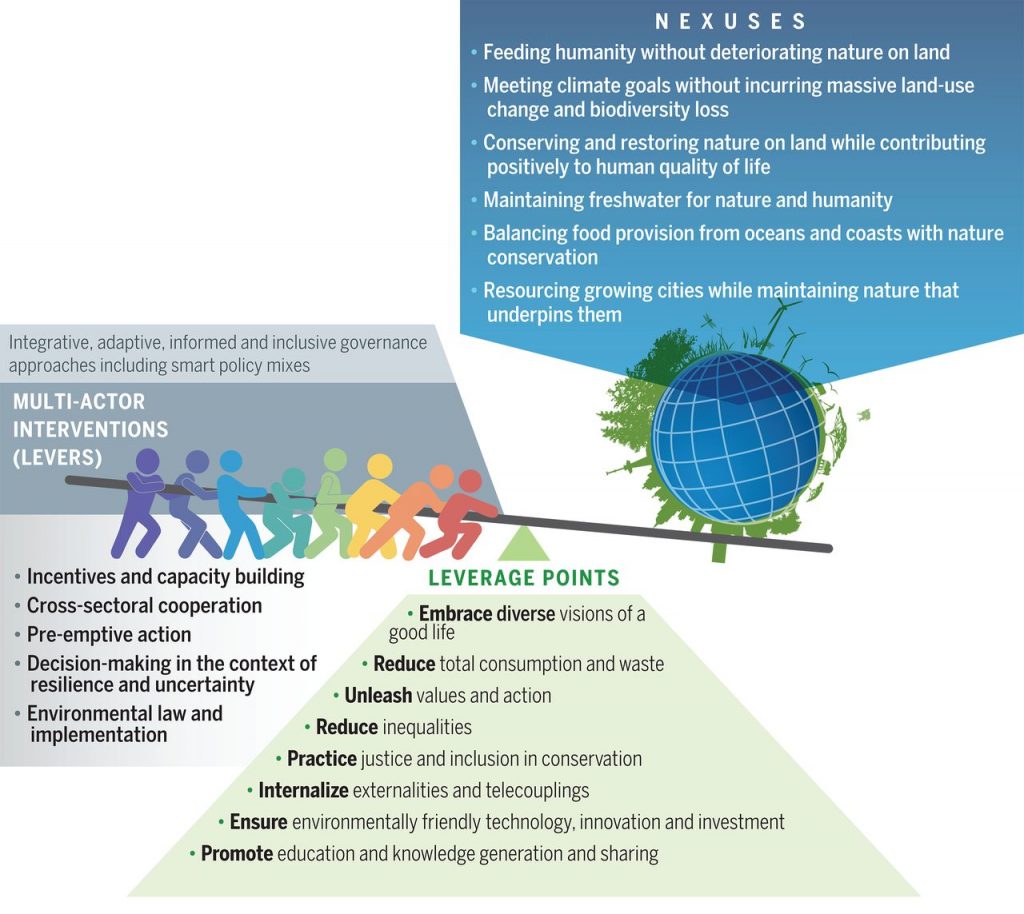
Review: Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyReading this review by Diaz et al. feels a bit like reading a bad report card. Although we know we’re failing in our role as Earth’s stewards, we don’t always want to be reminded of this. But, in this case we need to read and act on the suggestions for improvement. The authors review the findings…
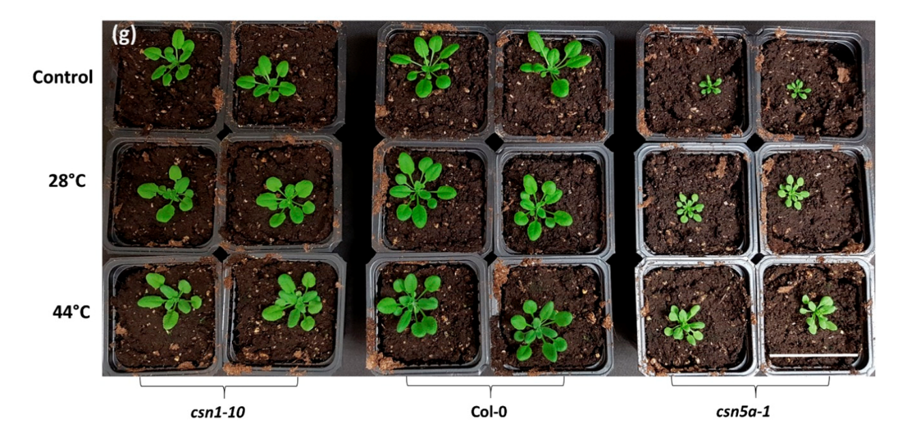

CSN5 of COP9 signalosome modulates heat-response of Arabidopsis (biomolecules)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCOP9 signalosome (CSN) is a conserved multi-subunit complex in higher eukaryotes that was originally identified as a regulator of plant photomorphogenesis. It functions by regulating ubiquitin-mediated protein stability, through the deneddylase enzymatic acitivity of the CSN5 subunit. CSN5 is encoded…
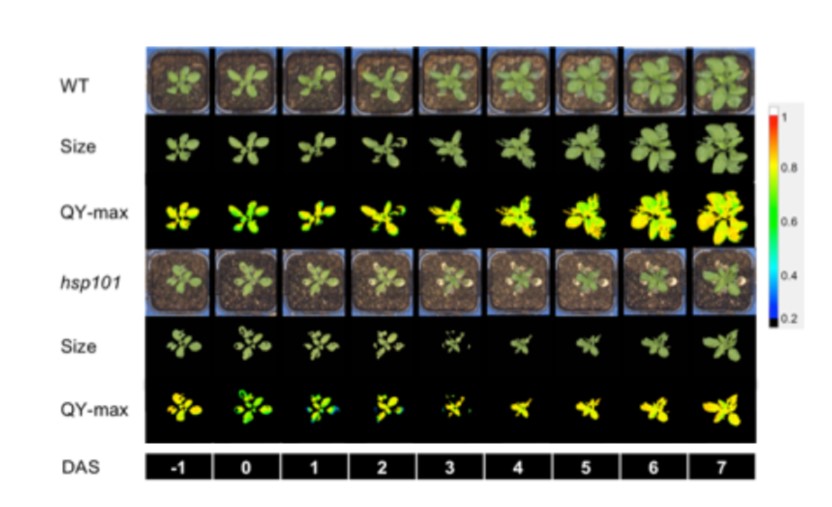
The use of high throughput phenotyping for assessment of heat stress-induced changes in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith global temperatures rising, tolerance