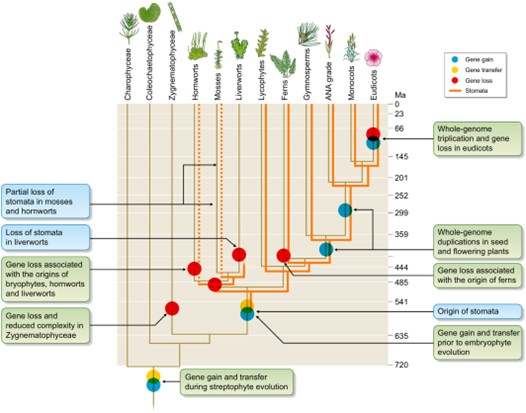
Review: Genome evolution in plants and the origins of innovation
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plants have enormous diversity; however we do not fully understand how this has arisen. In this review article James Clark discusses how genome dynamics and gene loss contribute to genome evolution and the generation of diversity and complexity. He explains how genome evolution is non-homogenous…
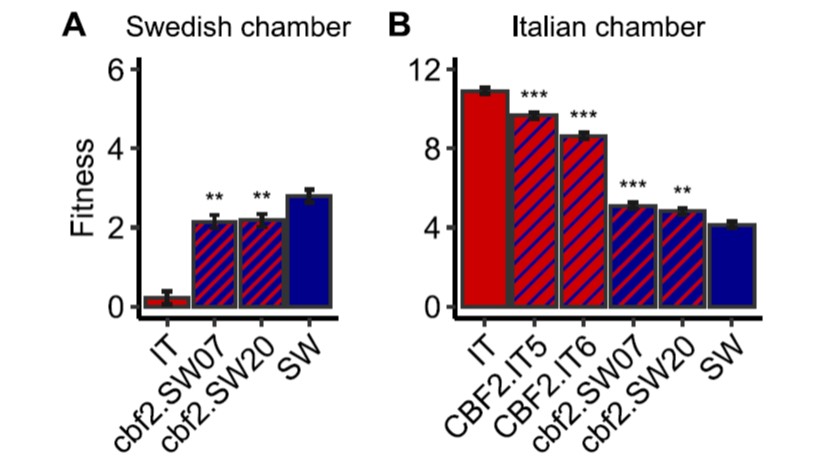
A large effect genetic trade-off is caused by a single mutation in CBF2
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnderstanding the genetic basis of local adaptation of a species is an important but thorny problem. Now that whole genomes are readily characterized, it’s not hard to see lots of differences between populations, but pulling meaning and demonstrating functional consequences out of those differences…
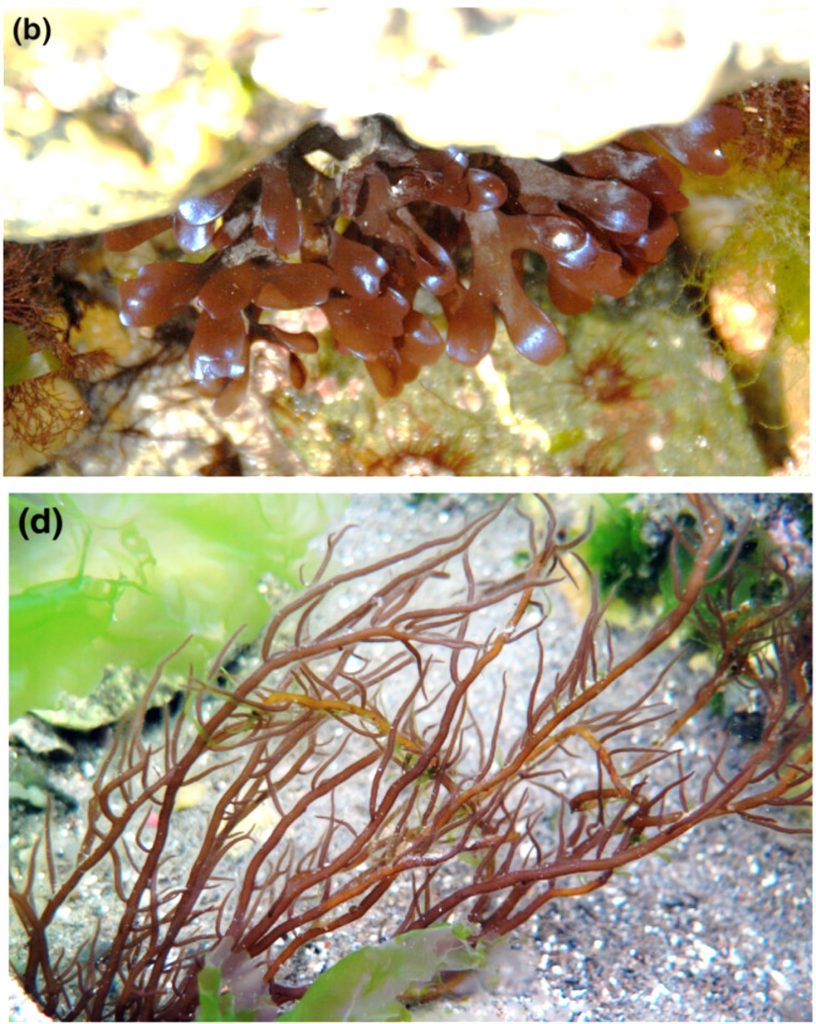

Review: Red macroalgae in the genomic era
