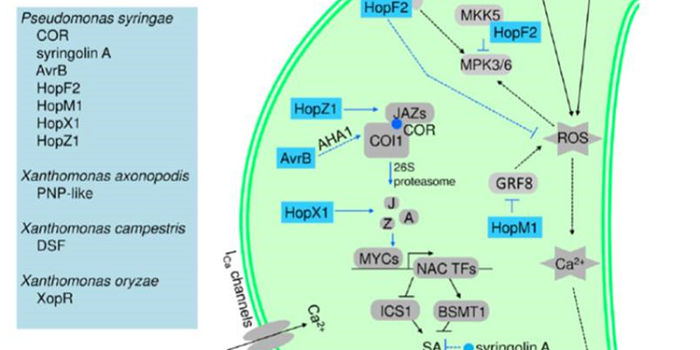
Update: Stomatal defense a decade later
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Stomatal defense, recognition of pathogens at the stomatal pore accompanied by stomatal closure to prevent their entry, was discovered ten years ago. Melotto et al. review what we’ve learned in the past decade about this key defense strategy. They discuss pathogen recognition, in which microbe-associated…
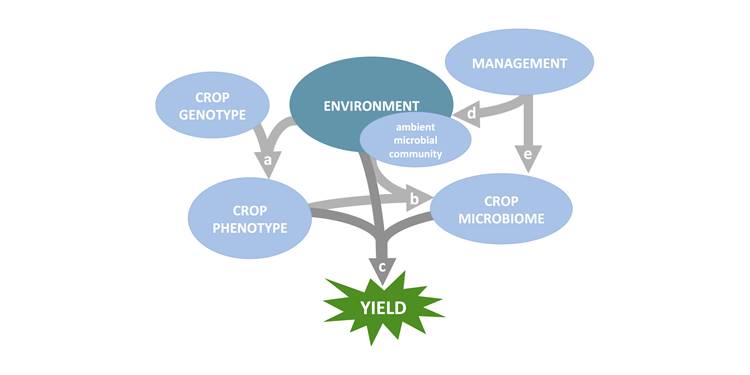
Perspective: Research priorities for harnessing plant microbiomes in sustainable agriculture
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBeneficial microbes help plants take up nutrients, confer protection against pathogens, and can even affect flowering time. Busby et al. argue for a coordinated effort between researchers and farmers to study plant microbiomes with the goal of using them to enhance productivity. The authors define and…

Review: Mechanisms to mitigate the tradeoff between growth and defense ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIt is widely recognized that defense incurs a cost in terms of reduced growth. Karasov et al. explore the nature of this tradeoff. They observe that rather than tradeoff being driven directly by metabolic competition, it appears to occur upstream through regulatory processes including antagonism between…
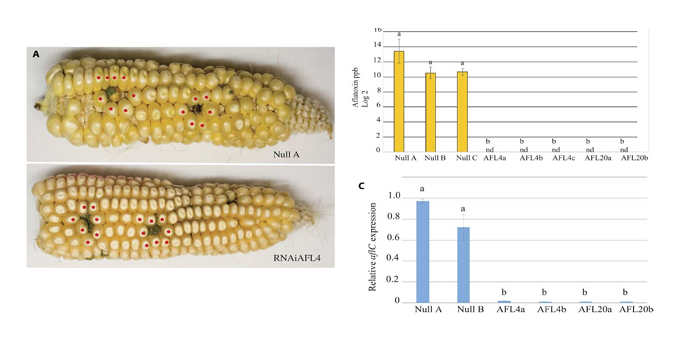
Aflatoxin-free transgenic maize using host-induced gene silencing
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAflatoxins are toxic metabolites produced by some species of Aspergillus fungi that can occur on numerous crop plants. When ingested by animals, aflatoxins cause health problems including liver cancer and stunted growth. Thakare et al. used host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) to block aflatoxin production…
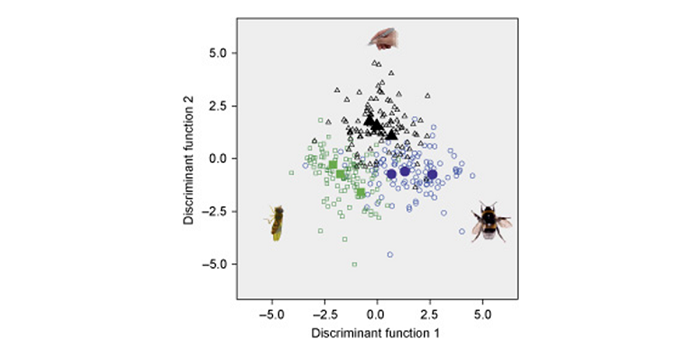
Divergent evolution driven by pollinators
