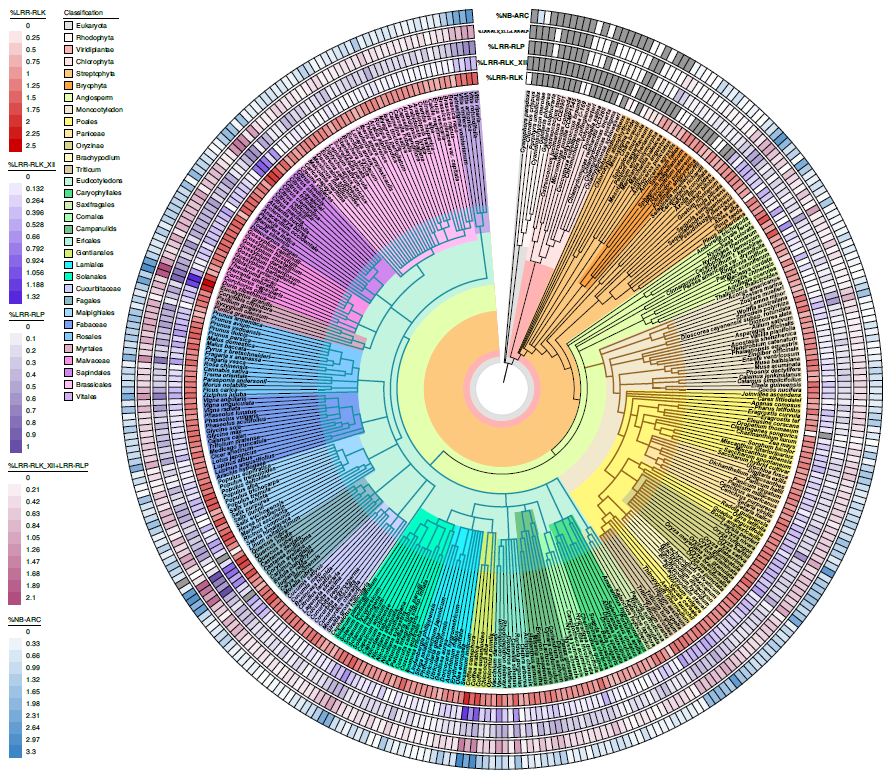
Concerted expansion and contraction of immune receptor gene repertoires in plant genomes (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant immunity is crucial for adaptation to pathogen attack and subsequent survival. Two systems support plant immunity. Cell-surface pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and prompt pattern-triggered immunity. Intracellular nucleotide-binding leucine-rich…
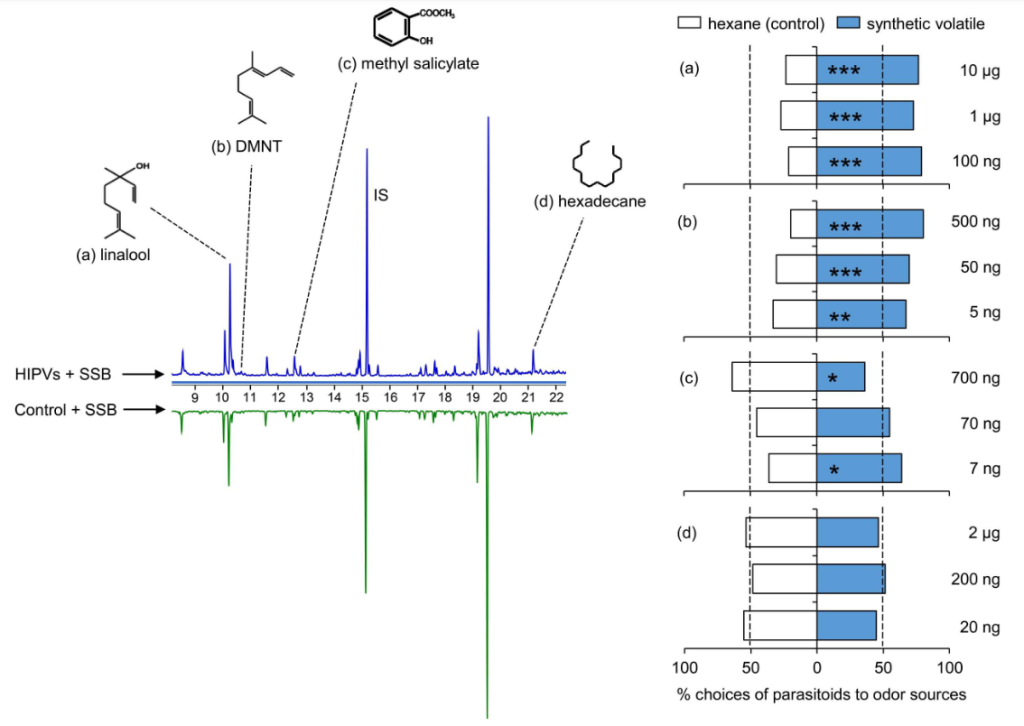
Stemborer-induced rice plant volatiles boost direct and indirect resistance in neighboring plants (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHerbivore attack can trigger release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in numerous plant species. These airborne compounds from an infected plant act as messengers in plant-plant interactions causing adaptation to the stress in adjacent plants. Globally, rice is a staple food for millions of people,…

