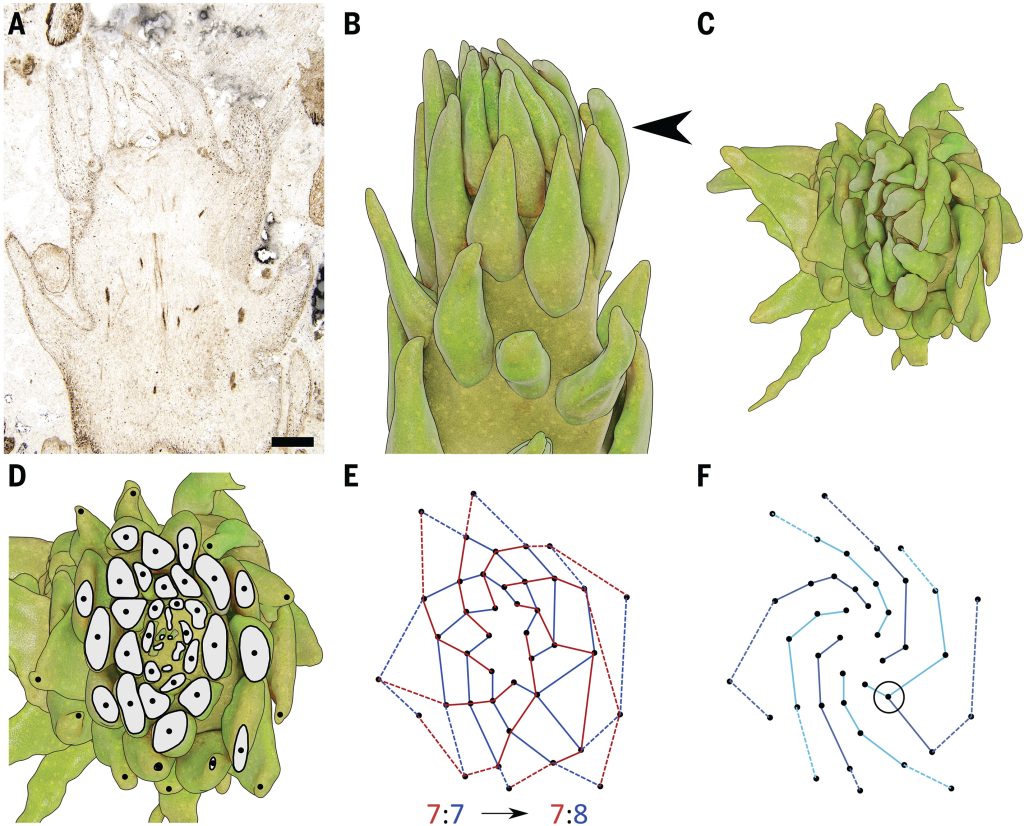
Going against the botanical grain: Non-Fibonacci spirals in early land plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis study by Turner et al. looks at the patterns of leaf and sporangia arrangement in early leafy plant species, questioning the widely held idea that these structures follow the Fibonacci sequence. The researchers investigated fossilized remains from the Early Devonian period. To evaluate the spatial…

Review: Computer models of cell polarity establishment in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s pretty obvious that plants are not simply balls of cells. Their shapes and patterns are determined in large part through processes that cause cells to grow and divide asymmetrically, through the establishment of cell polarity. When I set out to read this review I was a bit nervous, expecting to…
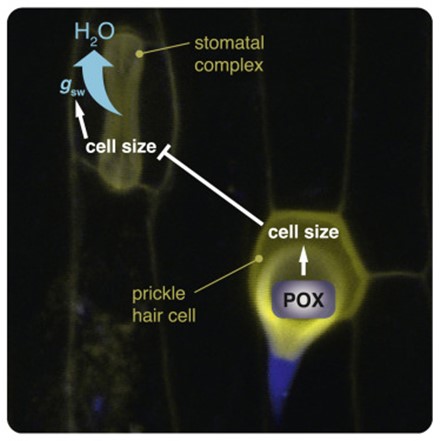
Regulation of hair cell and stomatal size by a hair-cell specific peroxidase in Brachypodium distachyon
