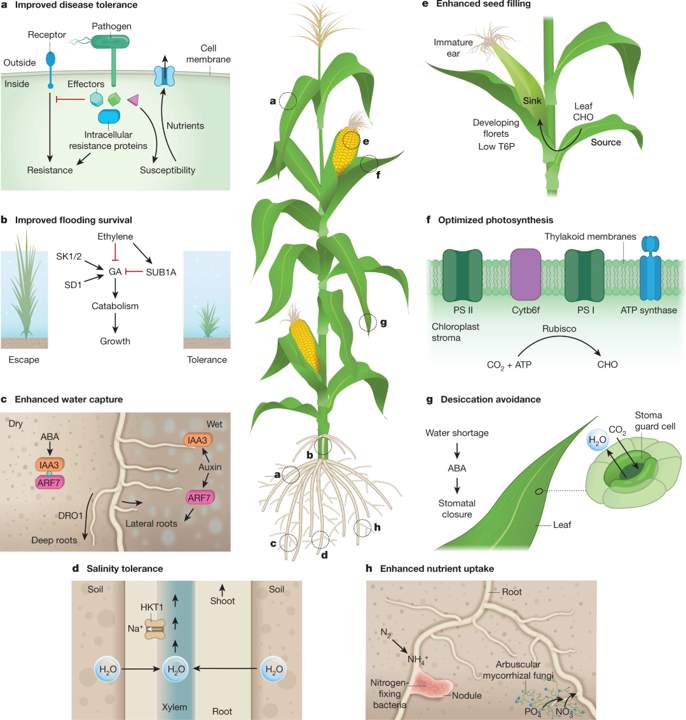
Review: Genetic strategies for improving crop yields (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklySimply put, as food demand increases due to population growth and increased affluence, crop yields are likely to decrease due to the changing climate. Plant scientists will be familiar with many research avenues that aim to address this disconnect, ranging from increasing crop resilience to abiotic stresses,…
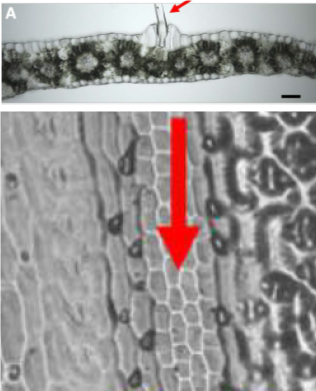
Machine learning enables high-throughput phenotyping for analyses of the genetic architecture of bulliform cell patterning in maize (G3)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBulliform cells lie in rows along the upper (adaxial) surface of the maize leaf, and through changes in volume contribute to leaf-rolling, which is a response to water deficit. Several mutants have been identified that affect bulliform cell formation and function, but as yet their occurance in natural…
