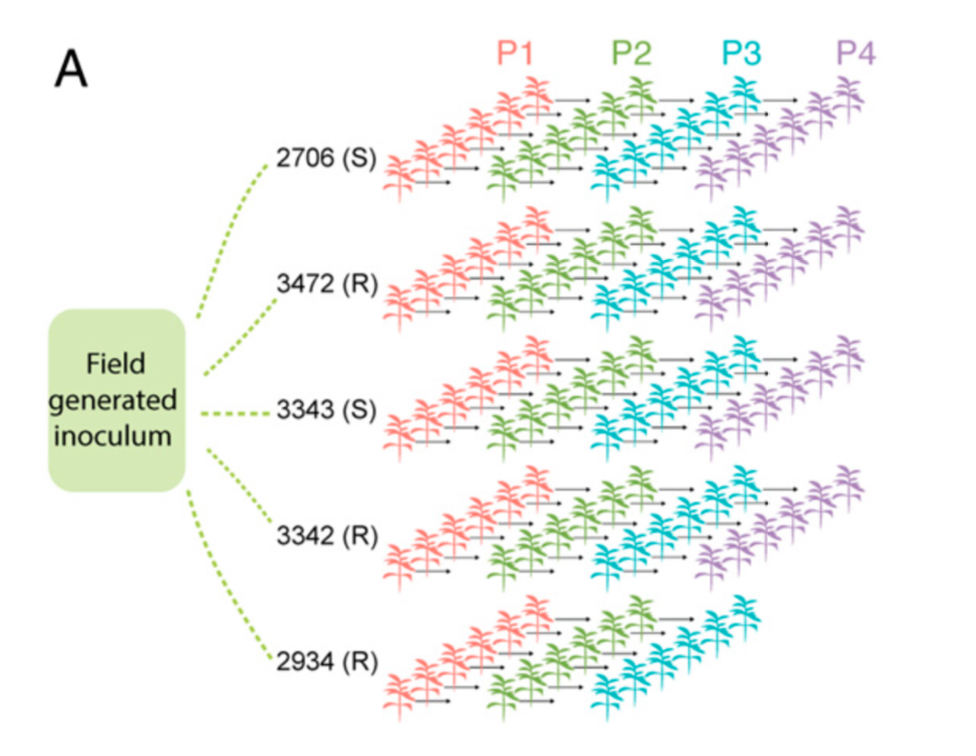
Successive passaging of plant associated microbiome reveals robust habitat and host genotype-dependent selection (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStudy of the plant microbiome can contribute to sustainable agricultural systems through improvements to plant health and nutrition. One goal has been to select and design microbiome communities for specific functions. In a recent article, Morella et al. have used an experimental evolution approach to…
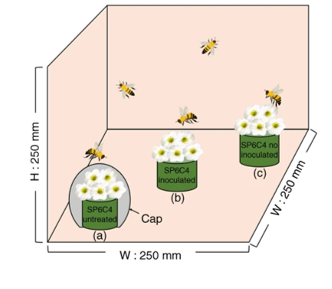
A mutualistic interaction between Streptomyces bacteria, strawberry plants and pollinating bees (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome species of Streptomyces bacteria produce antimicrobial compounds that have been shown to enhance plant resistance to pathogens. Kim et al. show that his protection can extend to a pollinator. The Streptomyces defends the plant against Botrytis cinerea and protects the bees against insect pathogens…

Ongoing accumulation of plant diversity through habitat connectivity in an 18-year experiment ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring the course of time, we have realized the importance of biodiversity for the maintenance of the ecosystem. However, the world has already been fragmented in small parts which resulted in a huge loss of habitat and threatening to biodiversity. Habitat connectivity, which means the degree to which…

