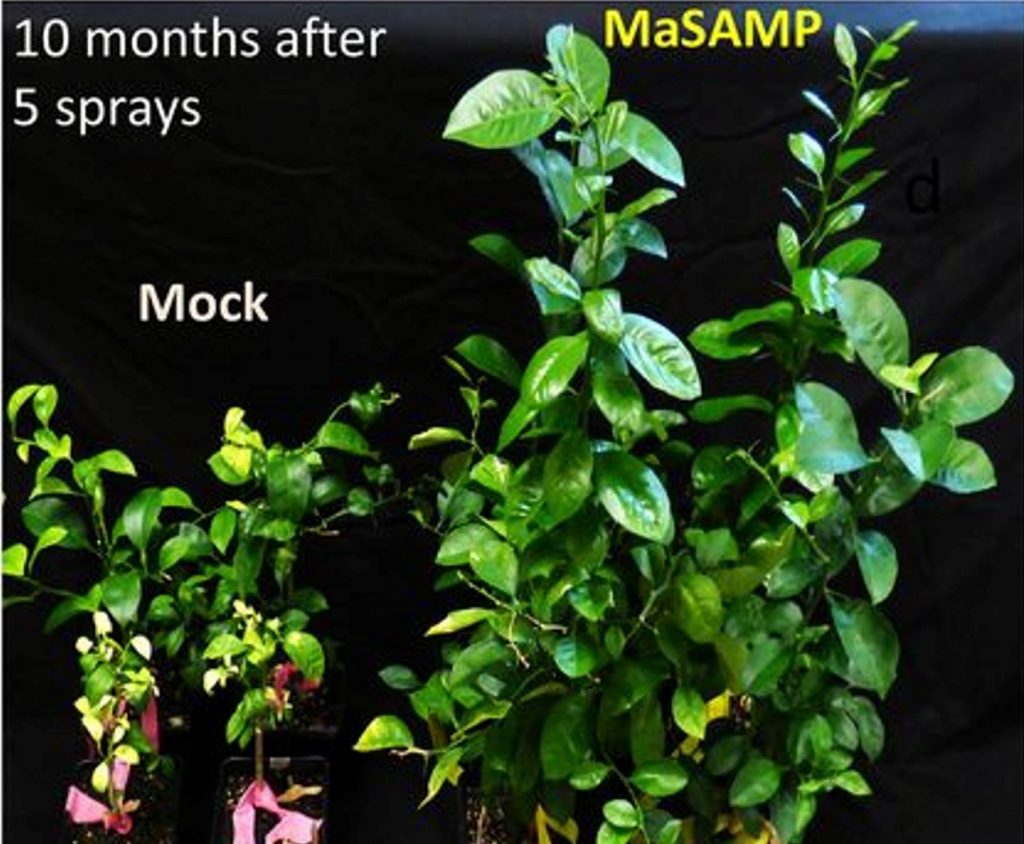

A stable antimicrobial peptide with dual functions of treating and preventing citrus Huanglongbing (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCitrus Huanglongbing (HLB) caused by the bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) is the most destructive disease of citrus and currently has no cure. Current management practices are also not effective. Huang et al. used comparative analysis of small RNAs and mRNAs between HLB-sensitive and…

Rhizobia use a pathogenic-like effector to hijack leguminous nodulation signaling (Sci Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic interactions between legume plants and compatible rhizobia bacteria lead to the formation of nitrogen-fixing nodules in the host plant root. Compatibility between rhizobia and host plants is determined by various factors like plant species-specific flavonoid secretion, extracellular polysaccharides…
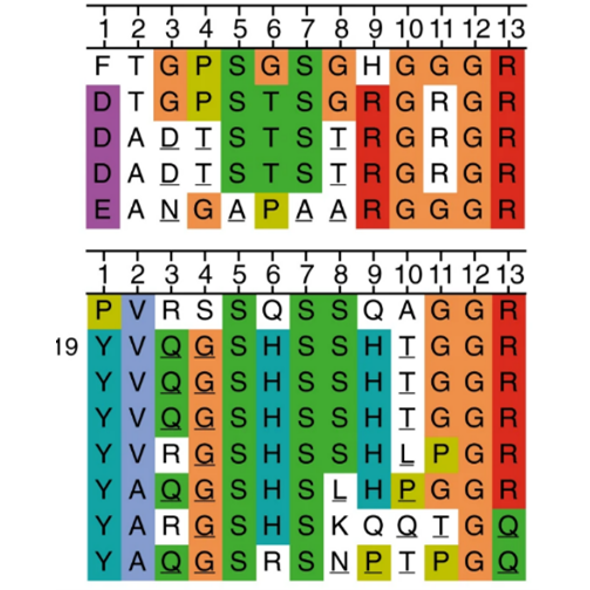
When fungi get ‘SCOOP’ed: MIK2 receptor kinase perceives SCOOP phytocytokines in Arabidopsis thaliana (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant cells sense endogenous and exogenous molecules through proteins localized to the cell surface. While numerous ligands that mediate a variety of developmental and stress processes are known, cognate receptors for many ligands remain unidentified. Rhodes and colleagues have now shown the Arabidopsis…
