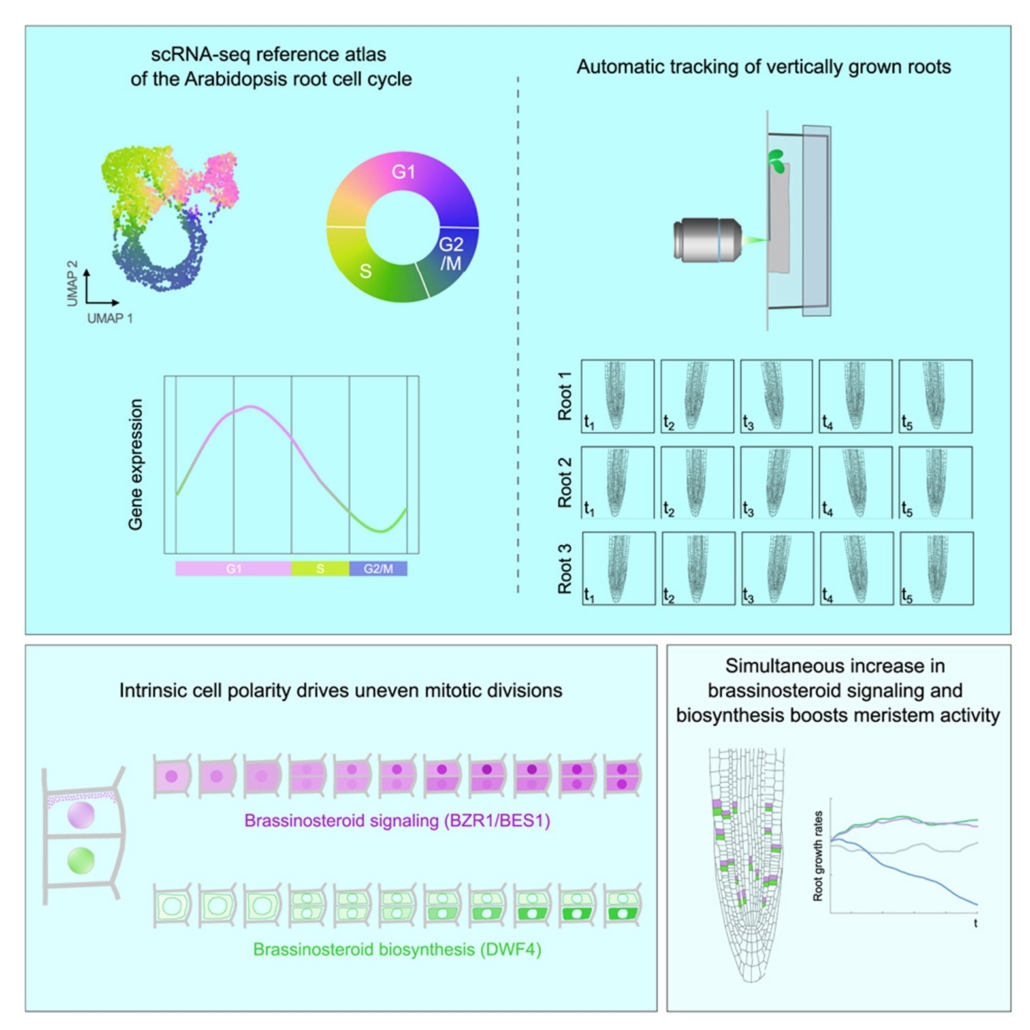
Brassinosteroids positively regulate growth through asymmetrical division
Plant Science Research WeeklyBrassinosteroids are plant hormones that play important roles in cell proliferation and expansion, but it is still unclear exactly what those roles are. Vukasinovic and colleagues show, in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells, that instrinsic brassinosteroid gradients signal anticlinal division. Single-cell…
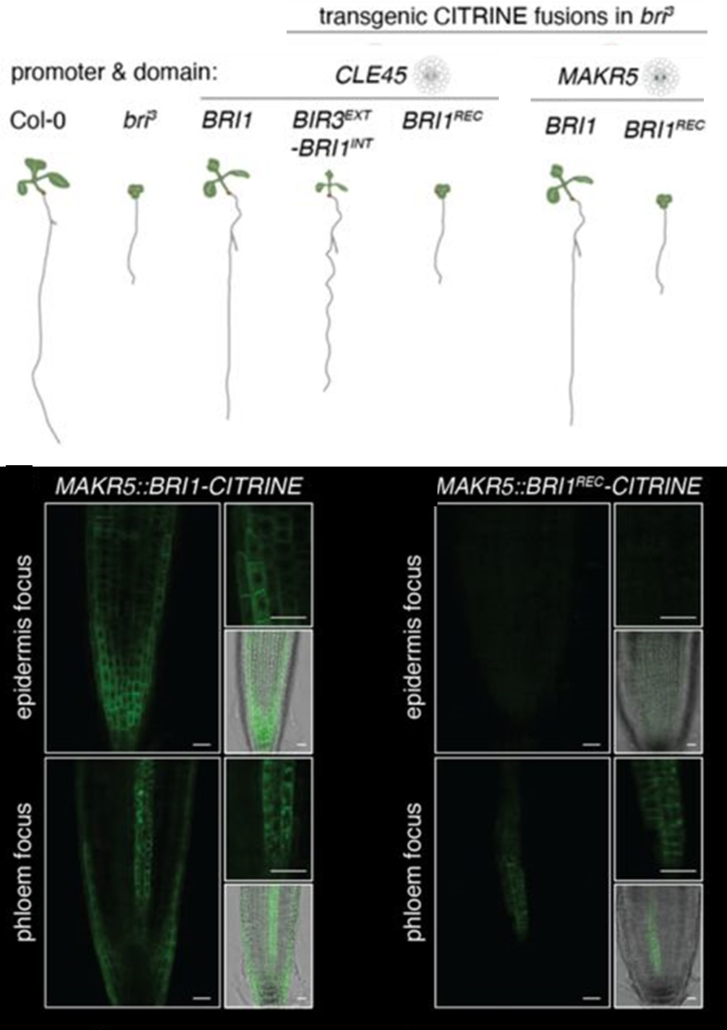
Alone or together: BRI1 signaling controls root growth in a cell-autonomous manner
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot growth is controlled by a dense network of hormone signals working in shared and distinct root zones and cell types. Brassinosteroids (BR) control root growth through activated signaling in vascular and epidermal tissues, but it is unclear how BR signals in each tissue contribute and whether there…
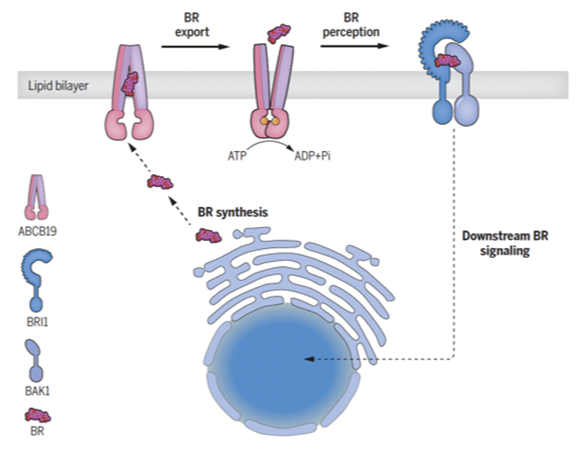