Plant Science Research WeeklyMature grass leaves contain two specialized types of epidermal cells: stomata and epidermal hairs (trichomes). Stomatal pores are crucial for CO2 uptake and water conservation, while epidermal hairs contribute to water regulation and provide protection against UV-B light. If stomatal identity is not…
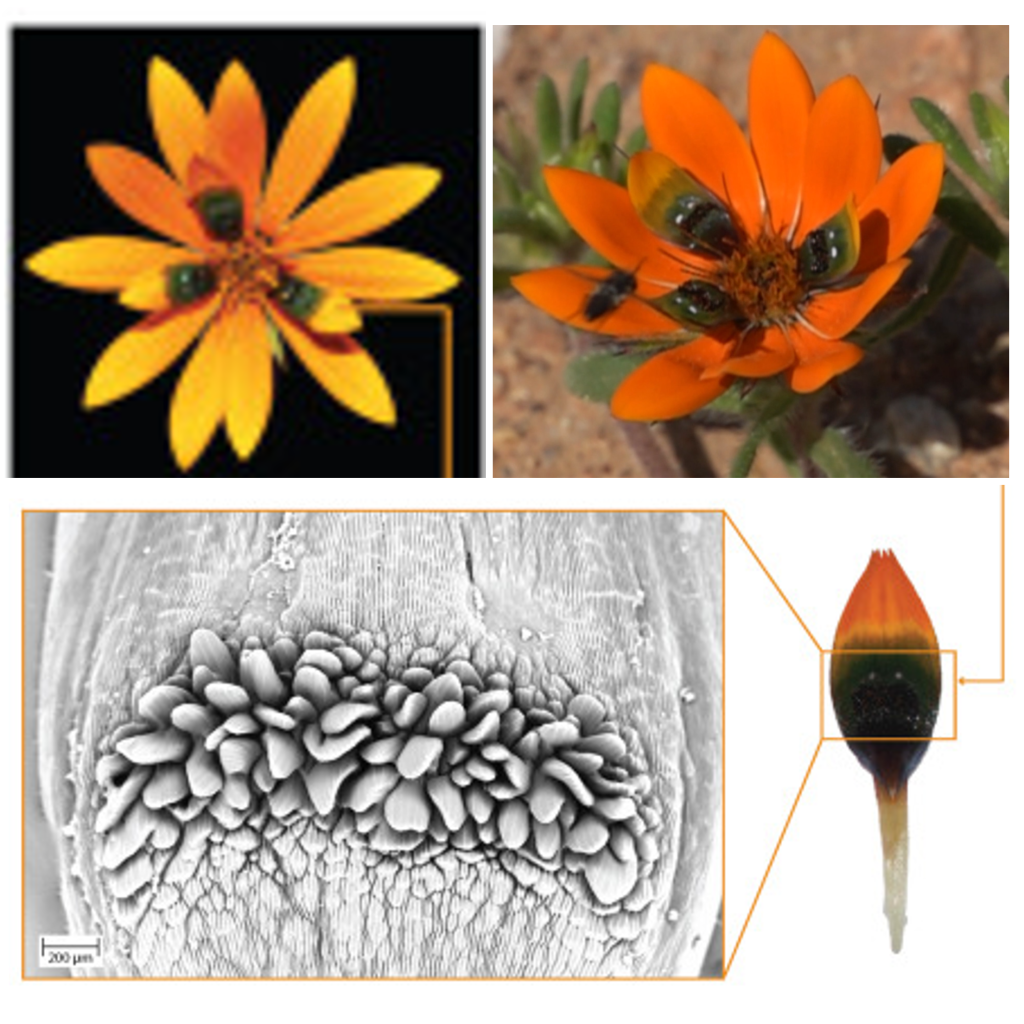

How did the daisy get its spots? Gene co-option and fly mimicry
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is one of those “straight into the textbook” stories. Kellenberger et al. investigated the unusual petal pigmentation pattern of a South African daisy Gorteria diffusa, which has petals with odd lumpy irregular spots that mimic female flies and enhance pollination through sexual deception. The…
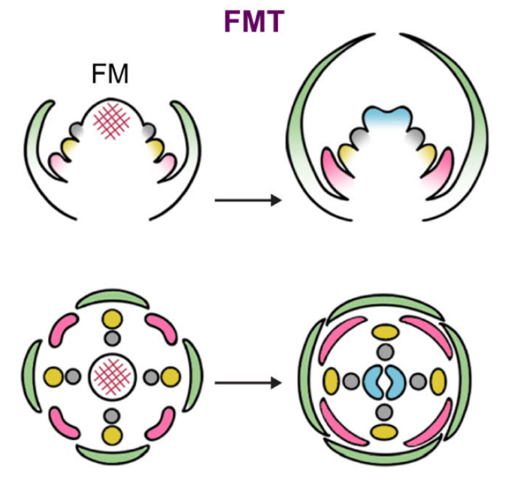
Review: How floral meristem termination shapes flowers
