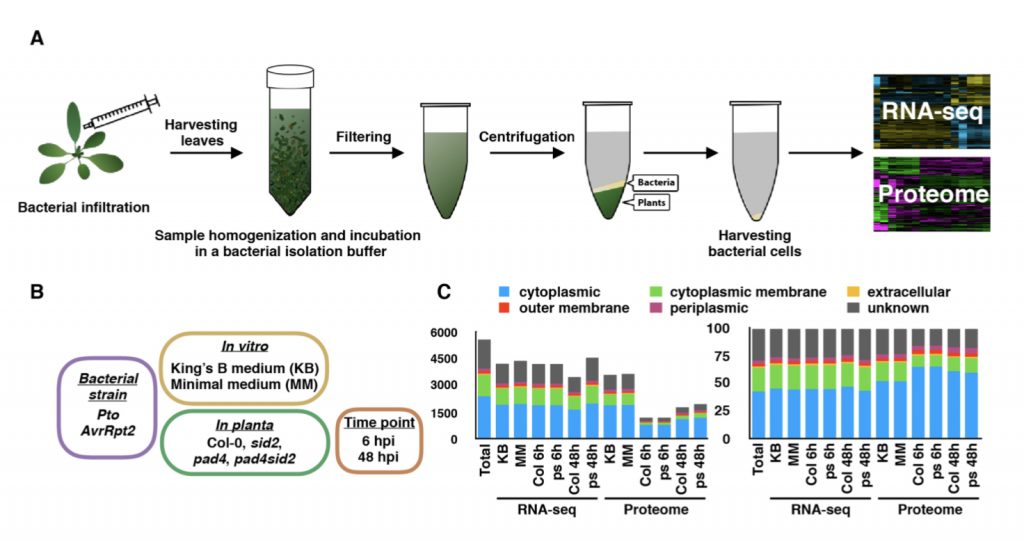
Understanding pathogenic bacterial gene expression in planta is essential to understand plant pathology (bioRxiv)
How exactly does the plant defense system target pathogens? Nobori et al. have analyzed interactions inside the plant between the foliar bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae and Arabidopsis thaliana at transcriptomic and proteomic levels by using RNAseq and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry…
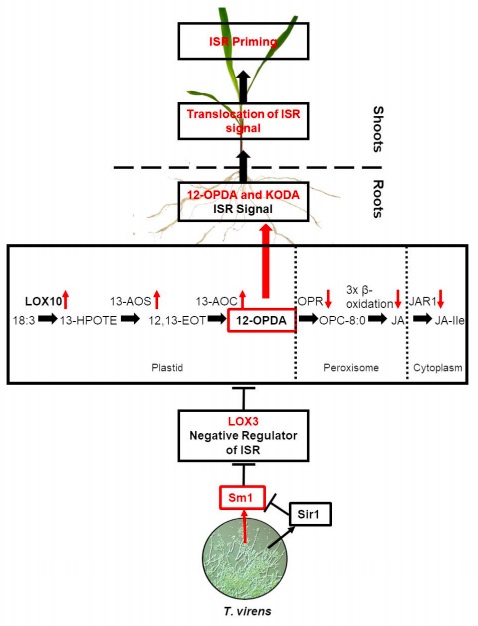
Oxylipins other than jasmonic acid regulate systemic resistance (Plant Cell)
Plant roots communicate with microbes in a sophisticated manner through chemical communication within the rhizosphere, thereby leading to biofilm formation of beneficial microbes and resulting in priming of defence, or induced resistance in the plant host to a wide range of pathogens (induced systemic…

Review: Exchange of small regulatory RNAs between plants and their pests (Plant Physiol)
Trans-species small RNAs are the latest class in the family of signals that move between plants and their attackers. Hudzik et al. review this topic, covering small RNAs that move from plant to pest and from pest to plant. The transmitted RNAs function by interfering with gene expression in the recipient.…
