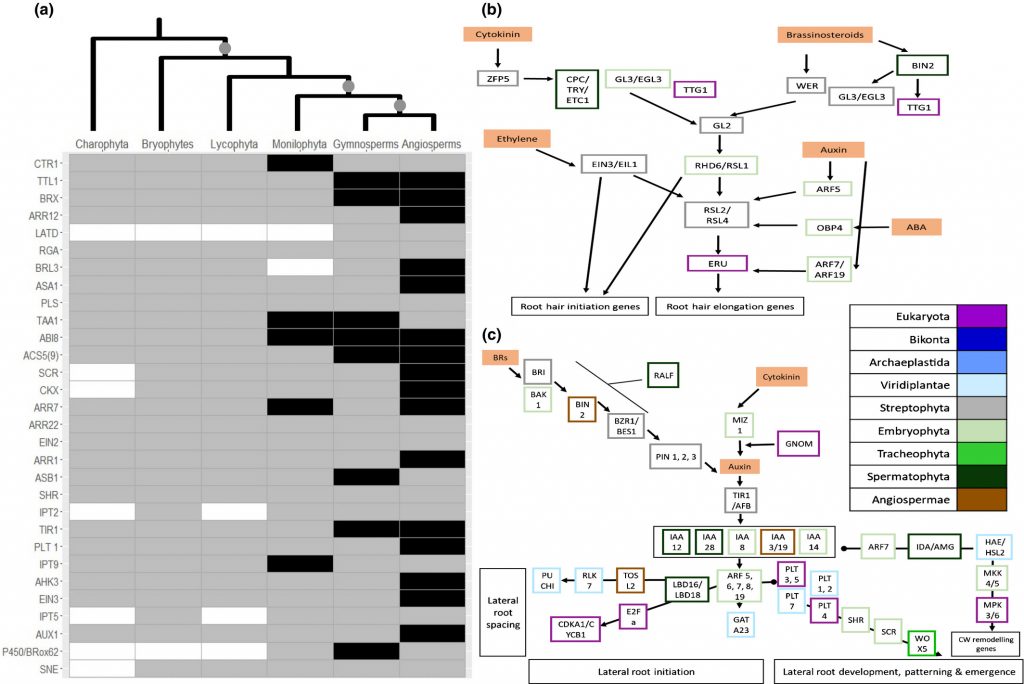
Water-related innovations in land plants evolved by different patterns of gene cooption and novelty (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe availability of genome data from across the kingdom of plants has provided insights into plant evolution, and particularly the emergence of land plants. Here, Bowles et al. explore the genetic origins of three key innovations that supported the expansion of land plants: stomata, vascular tissues,…