How do plants export brassinosteroids?
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you’ve ever wondered how plants grow, survive, and adapt to their dynamic environment, the secret lies in their vast array of chemical messengers, also called phytohormones. Brassinosteroids are important hormones that are crucial for plant development and defense against environmental stresses.…
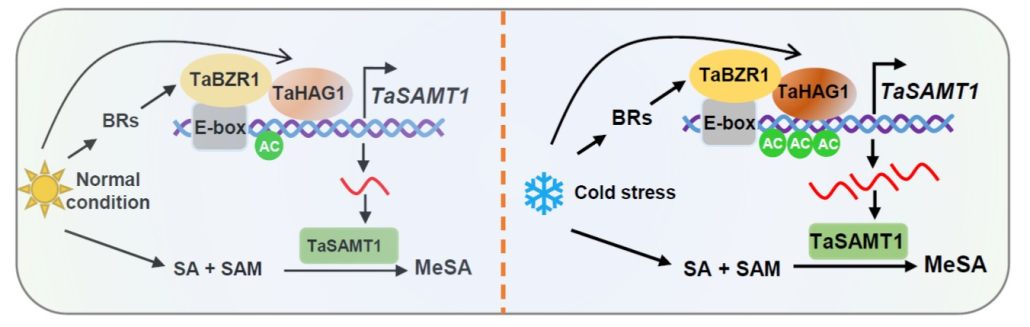
Methyltransferase TaSAMT1 mediates wheat freezing tolerance by integrating brassinosteroid and salicylic acid signaling
Plant Science Research WeeklyTemperature extremes, such as cold stress, severely affect wheat (Triticum aestivum) productivity and quality by impairing its vegetative and reproductive growth. Several phytohormones have roles in cold stress, such as brassinosteroids (BRs) and salicylic acid (SA). However, how BR interacts with SA…

Brassinosteroid coordinates cell layer interactions via cell wall and tissue mechanics