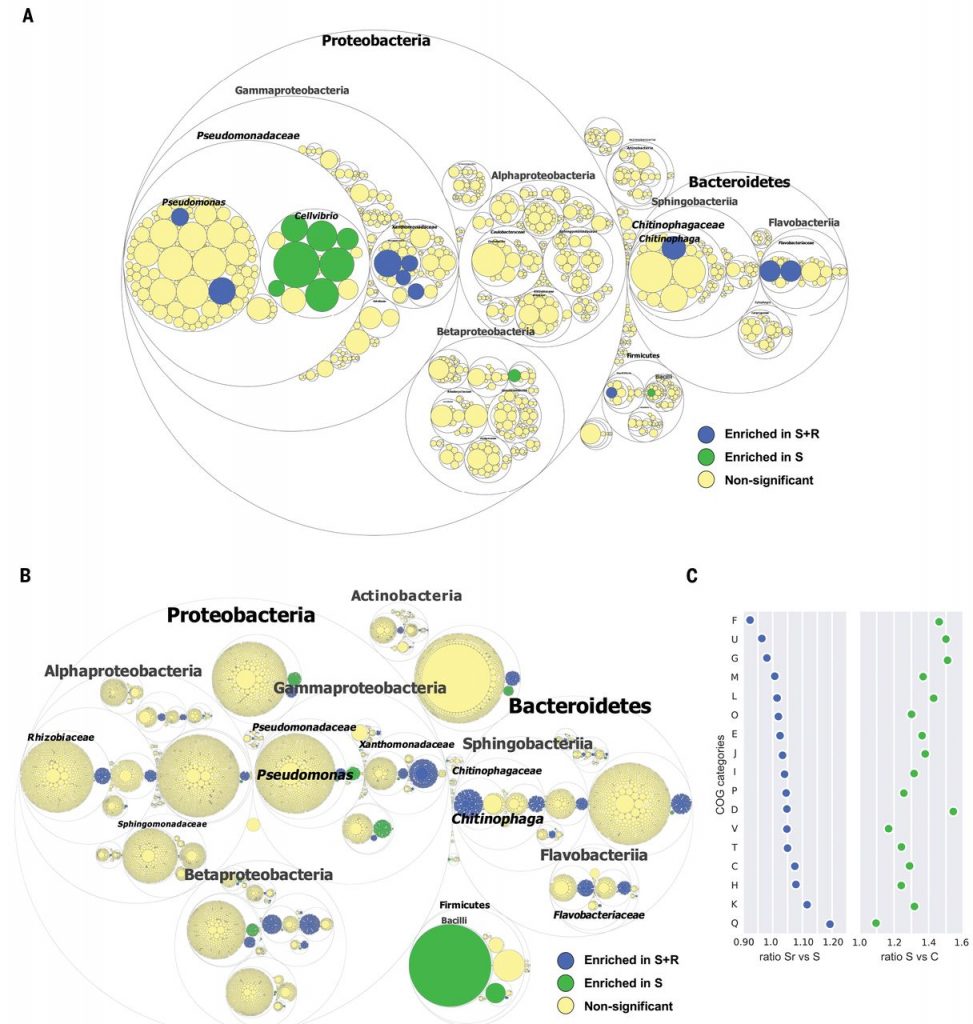
Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome ($) (Science)
Disease-suppressive soils have long been known, although it hasn’t always been clear how they function. Previous studies have suggested that soil microbes are responsible for disease suppression, because the suppressive property can be transferred to other soils and is lost when soil is sterilized.…
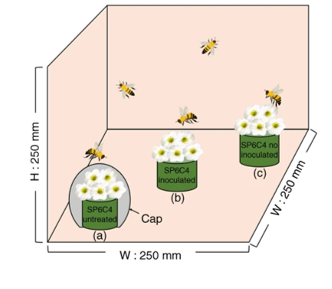
A mutualistic interaction between Streptomyces bacteria, strawberry plants and pollinating bees (Nature Comms)
Some species of Streptomyces bacteria produce antimicrobial compounds that have been shown to enhance plant resistance to pathogens. Kim et al. show that his protection can extend to a pollinator. The Streptomyces defends the plant against Botrytis cinerea and protects the bees against insect pathogens…
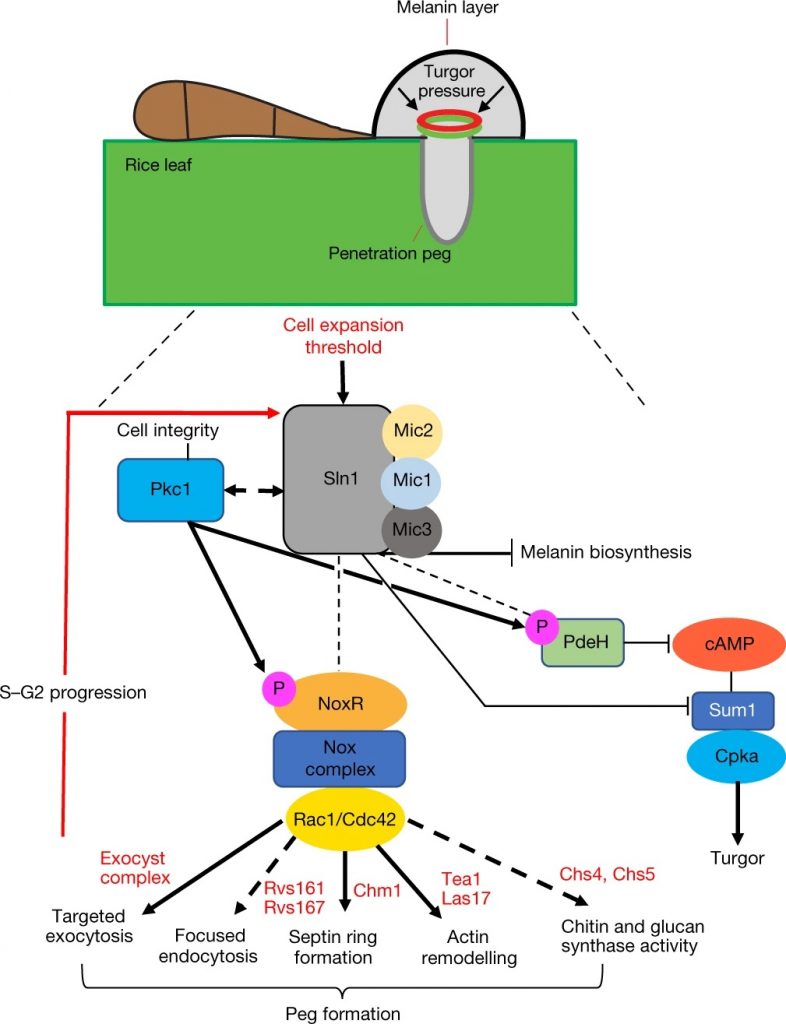
A sensor kinase controls turgor-driven plant infection by the rice blast fungus ($) (Nature)
Magnaporthe oryzae, the causal organism of blast disease in rice and wheat, is the most devasting pathogen in rice production. During infection, it develops a germ tube that forms an infection structure called the appressorium. Through septin-mediated reorganization of the cytoskeleton, a high amount…