Plant immunity is wired differently in different plants (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, microbial invasion is sensed by membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors. Our knowledge on the immune signaling that follows microbial recognition is mostly derived from studies on Arabidopsis thaliana. In this plant, receptor activation triggers immune responses that are distinct for each…
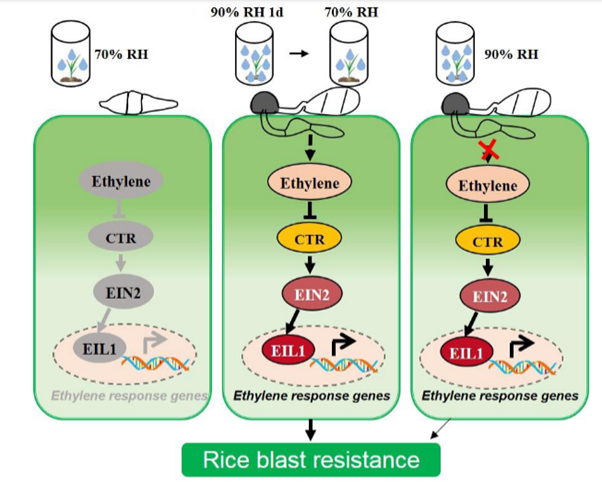
High humidity compromises plant immunity while promoting pathogen growth (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHumidity is considered a key component for the growth of fungal plant pathogens. For many infection assays we either maintain plants in high humidity, or wrap the infected area and keep spraying it with water. This is generally performed to facilitate fungal growth and the assumption that this may not…
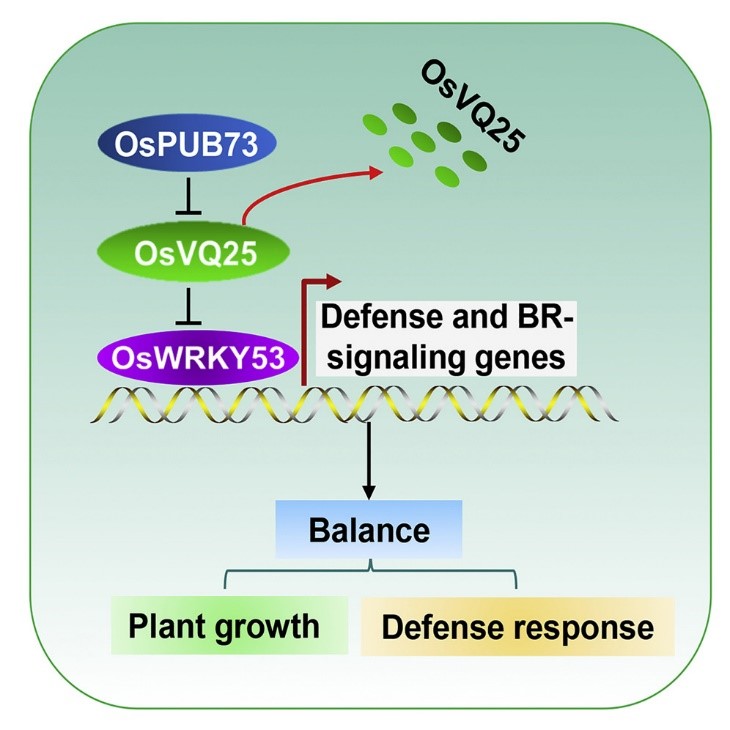
Identification of a cell signaling cascade that regulate s broad-spectrum resistance (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany different pathogens attack plants, and many genes have been identified that confer