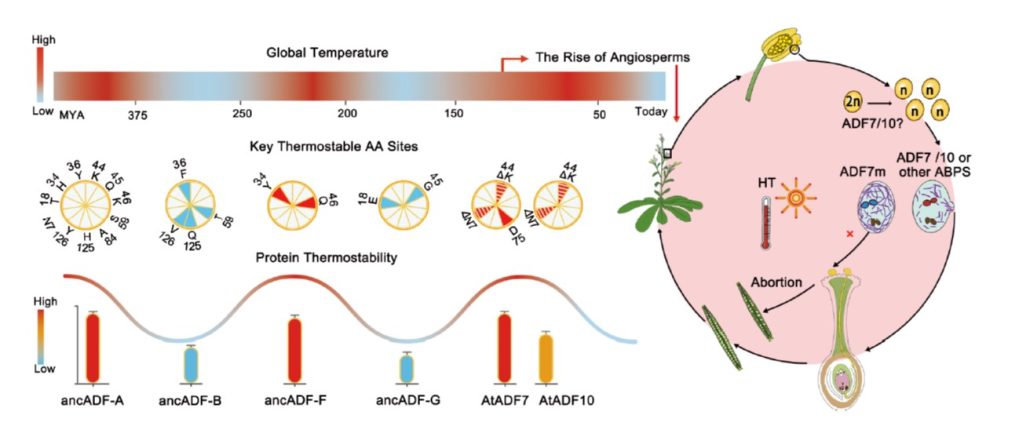
Evolution of the thermostability of actin-depolymerizing factors enhances pollen germination at high temperature
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn angiosperms, pollen germination leads to a period of extensive polarized growth of the pollen tube, which carries the sperm nuclei to the ovule. Studies of tip growth in both pollen tubes and root hairs have contributed to a descriptive model that involves polarized vesicle movement along the cytoskeleton…
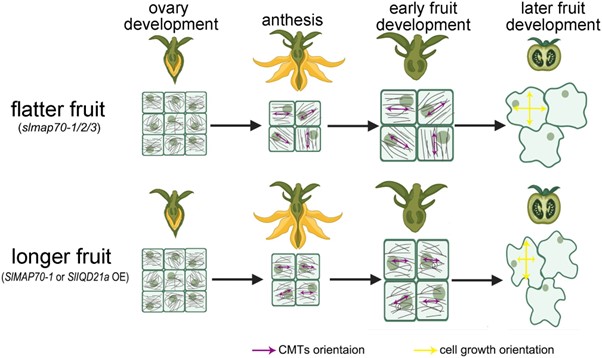
Microtubule-associated proteins regulate fruit shape in tomato
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicrotubule binding proteins are important in determining fruit shape by driving changes in microtubule arrangement. However, in depth molecular studies on these in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) have been limited. Here, Bao et al. investigated the microtubule binding protein Microtubule-Associated Protein…
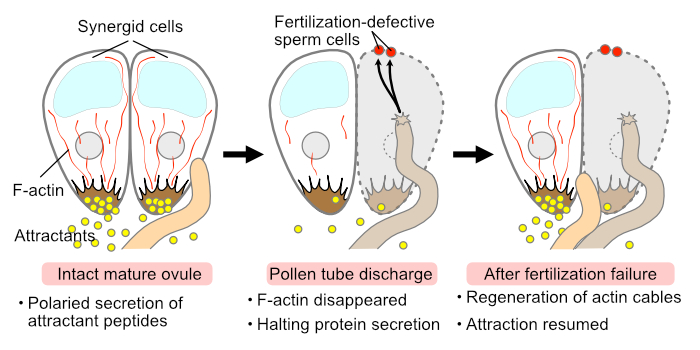
F-actin in the synergid cell regulates the secretion of pollen tube attractants like a fishing rod
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSusaki et al. explore the role of the cytoskeleton of synergid cells during sexual reproduction of angiosperms.
By Daichi Susaki, and Daisuke Maruyama
Kihara Institute for Biological Research, Yokohama City University, Japan.
Background: The two synergid cells embedded in the ovule of angiosperms…

Cortical microtubules contribute to division plane positioning during telophase in maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring plant cell division, the new cell wall is built along a plant-specific structure named the phragmoplast. The phragmoplast is a complex array of microtubules and microfilaments that originates at the middle of the cell and expands outwards to the division site at the cell cortex. The proper orientation…
Microtubule control during stomatal movement
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. investigate the function of SPR1 in ABA-induced stomatal closure
By Pan Wang and Sijia Qi
State Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry; Department of Plant Sciences, College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China
Background: Drought…