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrganismal growth requires extensive coordination between cells and tissues with different identities, and this is particularly important for plants with their rigid cell walls and lack of cell motility. A key mechanism for tissue coordination involving brassinosteroids has been identified by Kelly-Bellow…
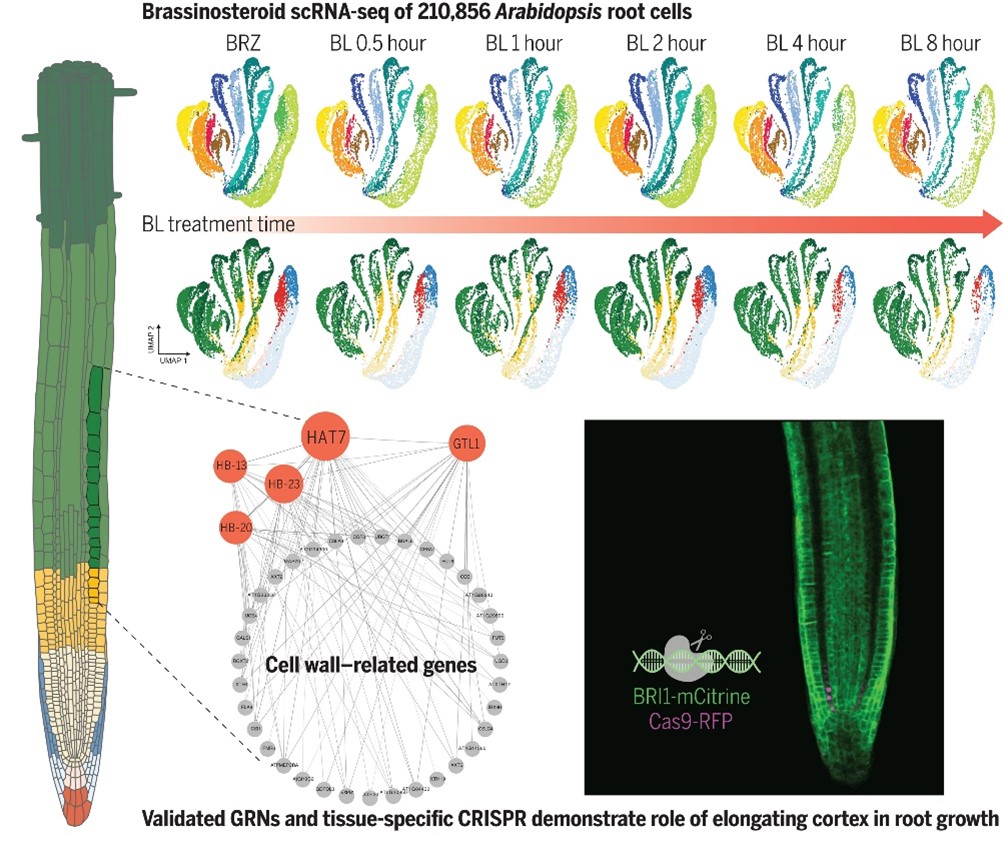
Uncovering the brassinosteroid gene regulatory networks in Arabidopsis root using single-cell RNA sequencing
Plant Science Research WeeklyBrassinosteroid hormones regulate root growth and development by controlling cell division and elongation. However, it has been unclear why and how root cells with different identities and developmental stages respond to brassinosteroids differently. Nolan et al. used cutting-edge single-cell RNA sequencing…
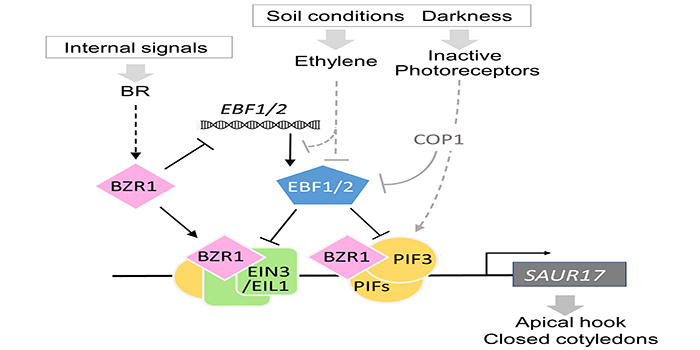
How do brassinosteroids promote etiolation of apical organs in Arabidopsis?
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. explore how plants maintain apical etiolation.