Plant Science Research WeeklyI highly recommend this excellent and accessible article by Borg et al. that provides an overview of the red macroalgae, which “may have been the first eukaryotic lineage to have evolved complex multicellularity”. It’s full of fascinating information: although 97% of red algal species are marine,…
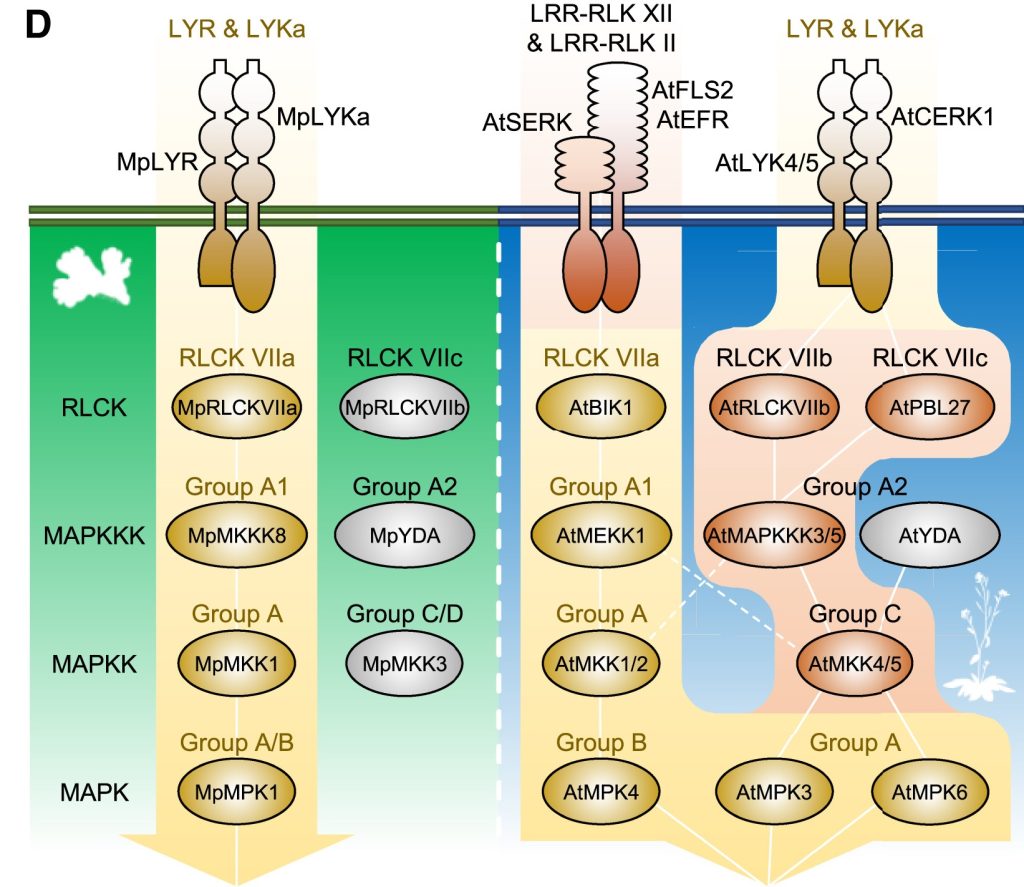
LysM-mediated signaling in Marchantia polymorpha and conservation of PTI in land plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyMarchantia polymorpha, the common (but adorable) liverwort, has earned its spot in the ranks of very important plant model systems, joining Physcomitrium patens as representatives of the bryophyte clade. Many systems first characterized in Arabidopsis and other angiosperms are now being studied in these…
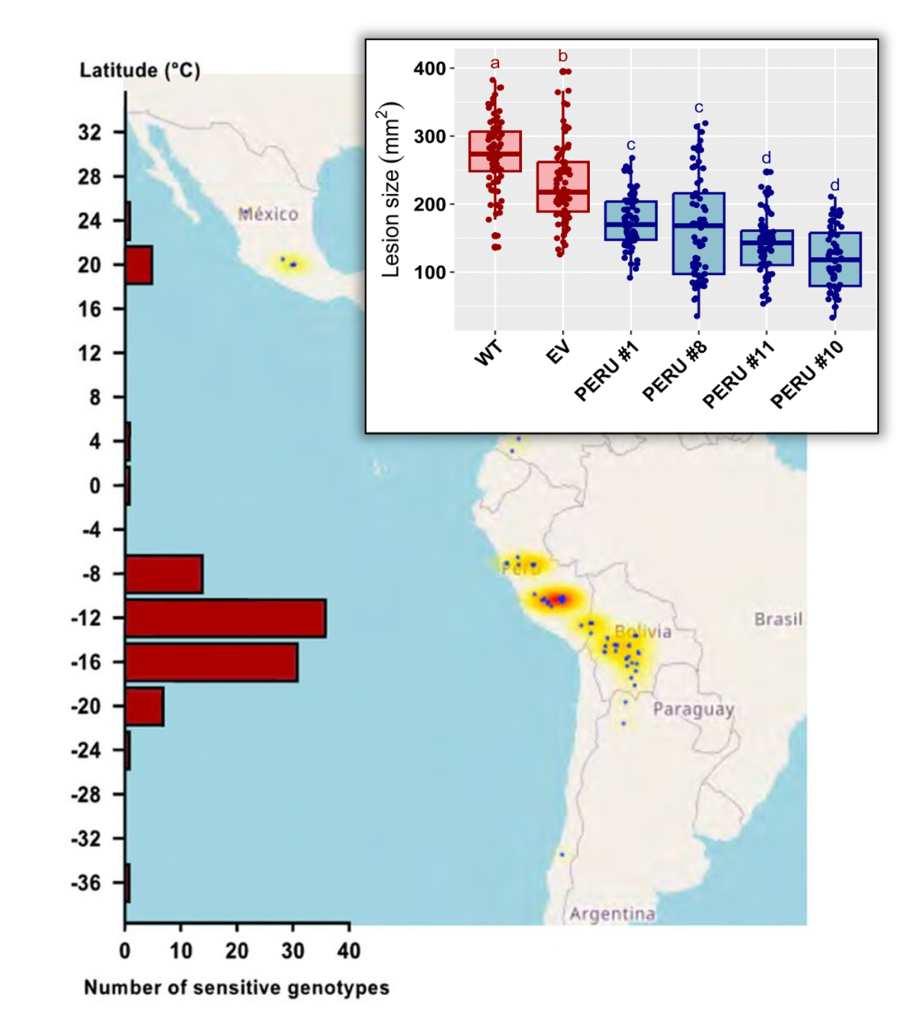
Functional diversification of a wild potato immune receptor at its center of origin
