
Stretched by Stress: PIEZO1 is a mechanosensitive ion channel in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are constantly susceptible to mechanical stress and they have evolved intracellular signaling mechanisms to adapt to mechanical stimulation. Whilst it is known that ion channels activate signaling pathways in response to mechanical stress, only few of these mechanosensitive channels have been…
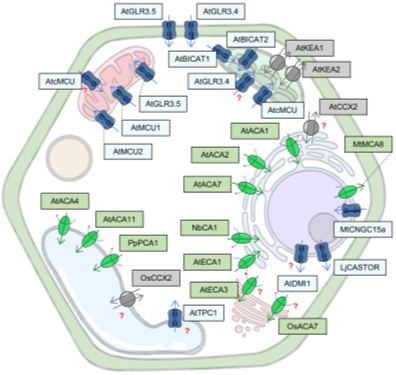
Review: One cell, many signatures: Organellar Ca2+ signaling (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium ions (Ca2+) occupy a primary position in plant cell signaling processes by virtue of their role as the so-called second messengers. Ca2+ signaling underlies plant response to various abiotic, biotic and developmental cues. Whilst this Ca2+ signaling was thought to predominantly occur in the cytoplasm,…
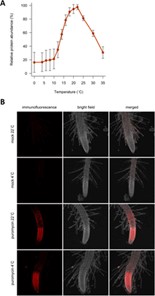
Cold translation: Ribosome-mediated translation inhibition senses cold stress in plants (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA drop in ambient temperature adversely affects plant growth and development. While the primary molecular pathway in response to cold stress involves the expression of CBF transcription factors, Guillaume-Schöpfer and colleagues found cold stress-induced inhibition of ribosome translation machinery…
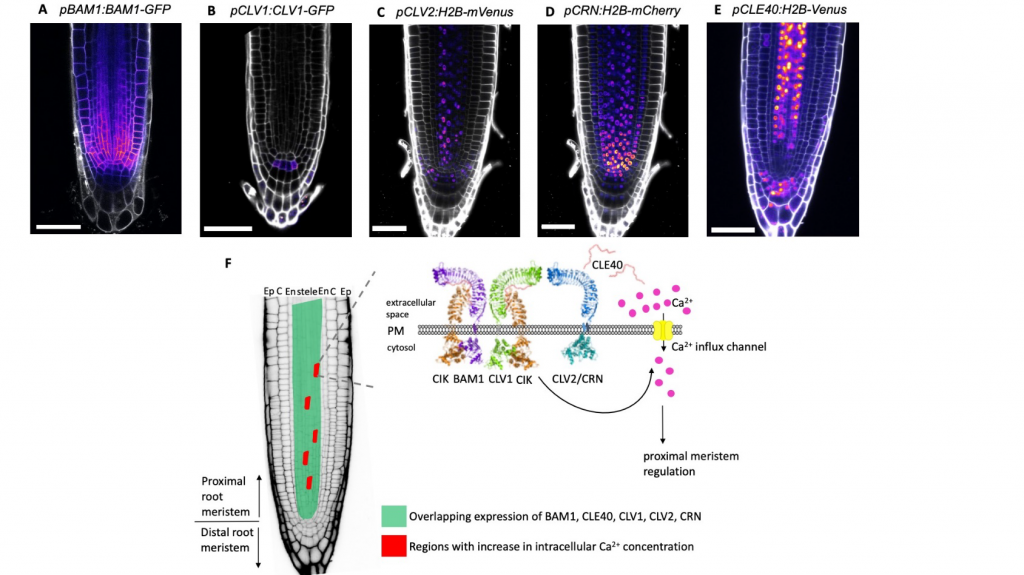
CLE40 induces localized root Ca2+ transients through CNGC9 (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCLE40 induces localized root Ca2+ transients through CNGC9
Growth and differentiation of cells in the meristematic region are tightly regulated by different signaling pathways. In the root meristem, the small peptide CLE40 acts as a ligand that binds to cell surface receptors and regulates cellular…

Phosphorylation-dependent sub-functionalization of the calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium-dependent protein kinases (CPKs) form an important class of sensor-responder proteins that bind Ca2+ to ‘sense’ intracellular Ca2+ levels, and ‘respond’ by phosphorylating target proteins. CPK28 has distinct roles in growth and defense. To analyze the importance of Ca2+ in fine-tuning…