Insect herbivory selects for volatile-mediated plant-plant communication ($) (Current Biology)
Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in response to insect herbivory. The potential for VOCs to serve as diffusible signals has long been recognized. For example, VOCs can signal neighbors to prime for defense, signal distant parts of the emitting plant, and even attract predatory insects…
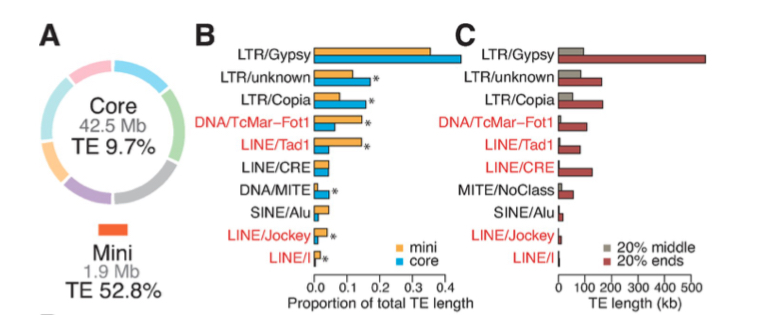
Effector gene reshuffling involves dispensable mini chromosomes in wheat blast fungus (PLOS Genetics)
The emerging disease wheat blast is devastating and has the capacity to cause 100% yield loss. Wheat blast is caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum (MoT). This pathotype is distinct from most of the pathotypes that causes disease in other plants such as M. oryzae Oryza (MoO) in rice.…
Plant microbe co-evolution: Allicin resistance in Pseudomonas fluorescens (bioRxiv)
Garlic (Allium sativum L.) produces allicin (diallylthiosulfinate), which is an antibiotic defense substance. It can oxidize thiols in celular targets such as cysteines and glutathione. Because allicin has multiple sites and mechanisms of action, it is difficult for an organism to become resistant.…