PIF4 regulates microtubule organization to mediate high temperature–induced hypocotyl elongation
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant growth adaptation to heat stress (thermomorphogenesis) is regulated by changes in plant morphology such as petiole and hypocotyl elongation. One of the known players in this response is PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4), a central regulator of hypocotyl elongation. However, the mechanisms…
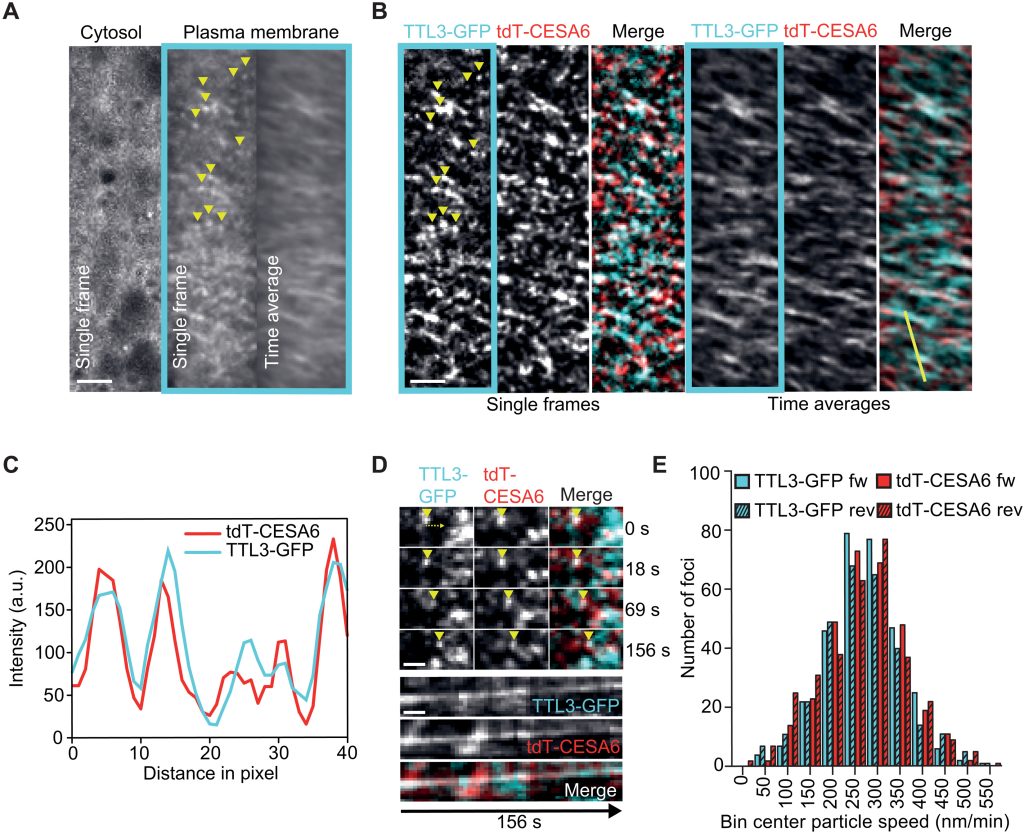
TTL bridges microtubules and cellulose synthase complexes
Plant Science Research WeeklyCellulose synthase (CESA) complexes (CSCs) synthesize the main polysaccharide component of plant primary cell wall, cellulose. The trafficking and dynamics of CSC are tightly regulated. Kesten et al. identified a new family of CSC- and microtubule-interacting proteins, named TETRATRICOPEPTIDE THIOREDOXIN-LIKE…
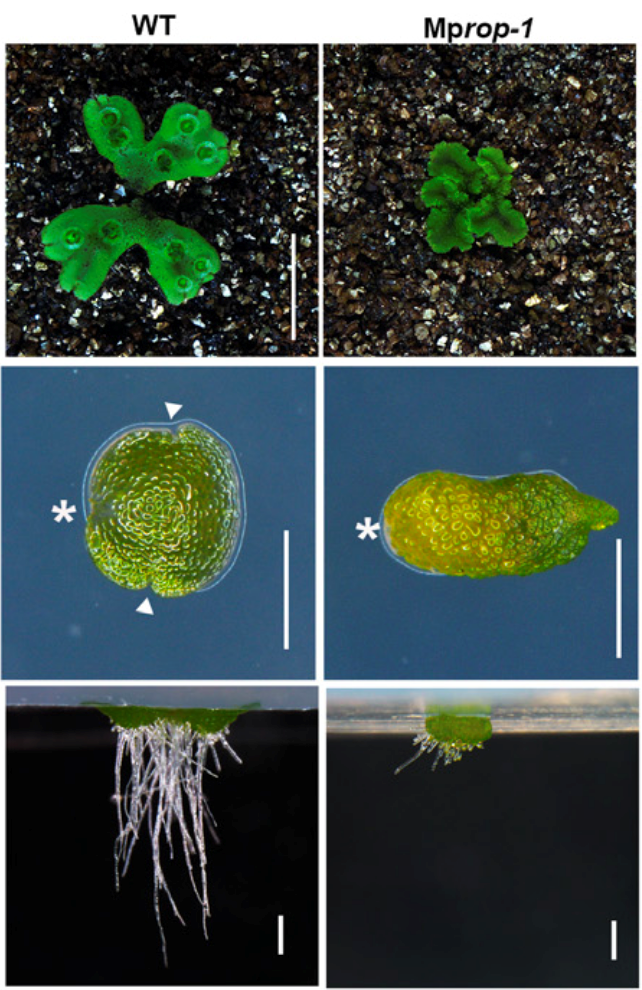
Developmental functions of Marchantia ROP
Plant Science Research WeeklyPrecise control of cell division is an important requirement for proper development in multicellular organisms. Rho-like GTPases from Plants (ROPs) are key conserved regulators of cell polarity and morphogenesis, however, it is unknown if ROP signaling pathways regulate cell division patterning and meristem…

TOR complex regulates actin cytoskeleton dynamics through controlling ATP levels (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTOR (Target of Rapamycin) complex is an information hub that integrates nutrition and energy signals and serves as a master regulator for multiple downstream cellular processes. The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is highly dynamic, with rapid changes of its organization and constant turnover between…

