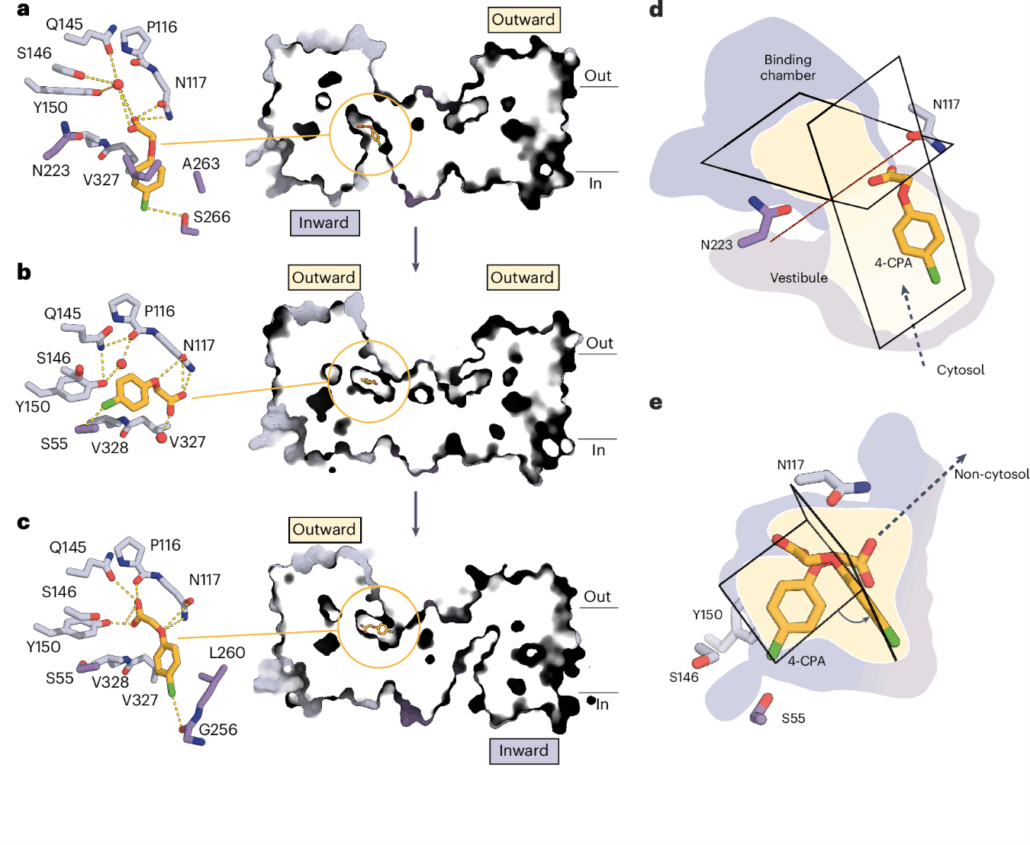
PIN auxin transporters facilitate polar transport of synthetic phenoxyacetic acid herbicides
Plant Science Research WeeklySynthetic herbicides are widely used in agriculture to control weeds, often by targeting the physiological pathways regulated by auxins, plant hormones that induce root growth and development. PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin transporters facilitate the polar transport of natural auxins such as indole-3-acetic…
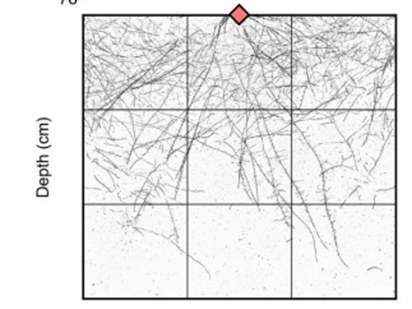
Altering root system architecture in barley without impacting above-ground traits
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots are important for acquiring water and nutrients from the soil; however root system architecture is poorly understood in cereal crops. Here Aldiss et al. used CRISPR/Cas9 to generate barley mutants in the auxin transporter PIN-FORMED2 (PIN2). Seedlings were grown in chambers and after four days…
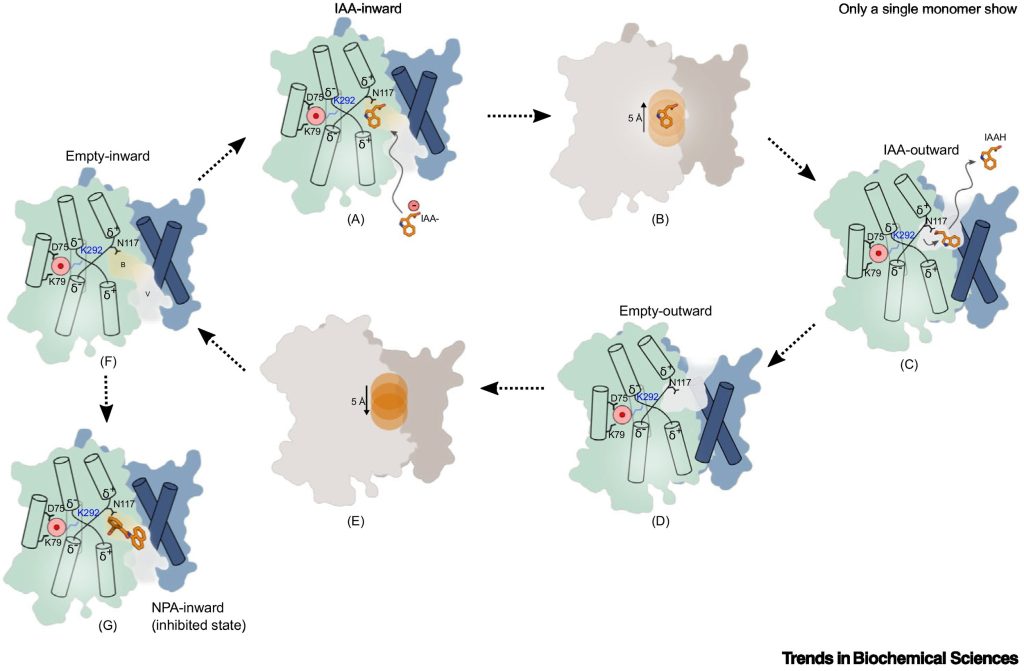
Review: Substrate recognition and transport mechanism of the PIN-FORMED auxin exporters
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe PIN-FORMED family of auxin transporters were first identified through genetic screens of Arabidopsis thaliana in the 1980s. Recessive pin mutants form a flowerless, pin-like inflorescence. Subsequent work showed that the encoded genes are membrane-localized auxin transporters and contribute to the…