to heat is becoming increasingly important as a breeding target for crop plants, but it is a highly complex response that includes processes including plant cooling capacity, growth recovery, and maintenance of photosynthesis. Using Arabidopsis, Gao et al. developed…

Review: The role of peptides cleaved from protein precursors in eliciting plant stress reactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough the first signaling peptide identified in plants, systemin, is involved in stress responses, developmentally important peptide signals have largely occupied the limelight. This Tansley Review by Chen et al. summarizes recent insights into peptides with a role in stress responses: wounding, pathogen…
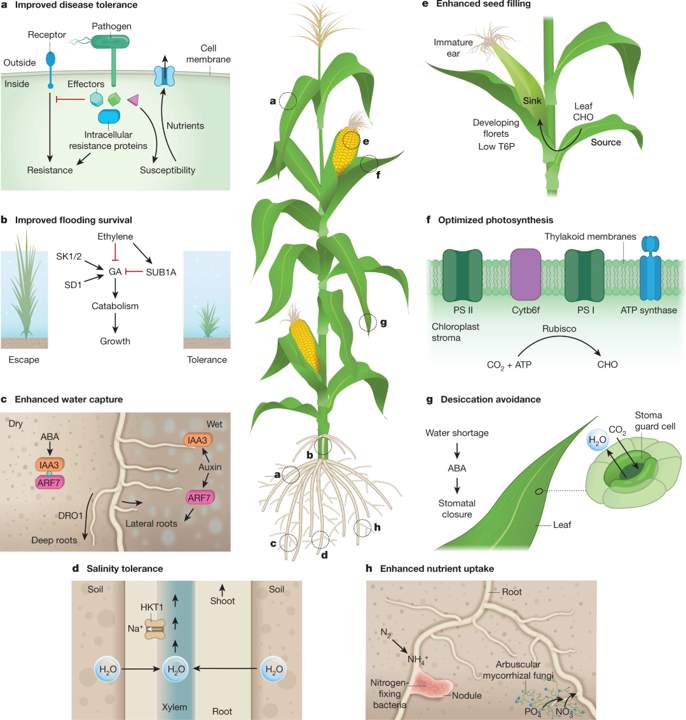
Review: Genetic strategies for improving crop yields (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklySimply put, as food demand increases due to population growth and increased affluence, crop yields are likely to decrease due to the changing climate. Plant scientists will be familiar with many research avenues that aim to address this disconnect, ranging from increasing crop resilience to abiotic stresses,…