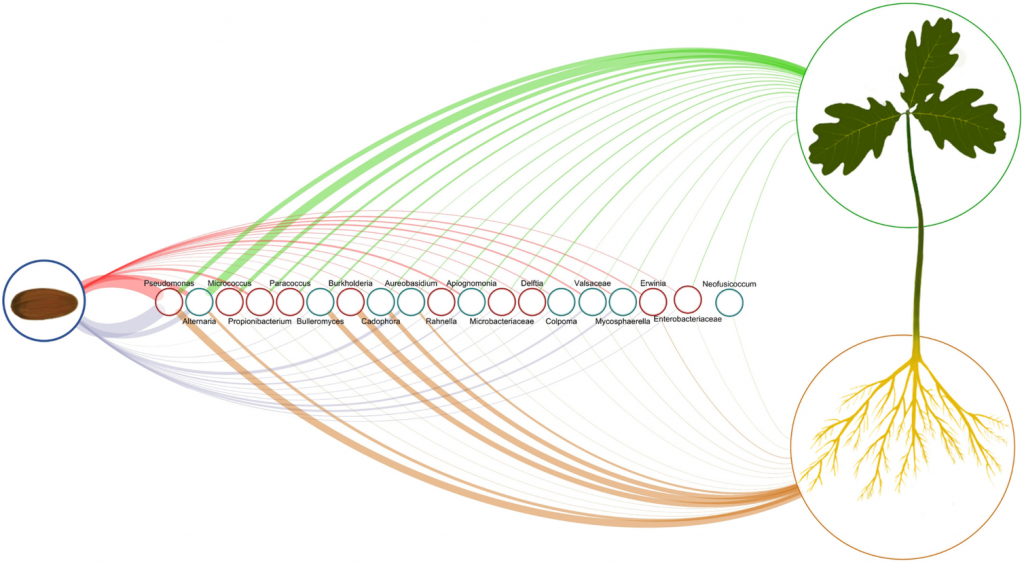
Experimental evidence of microbial inheritance in plants and transmission routes from seed to phyllosphere and root (Environ. Microbiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAll plant species are associated with a diverse yet distinct assemblage of microorganisms known as the microbiome. Traditionally, the environment is considered the primary source of these microbes. However, Abdelfattah and colleagues' fascinating research shows that seeds can act as vehicles to share…
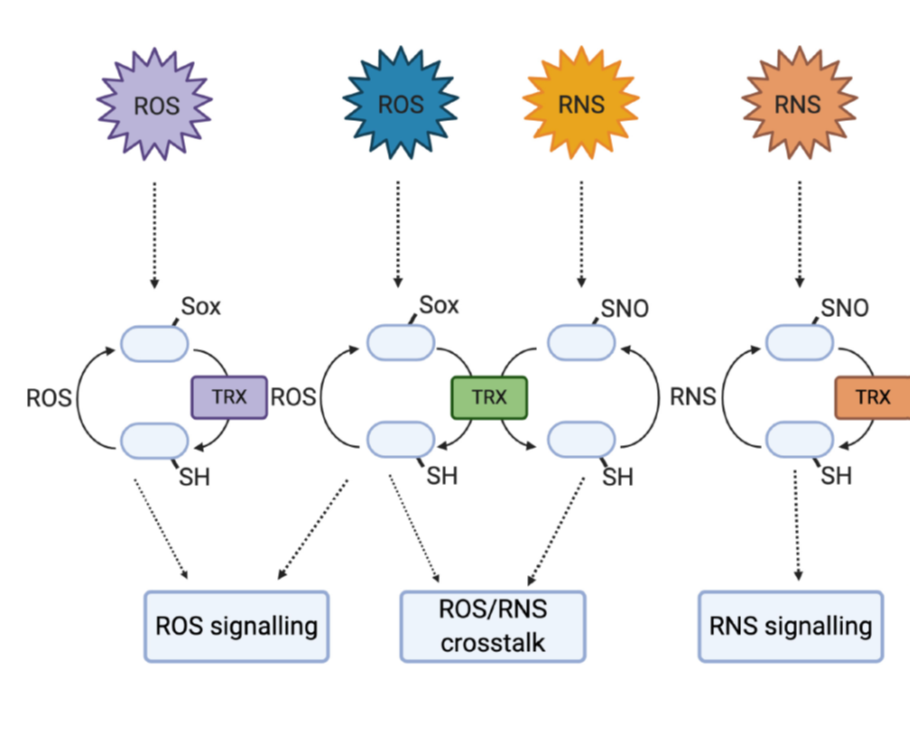
Review: Selective redox signaling shapes plant-pathogen interactions (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyReactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are often presented as something of enigmas. They are damaging by-products of metabolism and stress, but also intentionally produced as a signal and defense response to pathogens. This excellent Update by Bleau and Spoel synthesizes new…
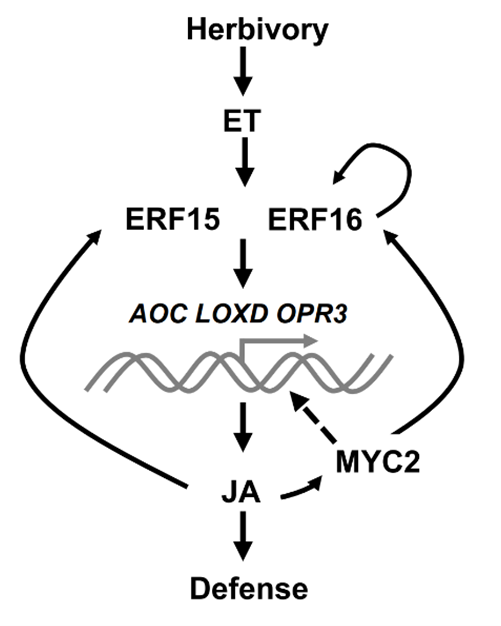
Ethylene response factors 15 and 16 trigger jasmonate biosynthesis in tomato during herbivore resistance (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop damage and yield losses caused by herbivores have become major threats to global food security. Upon wounding and herbivory, plants rapidly accumulate high levels of jasmonates (JA). However, the mechanism underlying how JA biosynthesis is triggered by herbivore attack remains unclear. It is therefore…