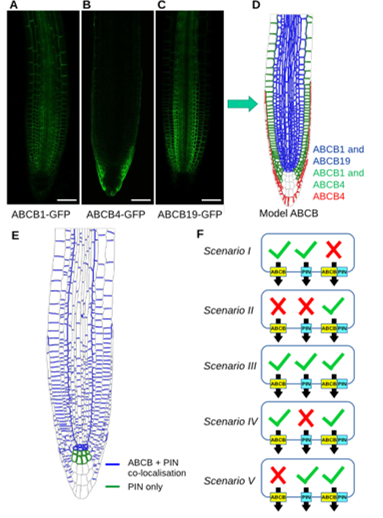
Systems approaches reveal that ABCB and PIN proteins mediate co-dependent auxin efflux (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plant development, advanced computer model simulations allow the understanding of the non-intuitive relations between local morphogenetic processes and global patterning. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the hormone auxin is involved in several processes of plant development. Auxin transporters play an important…

KAI2 regulates seedling development by mediating light-induced remodeling of auxin transport (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination is can be described as having two phases depending on light availability, skoto- and photomorphogenesis. Skotomorphogenesis, which occurs while the seed is still buried, is characterized by the elongation of the coleoptile and the inhibition of the root system. When the seed reaches…
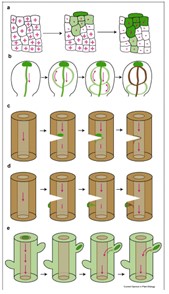
Review. Auxin canalization: From speculative models toward molecular players (Curr Opin Plant Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe versatility of roles that the hormone auxin plays led Paque and Weijers to suggest a new meaning to the acronym IAA (originally- Indole Acetic Acid)- ‘Influences Almost Anything’. It is known that PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin exporters are responsible for cell-to-cell directional auxin flow and auxin…