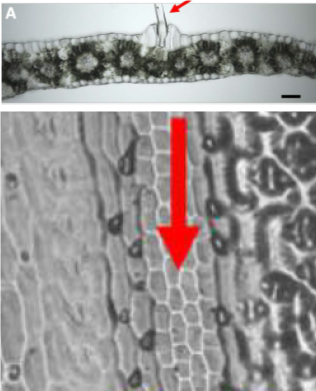
Machine learning enables high-throughput phenotyping for analyses of the genetic architecture of bulliform cell patterning in maize (G3)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBulliform cells lie in rows along the upper (adaxial) surface of the maize leaf, and through changes in volume contribute to leaf-rolling, which is a response to water deficit. Several mutants have been identified that affect bulliform cell formation and function, but as yet their occurance in natural…
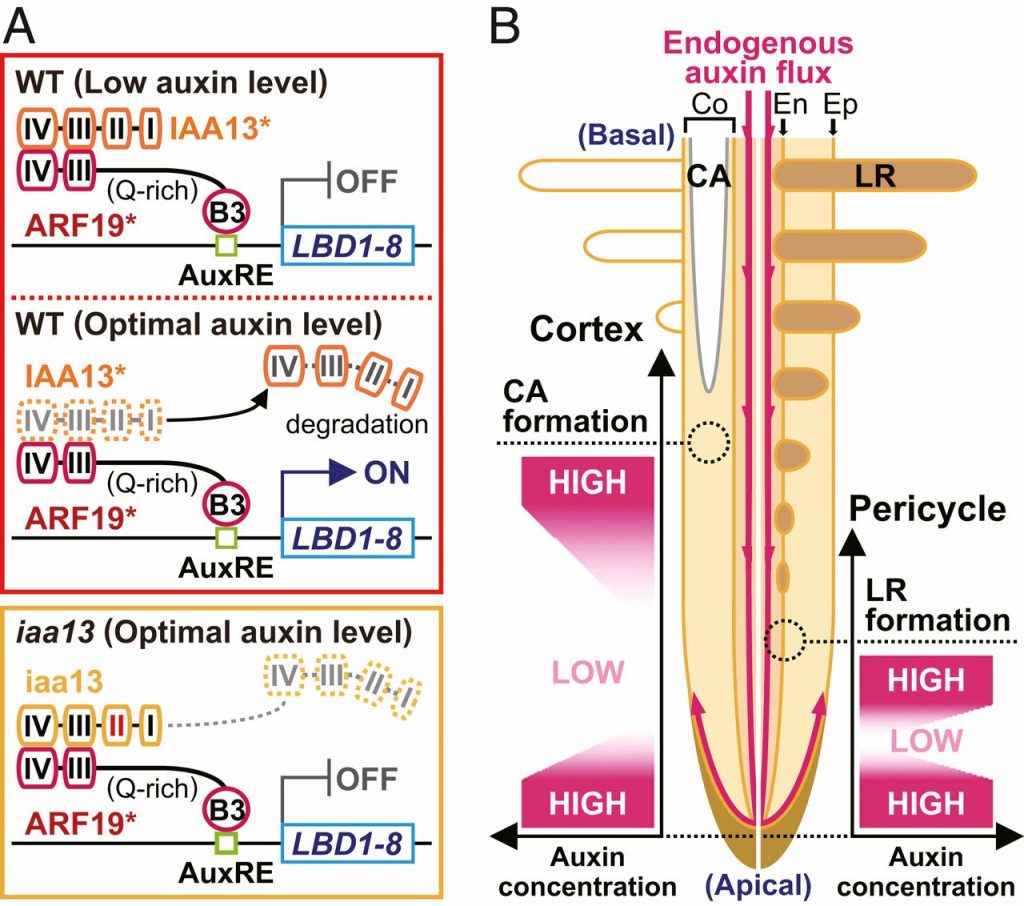
Fine control of aerenchyma and lateral root development through Aux/IAA- and ARF-dependent auxin signaling ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin plays a major role in plant development and can alter the developmental program following the stress response. In this paper, Yamauchi et al., have identified the auxin signaling cascade involved in the development of aerenchyma and regulators of this auxin signaling might also be involved in lateral…