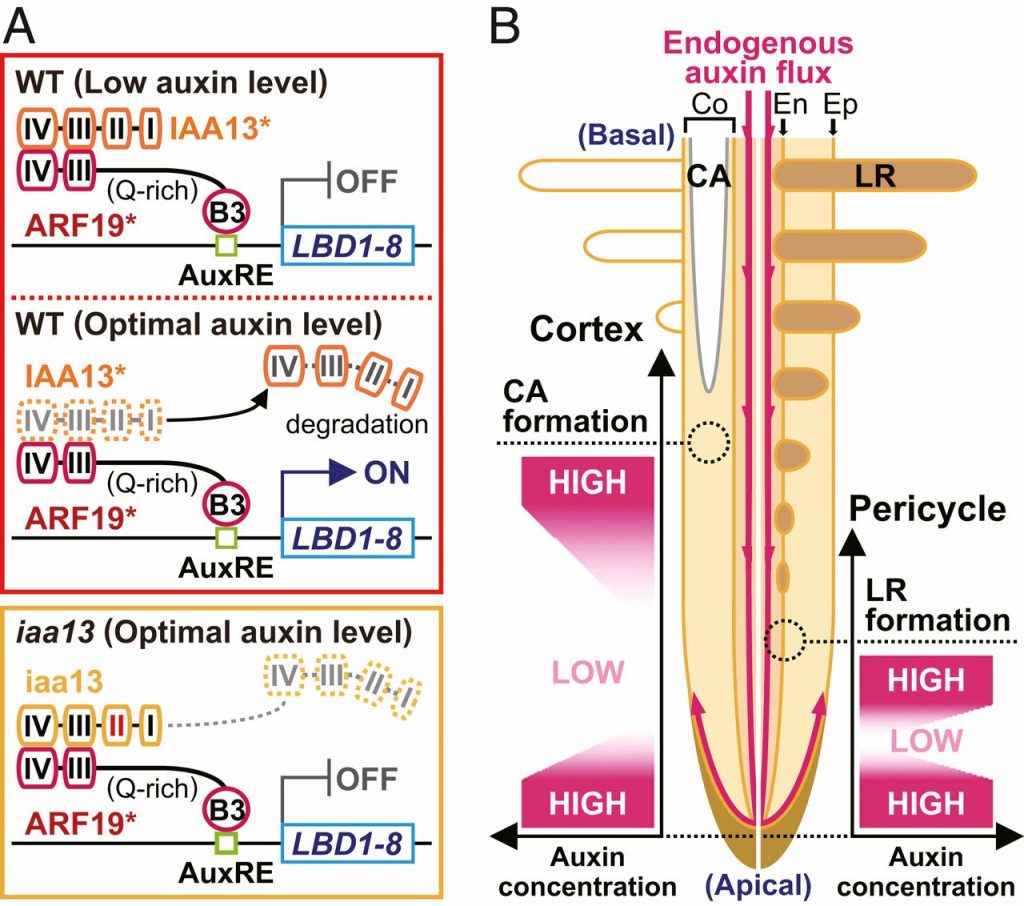
Fine control of aerenchyma and lateral root development through Aux/IAA- and ARF-dependent auxin signaling ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin plays a major role in plant development and can alter the developmental program following the stress response. In this paper, Yamauchi et al., have identified the auxin signaling cascade involved in the development of aerenchyma and regulators of this auxin signaling might also be involved in lateral…
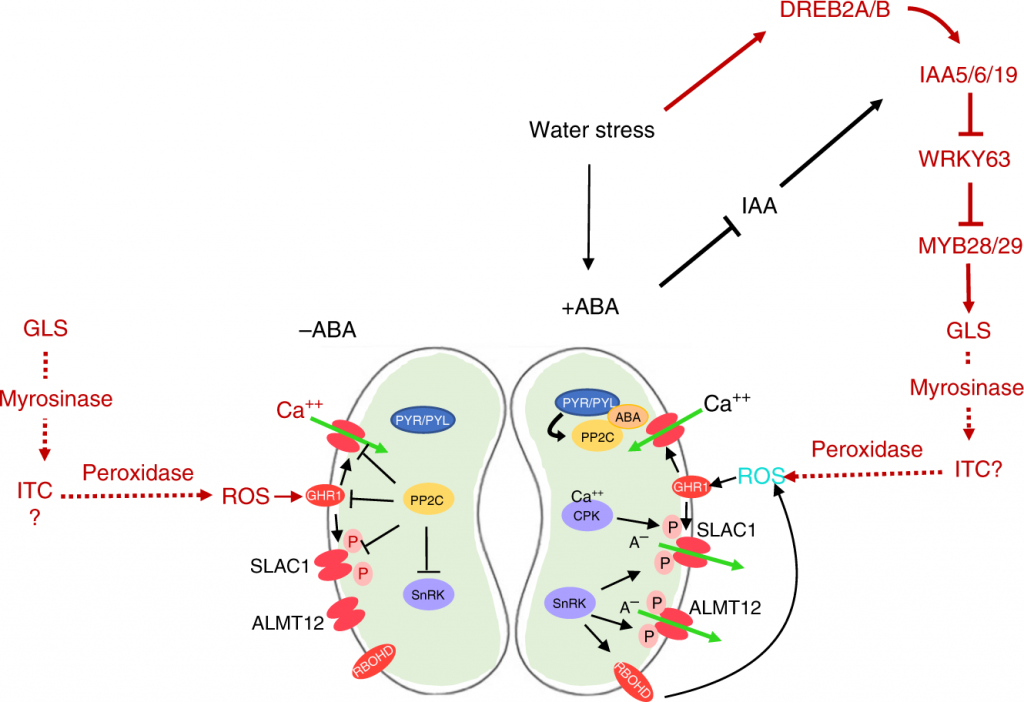
Auxin-sensitive AUX/IAA proteins mediate drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating glucosinolates levels ($) (Nature Communication)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlucosinolates are secondary metabolites synthesized by plants as a defense compound against pathogen and herbivore. In this paper Salehin et al., have demonstrated regulation of aliphatic glucosinolate levels by auxin signaling that promotes drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. The Aux/IAA proteins are…