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlowers come in a breathtaking variety of shapes and sizes. The structures making up a flower, called sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels, all derive from the tightly regulated differentiation of a pool of stem cells in the so-called floral meristem. Floral meristem termination (FMT) is a crucial stage…

Anisotropic cell growth at the leaf base promotes age-related changes in leaf shape
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe Arabidopsis thaliana leaf exhibits dramatic phenotypic changes across the juvenile-to-adult phase transition during vegetative development. For example, juvenile leaves are small, round, and lack trichomes (leaf hairs). By contrast, adult leaves contain trichomes on the abaxial (or lower) leaf surface,…
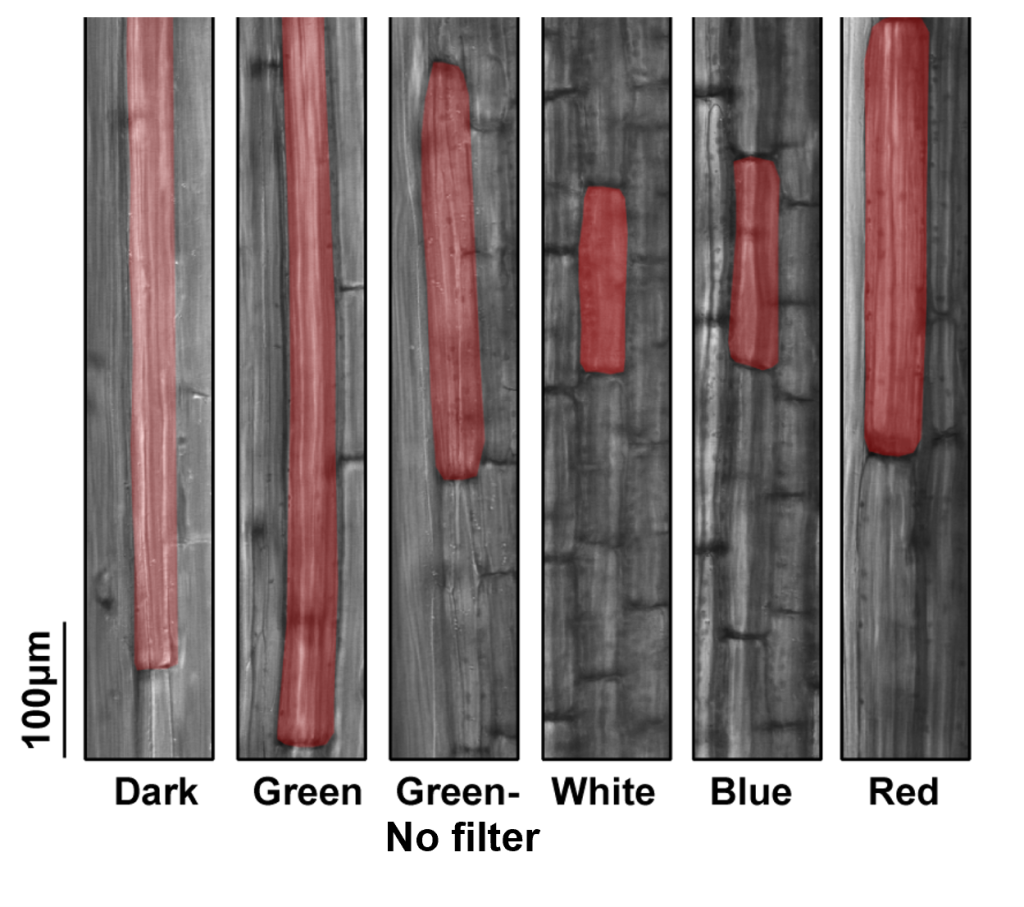

Green means go: Green light promotes hypocotyl elongation via BRs
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenerally, light inhibits hypocotyl elongation. Like red and blue light, green light was previously reported to inhibit hypocotyl elongation in several plants. Here, Hao et al. discovered that the inhibition of hypocotyl growth by green light is due to wavelength impurities in the green lights used.…