pathogen-specific resistance. In a recent study, Hao et al. identified a signaling cascade that regulates broad-spectrum disease resistance. This pathway is composed of a rice ubiquitin ligase OsPUB73, a VQ motif-containing…
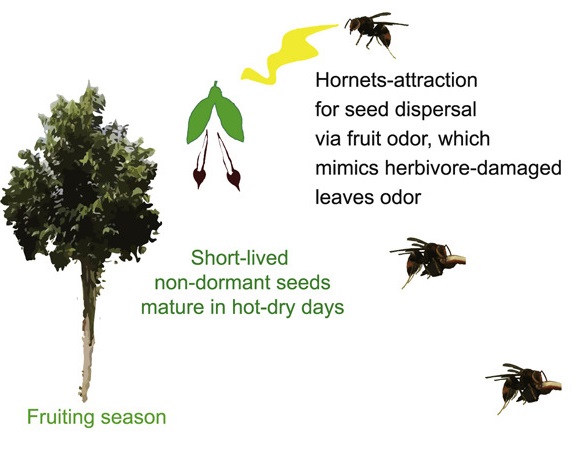
Agarwood harnesses hornets for rapid dispersal of non-dormant seeds (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe seeds of the Agarwood tree (Aquilaria sinensis) lose viability within a few hours of the fruit splitting, so need to reach the ground as soon as possible. Qin et al. report that agarwood achieves this by fooling hornets (Vespa spp.), which generally eat herbivore insects such as caterpillars. When…
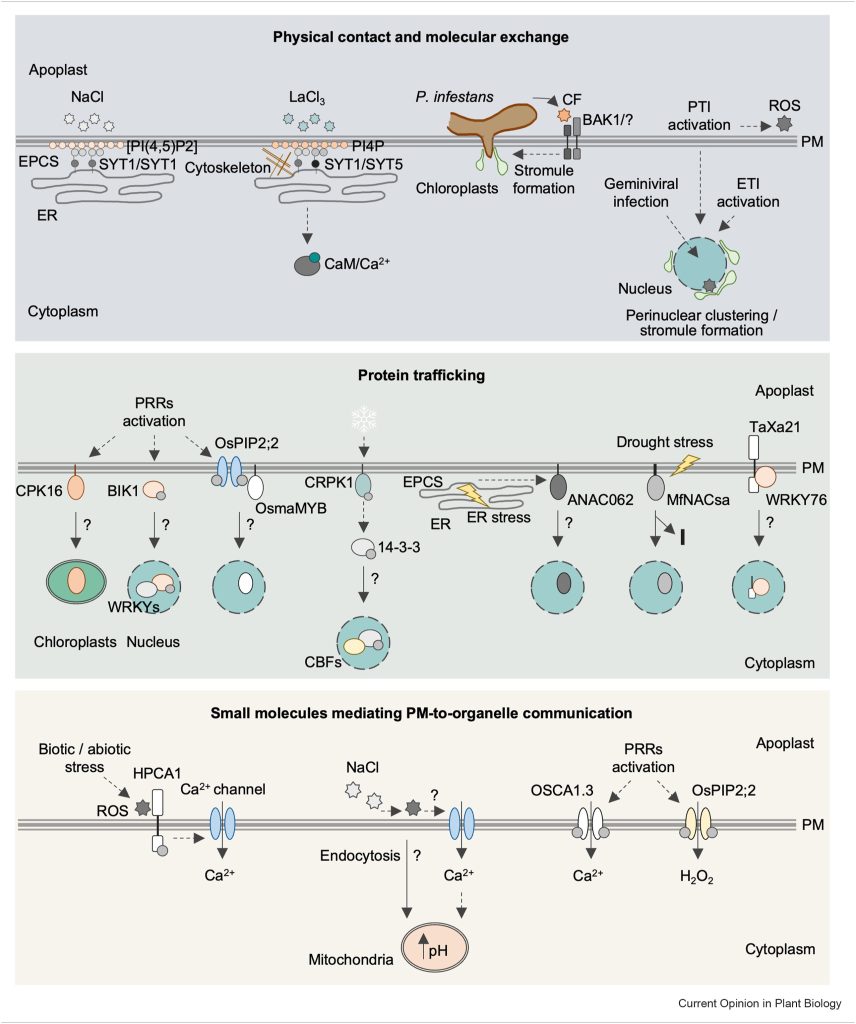
Review: Plasma membrane-to-organelle communication in plant stress signaling (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plasma membrane (PM) is a critical interface between the cell and its environment and serves crucial sensing and transducing roles. This timely review by Medina-Puche and Lozano-Durán updates exciting new developments in understanding communication between the PM and intracellular organelles, focusing…