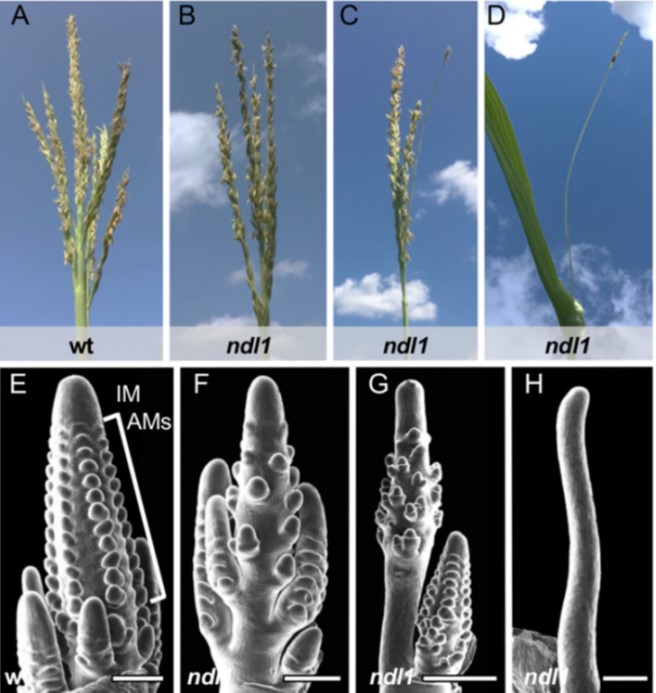

NEEDLE1 encodes a mitochondria localized ATP-dependent metalloprotease required for thermotolerant maize growth ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPreviously, the needle1 (ndl1) maize mutant was identified as showing a variable phenotype mainly affecting the tassel. Here, Liu et al. showed that this variability arises due to its temperature sensitivity, with strongest effects at warmer temperatures. In some cases, the plants arrest before reaching…
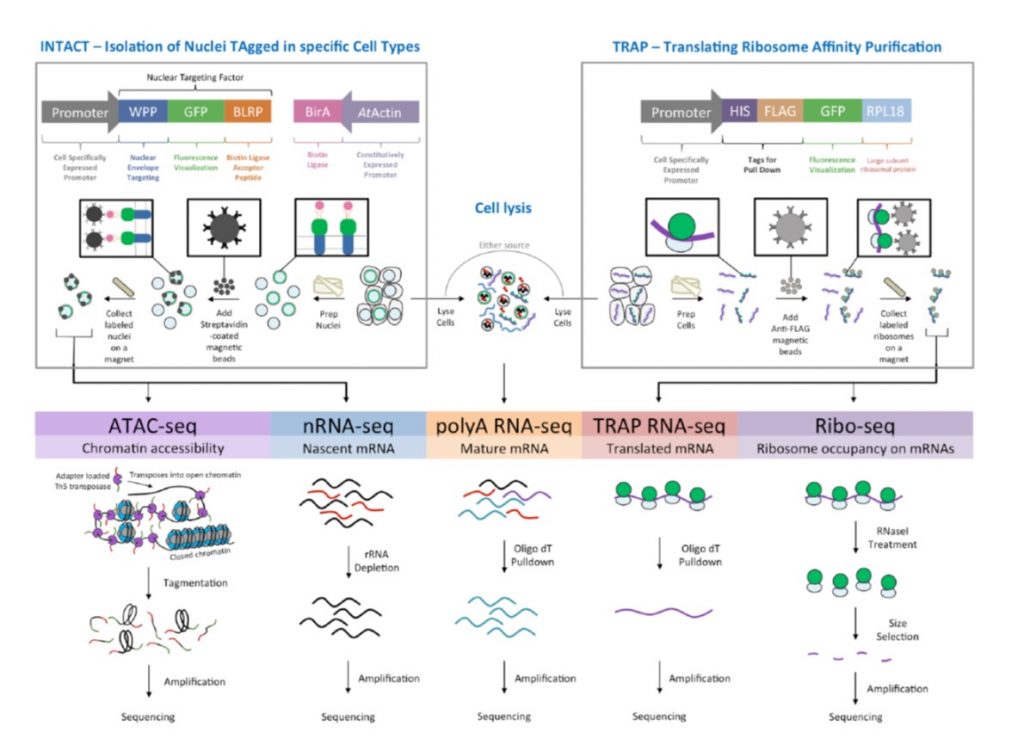
Evolutionary flexibility in flooding response circuitry in angiosperms ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlooding is unpredictable and can lead to plant death due to insufficient oxygen (hypoxia). Some plant species and varieties are better able to survive periods of submergence. Here, Reynoso et al. looked at gene networks induced transcriptionally and translationally by flooding in rice, Medicago and…