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn many biology textbook, plant pathology is introduced through the historical context of the 1840s great potato famine, caused by colonial ideologies and a virulent pathogen. This causal agent, Phytophthora infestans, is an oomycete that is still present in the environment and causing outbreaks of late…
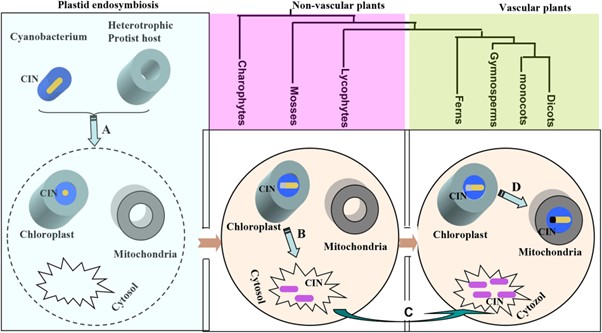
Evolution of cytosolic and organellar invertases empowered the colonization and thriving of land plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyInvertases catalyse the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose. In plants, invertases fall into two clades – the mitochondrially/plastid localized α clade and the cytoplasmically localized β clade. However, we do not fully understand how these clades evolved. Here Wan et al. identified 665…

Adaptive evolution of the enigmatic Takakia moss now facing climate change in Tibet
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this fantastic, engaging paper, Hu et al. carries the reader from the origins of life on land through the dramatic uplift of the Tibetan plateau and into the modern age of climate change, all through the lens of the “enigmatic” Takakia moss. It’s enigmatic because it has features that are more…