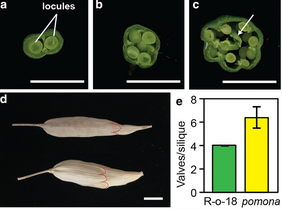
A novel CLAVATA1 mutation causes multilocularity in Brassica rapa
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase and its ligand CLAVATA3 (CLV3) are associated with the CLAVATA-WUSCHEL pathway, which partly controls locule number (the seed-bearing structure of fruits). An increase in locule number is believed to increase the number of seeds and subsequently increase fruit size.…
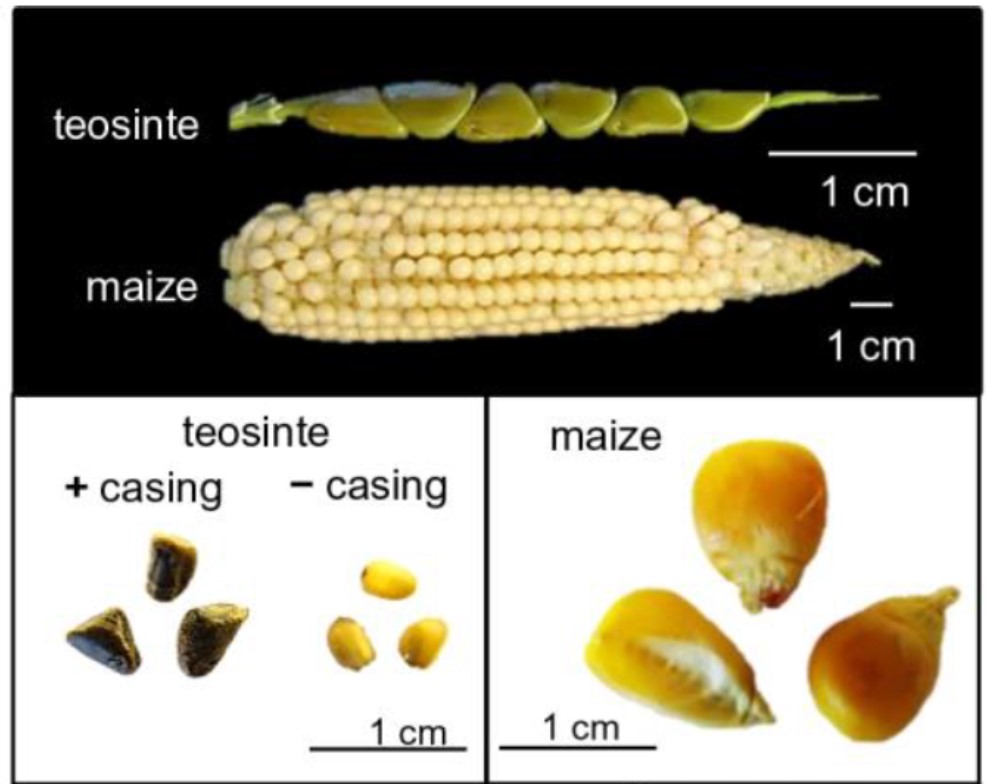

Contribution of strigolactones to maize kernel domesticated phenotype
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe’ve all seen striking photographs comparing the modern maize (Zea mays spp. mays L.) ear to the seed head of its wild-grass ancestor teosinte (Zea mays spp. parviglumis). Besides the huge increase in size, one of the features that allows us to munch on “corn on the cob” is the absence of the…