Insect herbivory selects for volatile-mediated plant-plant communication ($) (Current Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in response to insect herbivory. The potential for VOCs to serve as diffusible signals has long been recognized. For example, VOCs can signal neighbors to prime for defense, signal distant parts of the emitting plant, and even attract predatory insects…
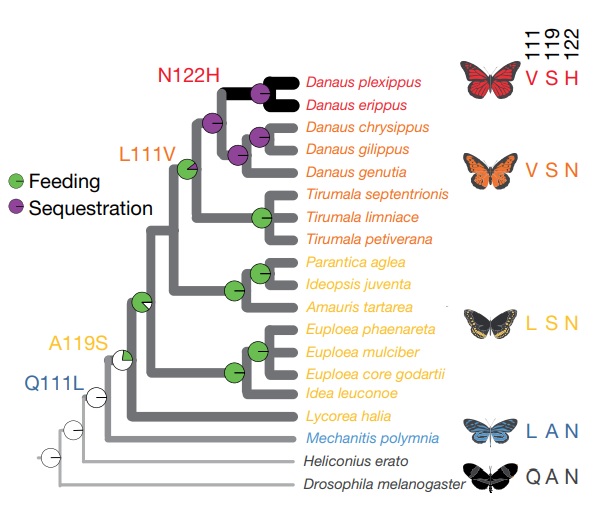
Genome editing retraces the evolution of toxin resistance in the monarch butterfly ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen a few species from several distantly related groups produce a similar but unusual trait, we usually assume that this trait is an example of convergent evolution; starting from different places but ending up at the same place. The ability to eat plants that produce cardiac glycosides, which are toxic…
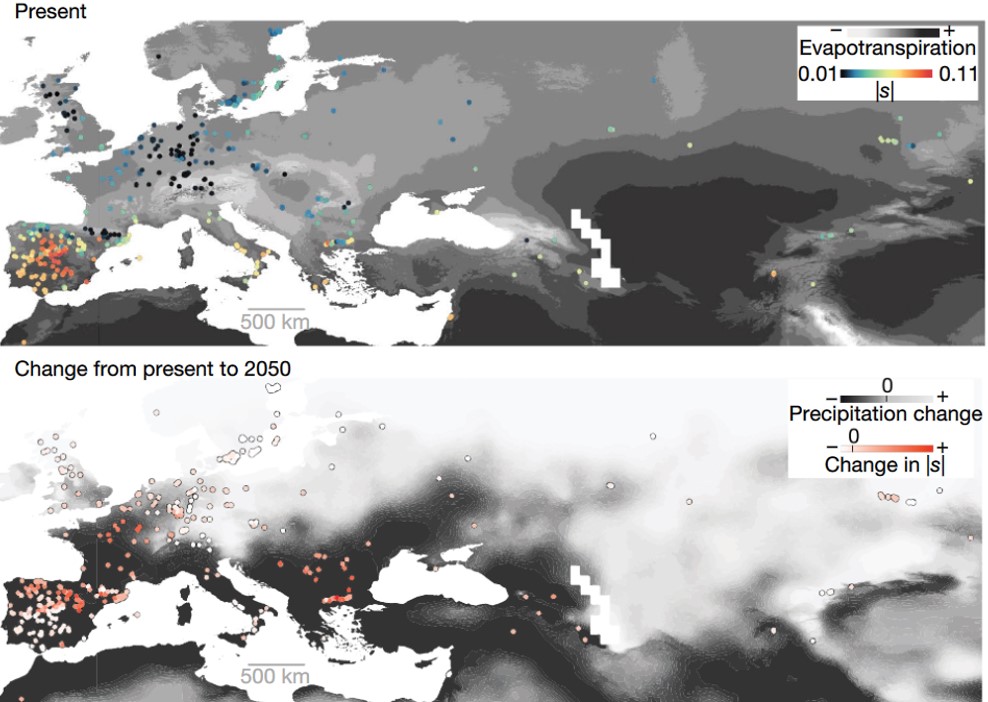
Natural selection on the Arabidopsis thaliana genome in present and future climates (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rapidly changing climate will have profound effects on Earth’s ecosystems, but as yet it is difficult to determine exactly what these effects will be. Exposito-Alonso et al. have set up a large experiment to try to identify how a population’s genetic diversity will enable it to survive a future…
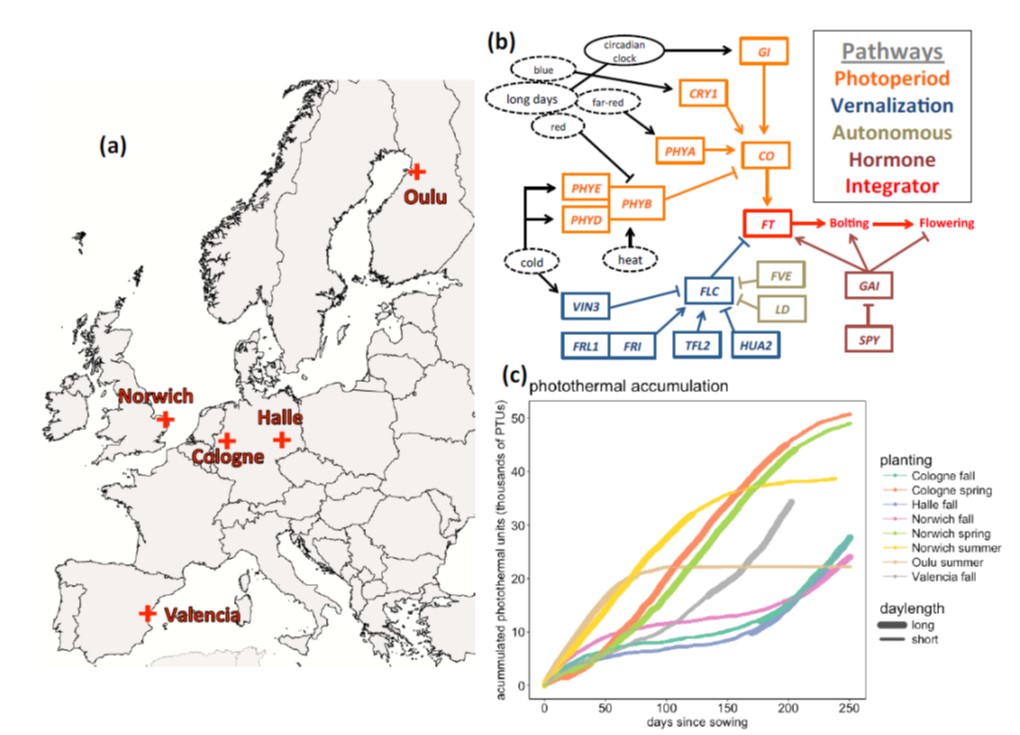