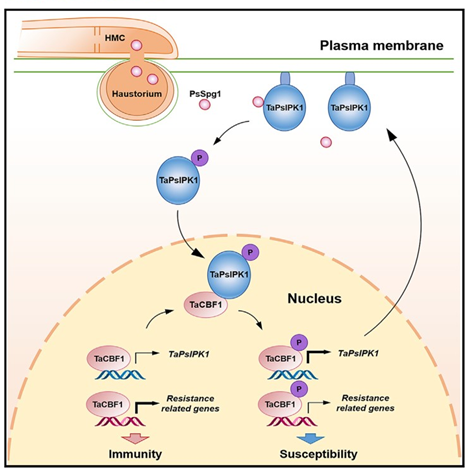
Removing one wheat protein kinase provides resistance to rust fungi (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTolerance against a pathogen can be achieved by either overexpressing a resistance-related gene, or removing a susceptibility-related gene. Overexpression of defense-related genes generally comes with side effects such as decreased growth and yield. On the other hand, a susceptibility factor might have…
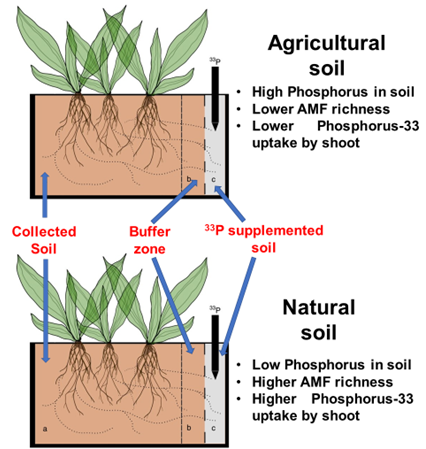
Modern agriculture practices negatively affect functions of beneficial plant microbes (Nature Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAre modern agricultural practices good for the environment? Or at least for the crops? If we look at a small field at a particular time point, it may seem they are good. But looking at a broader picture gives a different notion. In a recent study, Edlinger et al. collected 210 soil samples from traditional…