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA great variety of plants rely on pollinators to be fertilized successfully. This close relationship is thought to drive evolutionary diversification in plants, making the presence or absence of pollinators in response to climate change an increasingly relevant matter. Gervasi and Schiestl addressed…
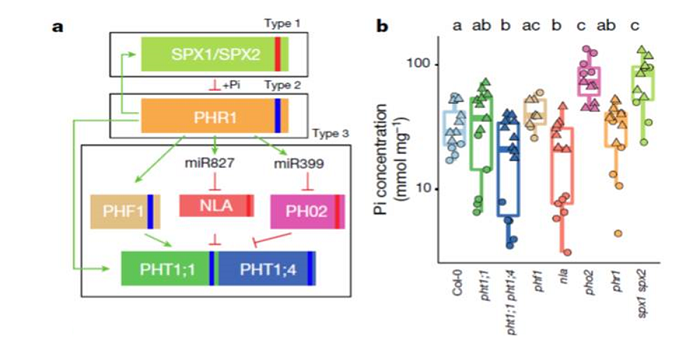
Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMany of the genes involved in the phosphate-stress response (PSR) have been identified from plants growing on sterile medium. Castrillo et al. examined how the root microbiota affectthe phosphate stress response, and how phosphate affects the association between roots and microbes. Plants deficient…
Reviews: Nature Insight: Plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNature journal published a special “Plant Insights” section featuring several excellent reviews. Zipfel and Oldroyd review Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity (10.1038/nature22009), Bevan et al. write about Genomic innovation for crop improvement (10.1038/nature22011), Scheres and van der…
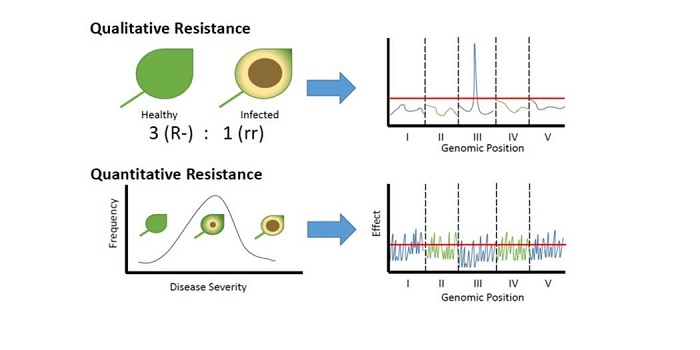
Review: Quantitative resistance: More than just perception of a pathogen
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSome forms of pathogen resistance function like an on/off switch: if a plant has an appropriate receptor it recognizes a pathogen and shows resistance. Corwin and Kliebenstein review the other kind of resistance, quantitative resistance, in which many genes make small contributions to the plant’s resistance.…
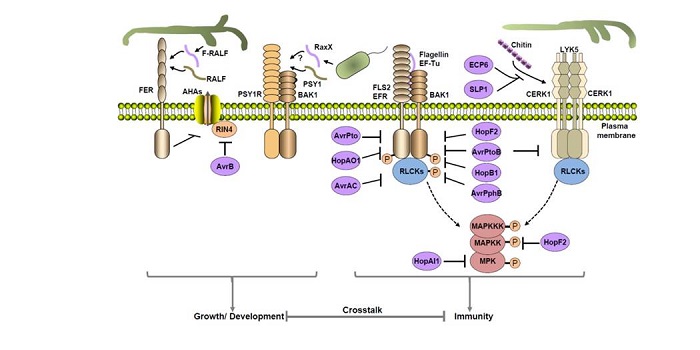
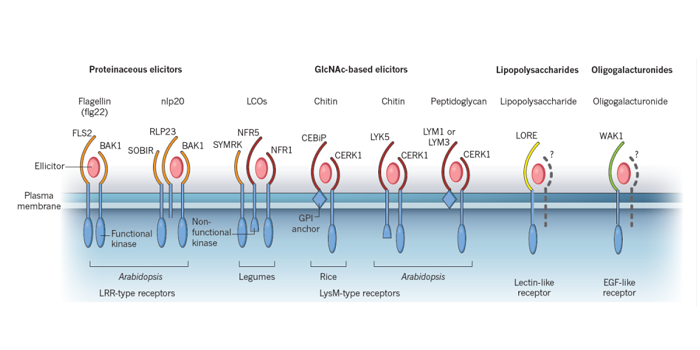
Review: Receptor kinases in plant pathogen interactions: More than pattern recognition
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchZhou et al. review the contributions of Receptor-Like Kinases (RLKs) and Receptor-Like Proteins (RLPs) as Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) that contribute to the recognition of pathogens, as well as the contributions of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs). The authors summarize recent studies…