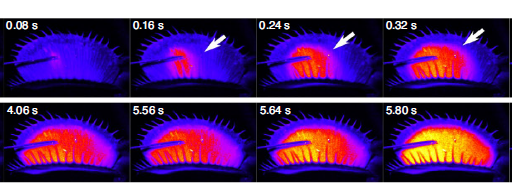
Calcium dynamics during trap closure visualized in transgenic Venus flytrap (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research Weekly
For centuries, carnivorous plants and the mechanisms they use to capture prey have been enigmas. While some clarity regarding the molecular mechanisms is beginning to emerge, Suda and colleagues have uncovered a vital role for calcium (Ca2+) signals in trap closure in Venus flytrap. The researchers…
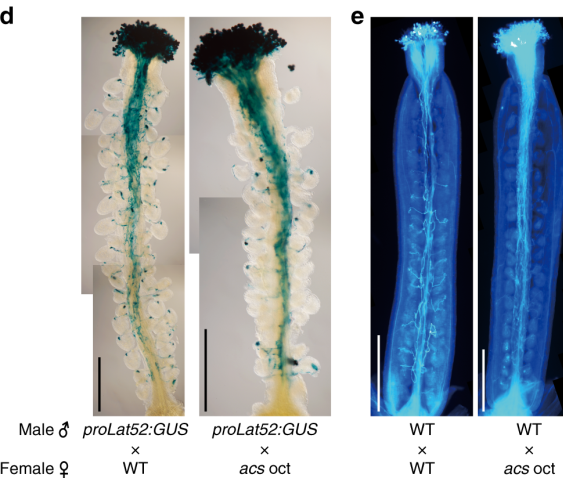
Going my own way: Ethylene-independent ACC signaling in pollen tube attraction (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research Weekly1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is the precursor of the phytohormone ethylene. Here, Mou and co-workers show ACC to act independent of ethylene in the ovule to attract growing pollen tubes. Mutants impaired in ACC biosynthesis had less fertilization and seed setting events. Fertilization…
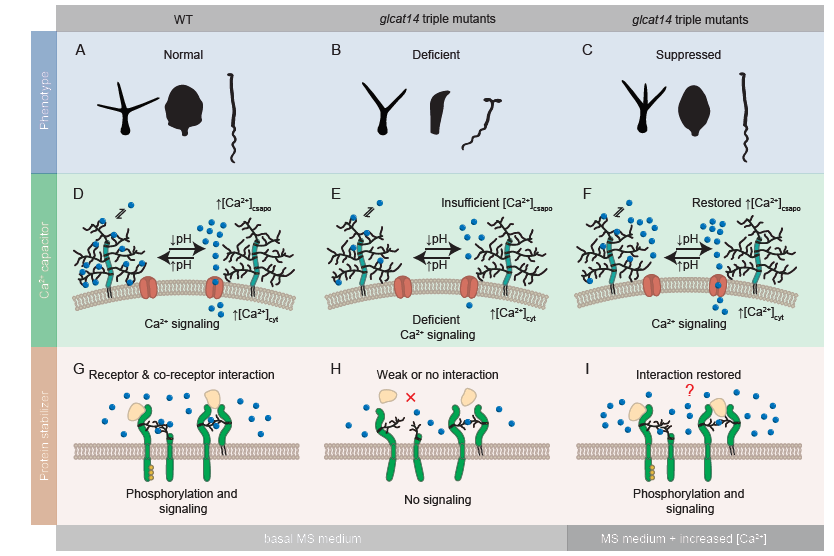
Calcium binding by arabinogalactan polysaccharides is important for normal plant development (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) are a class of apoplastic carbohydrate-binding proteins with a carbohydrate portion that can also bind to calcium (Ca2+) ions in a pH-dependent manner. Here, Lopez-Hernandez and colleagues have probed the role of AGPs and the functional significance of their Ca2+-binding…
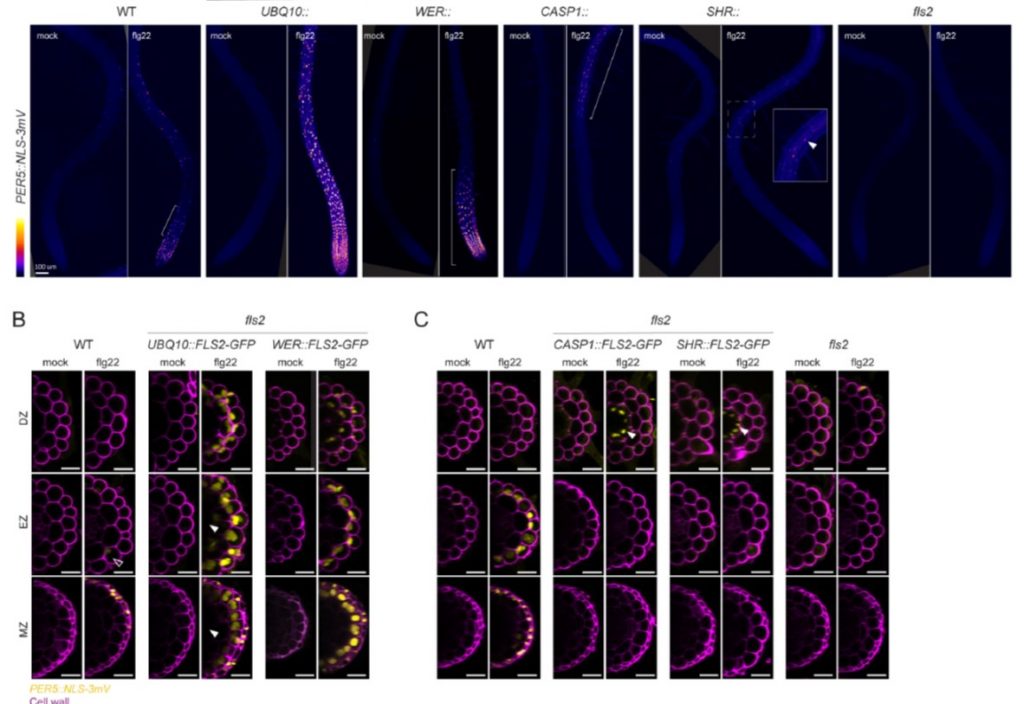
Spatial profiling of immune competence in plant roots (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots should prevent immune activation by innocuous soil microbiota, as constitutive immune activation is harmful to plant growth. Previous studies have indicated variable immune competence of different root cell types and developmental zones, but this is currently poorly understood with the fine…