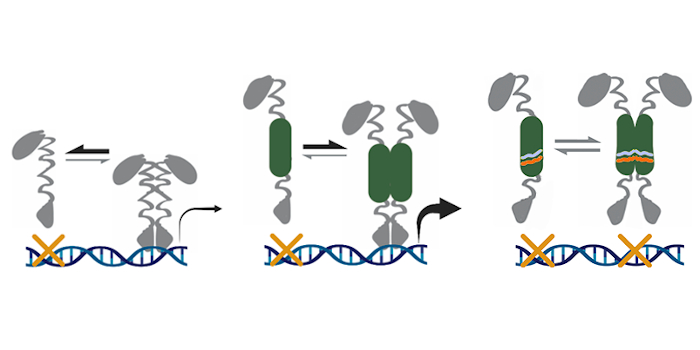
Ligands and regulatory properties of the HD-ZIPIII START domain
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHusbands et al. identify ligands and regulatory properties of the HD-ZIPIII START domain.
By By Aman Y. Husbands (University of Pennsylvania) and Marja C.P. Timmermans (University of Tuebingen).
Background: Development has been compared to a ball rolling down a hill. Cells initially have broad…
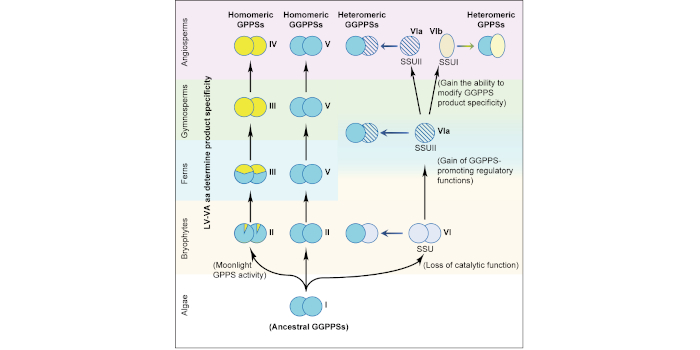
The functional evolution of geranyl diphosphate synthases with different architectures
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSong, Jin, Chen, He, Li, Tang, et al. establish that independent evolutionary processes in ancestral land plants led to homo- and heteromeric geranyl diphosphate synthases.
Shuyan Song and Shan Lu
School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
Background: Terpenoids are a…