Coordination between microbiota and root endodermis supports plant mineral nutrient homeostasis (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots have been described as the gut of the plant, as they are the main interface for nutrient and water intake from their surrounding environment. This interface is remarkably complex. Not only must the root allow for the proper diffusion of substances into the plant, but by virtue of being constantly…

Plant cell layer-specific responses against pathogenic and beneficial microbes (Cell Host & Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots are composed of concentric cell layers with distinct gene regulatory programs. Cell layer-specific responses are likely critical for plants to cope with microbes with various lifestyles, but little is known about root responses against microbes at cell-layer resolution. Fröschel et al. tackled…
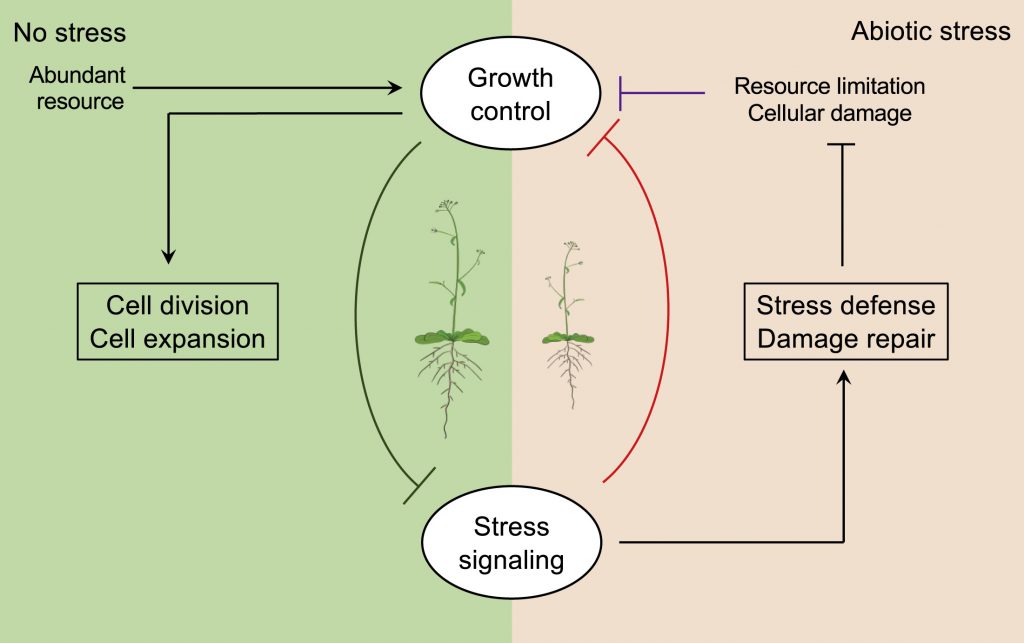
Review: Thriving under stress: How plants balance growth and stress response (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
What exactly is the growth/defense tradeoff? This review is an excellent place to ask. Zhang et al. review evidence that shows that it is much more than a competition for limiting resources – the plant actively responds to stress in ways that may slow growth but ultimately promote survival. The…