Large-effect flowering time mutations reveal conditionally adaptive paths through fitness landscapes in Arabidopsis thaliana (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have a tendency to think of genes carrying mutations as having a negative impact on fitness, which raises the question of why they might persist in a population. Taylor et al. tested whether large-effect mutations that affect flowering time might not be detrimental in all conditions, by comparing…

Increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduces global vegetation growth (Science Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant scientists know that when the air at the leaf surface is dry, the plant will tend to close its stomata, but we tend to think of this as a relatively localized effect. Yuan et al. have explored the global trends in vapor pressure deficit (VPD; difference between saturated and real water content…
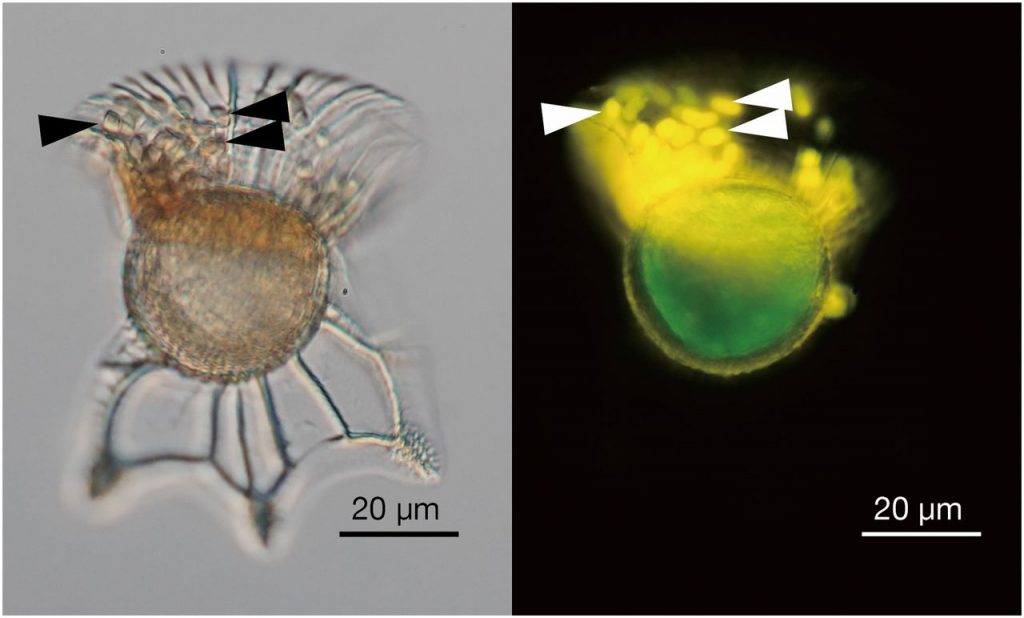
Single-cell genomics unveils an ectosymbiont cyanobacteria associated with a dinoflagellate host (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCyanobacteria are important contributors to global carbon fixation. They can be free-living in many different environments, but also form close symbiotic associations with various eukaryotic organisms. Nakayama et al. have idea identified a new type of cyanobacteria that lives as an ectosymbiont in a…

