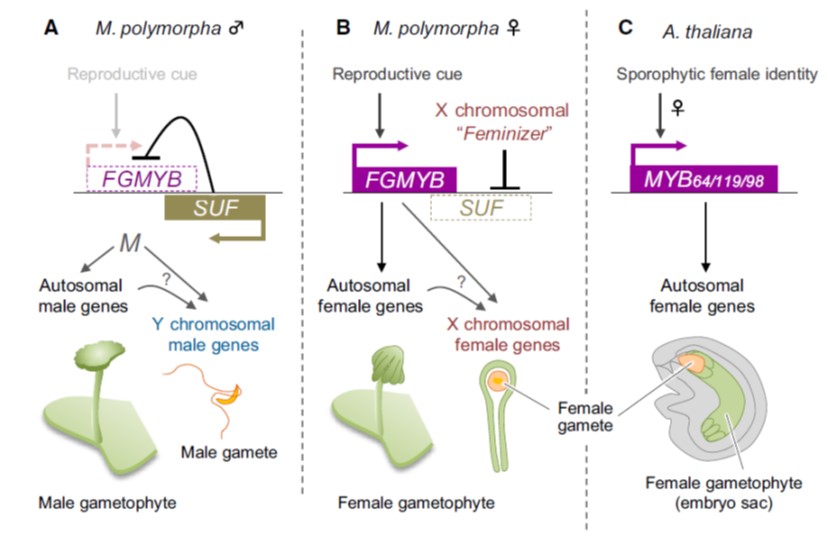
A bidirectional switch controls sexual dimorphism in the liverwort (EMBO J)
Bryophytes spend most of their lifecycle in the haploid, gametophytic form, of which there are two types, male (sperm forming) and female (egg forming). Hisanaga et al. investigated the genetic basis that determines sex in the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. Their findings are fascinating. A single…
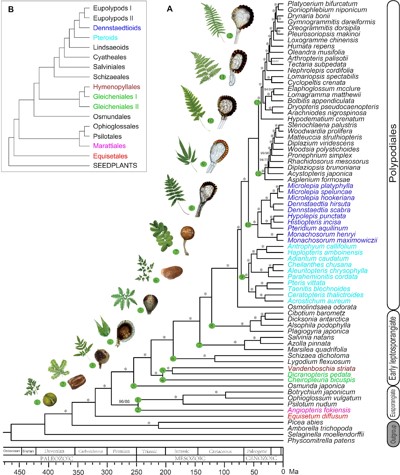
Large-scale phylogenomic analysis resolves a backbone phylogeny in ferns (GigaScience)
A look back at the most popular articles shared on Plantae social media in 2018.
Plantae Social Media Interns Katie Rogers and Juniper Kiss have been reviewing the 2018 stats. Previously they shared the most popular posts overall. Here, they share the posts to research and review articles that…

New journal launched – Plants, People, Planet
Congratulations to everyone involved in the launch of the new journal Plants, People, Planet, “… a new cross-disciplinary Open Access journal from the New Phytologist Trust focusing on the interface between plants and society.” I’m sure that we’ll be seeing some terrific articles in this new…
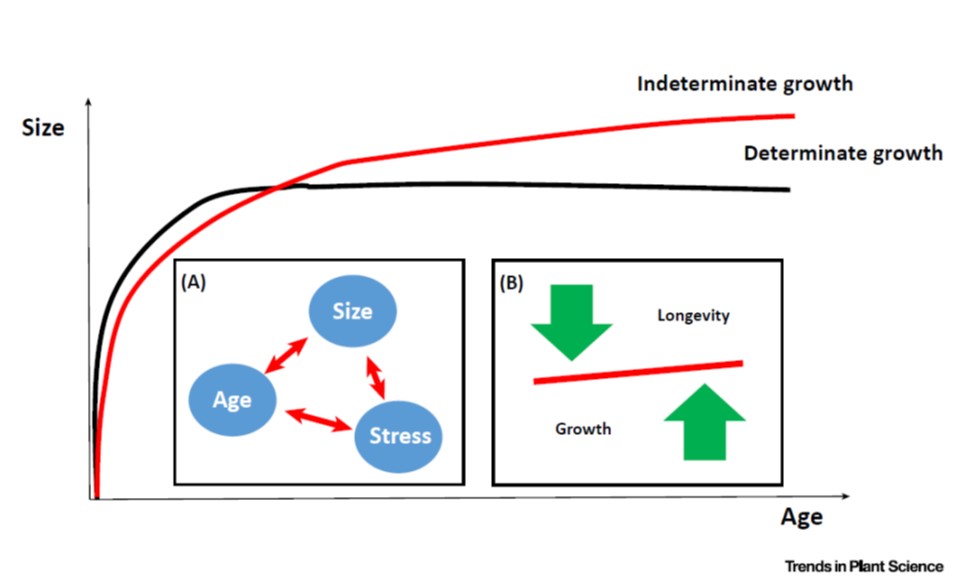
Opinion: Limits to tree growth and longevity (TIPS)
I think trees are awesome, and I mean that in the truest sense of the word. They dwarf us in height, and when we look at a tree that has lived for hundreds or thousands of years it is impossible not to think of that span in terms of human generations and human history. But, trees don’t live or grow…
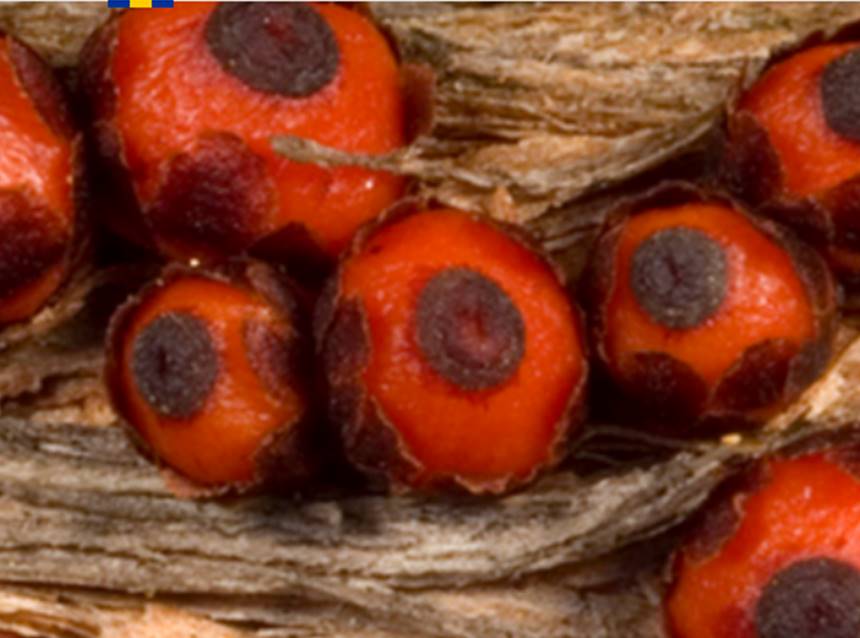