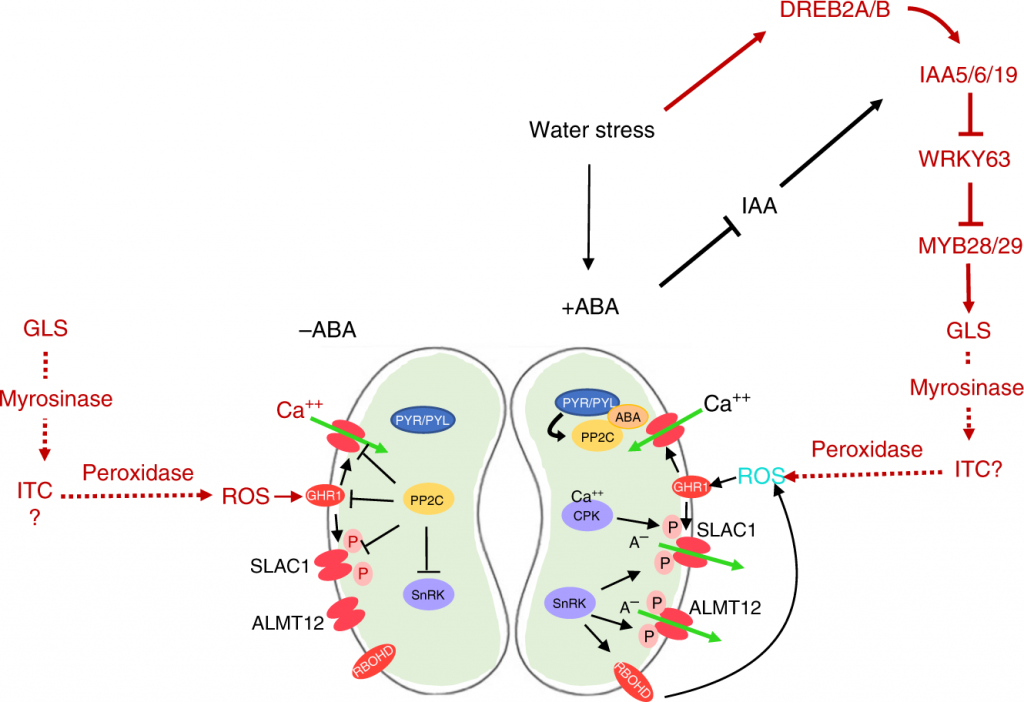
Auxin-sensitive AUX/IAA proteins mediate drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating glucosinolates levels ($) (Nature Communication)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlucosinolates are secondary metabolites synthesized by plants as a defense compound against pathogen and herbivore. In this paper Salehin et al., have demonstrated regulation of aliphatic glucosinolate levels by auxin signaling that promotes drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. The Aux/IAA proteins are…
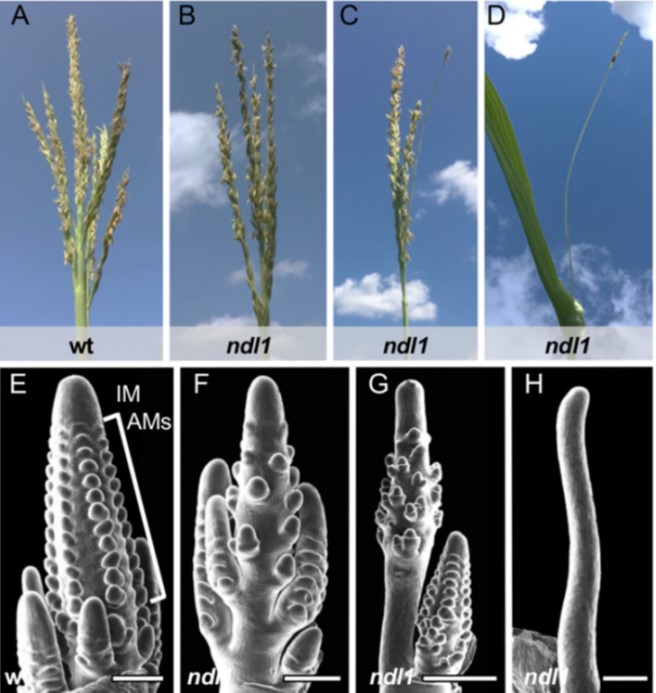

NEEDLE1 encodes a mitochondria localized ATP-dependent metalloprotease required for thermotolerant maize growth ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPreviously, the needle1 (ndl1) maize mutant was identified as showing a variable phenotype mainly affecting the tassel. Here, Liu et al. showed that this variability arises due to its temperature sensitivity, with strongest effects at warmer temperatures. In some cases, the plants arrest before reaching…