By Jiajun Wang (Southwest University, China), Haodong Chen (Tsinghua University, China), Xing Wang Deng (Peking University, China), Ning Wei (Southwest University, China)
Background: Seeds germinate underneath the soil; to help the shoot…
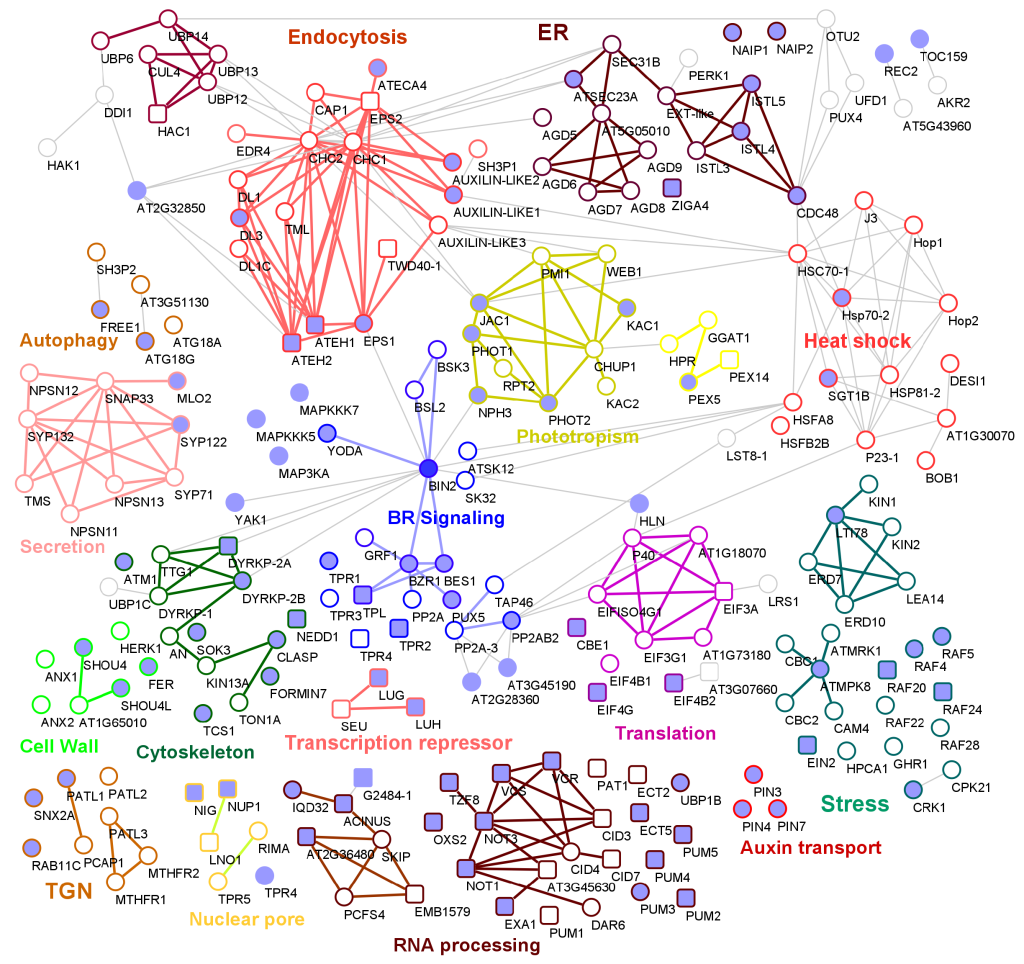
BIN2 signaling network constructed using proximity labeling and TurboID
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe brassinosteroid (BR) signaling pathway is essential for plant growth and development. BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE2 (BIN2) is a GSK3-like kinase, serving as a repressor of the BR signaling pathway. In the absence of BR, BIN2 phosphorylates BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT1 (BZR1) family transcription factors…
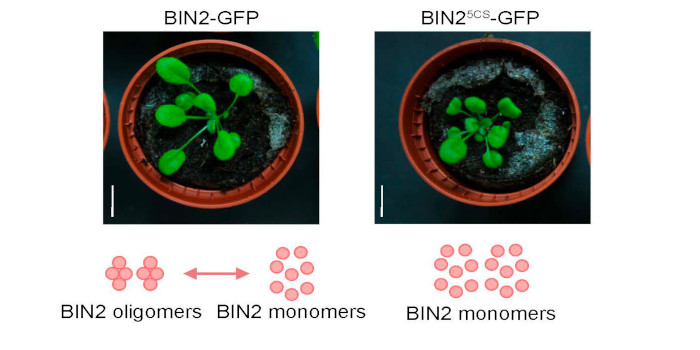
H2O2 regulates activity of the GSK3-like kinase BIN2
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLu et al. unravel a mechanism by which reactive oxygen species modulate brassinosteroid signaling through the GSK3-like kinase BIN2
Qing Lua,b, Eugenia Russinovaa,b
a Department of Plant Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Ghent University, 9052 Ghent, Belgium
b Center for Plant Systems Biology,…