The mysterious Pilostyles is a plant within a plant
Pilostyles are only visible when their fruit and flowers erupt out of their host plants.
The Conversation/Wikipedia
Steve Wylie; Jen Mccomb, and Kevin Thiele, University of Western Australia
In 1946, forestry officer Charles Hamilton found something unusual on a shrubby native pea plant…
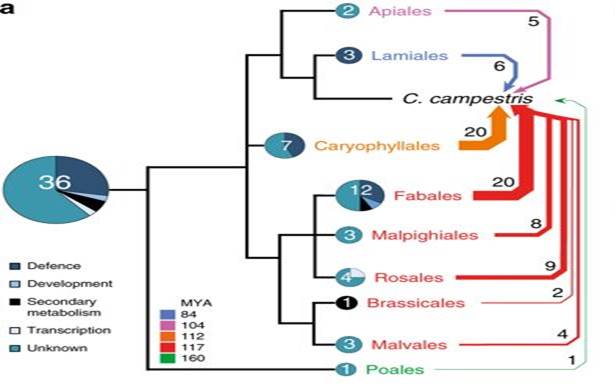
Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris (Nature Comms)
Even without knowing a lot about parasitic plants, you can probably guess some of the insights that come from the first parasitic plant genomic sequence. Because parasitic plants get their nutrients from another organism (functionally, they become heterotrophic), you might expect they would gradually…
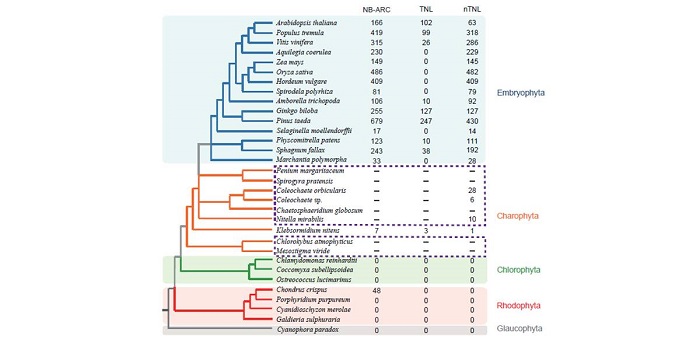
Origin of Plant R Genes
Plants rely on two branches of the innate immunity system to prevent or eliminate microbial infections: one involves cell surface receptors to respond to pathogen- or microbe- associated molecular patterns, and the other acts inside plant cells by using proteins with nucleotide-binding site (NBS) and…

Review: The origin and evolution of mycorrhizal symbioses (New Phytol)
Many fungi are pathogens that kill or weaken their plant hosts. However, there are also many species that form beneficial relationships with plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. One of these mutualisms is the mycorrhizal association between a fungus and a plant root, where the fungus provides the plant…
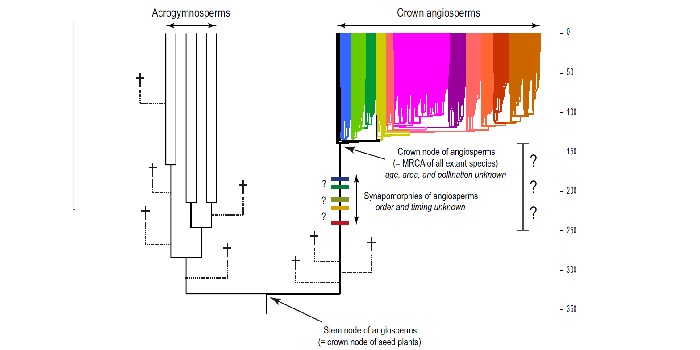
Review: Key questions and challenges in angiosperm macroevolution (New Phytol)
Are you curious about why and how angiosperms, flowering plants, are the youngest lineage of land plants and have become the most abundant group of plants? You are not alone. Generations of botanists and evolutionary biologists have wondered about this same thing. Many questions have been answered, such…