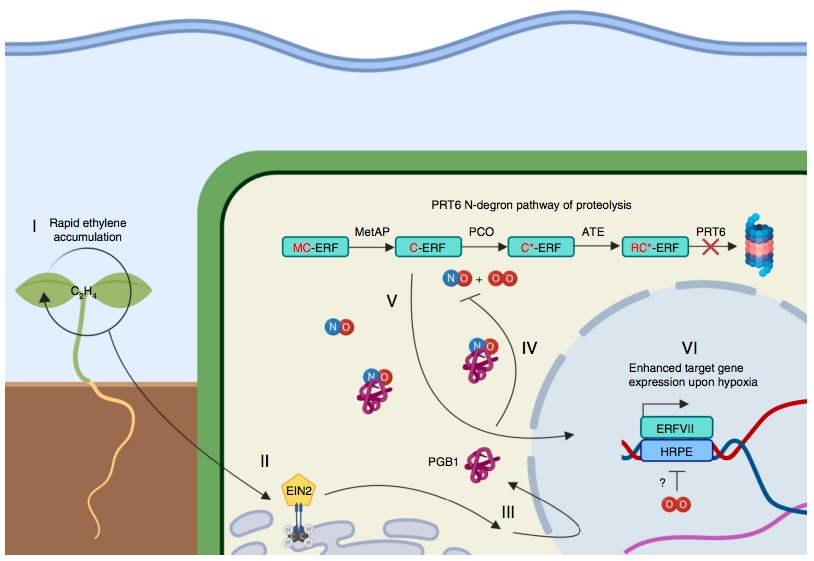
Ethylene-mediated nitric oxide depletion pre-adapts plants to hypoxia stress (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate projection models predict an increasingly wetter world with frequent and severe flooding events, causing loss of crops. As it is for other organisms, it is a challenge for plants to stay under water for long periods. However, how plants react to submergence is poorly understood. Environmental…
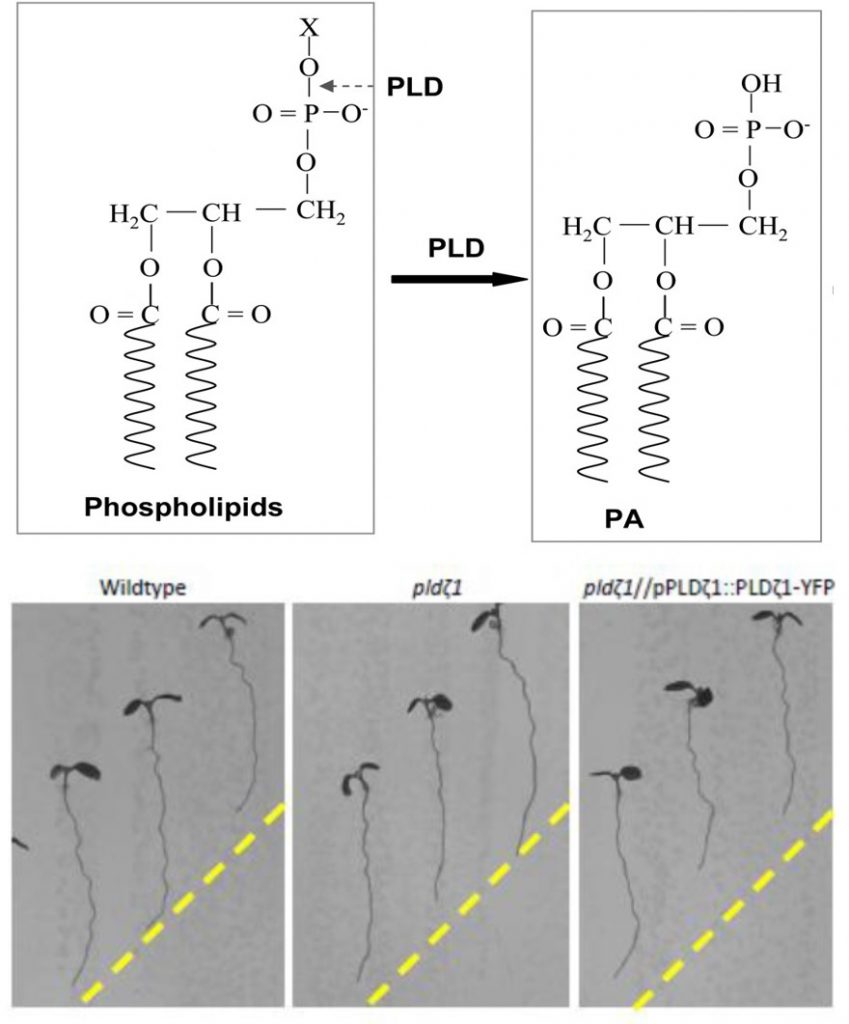
Halotropism requires phospholipase Dζ1‐mediated modulation of cellular polarity of auxin transport carriers ($) (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhospholipase D (PLD) enzymes cleave phosopholipds to release phosphatidic acid (PA), which is a signal that affects membrane dynamics. Previous studies have indicated a role for PLD and PA in root responses to osmotic and salt stress, but as the Arabidopsis genome has 12 genes encoding PLD questions…
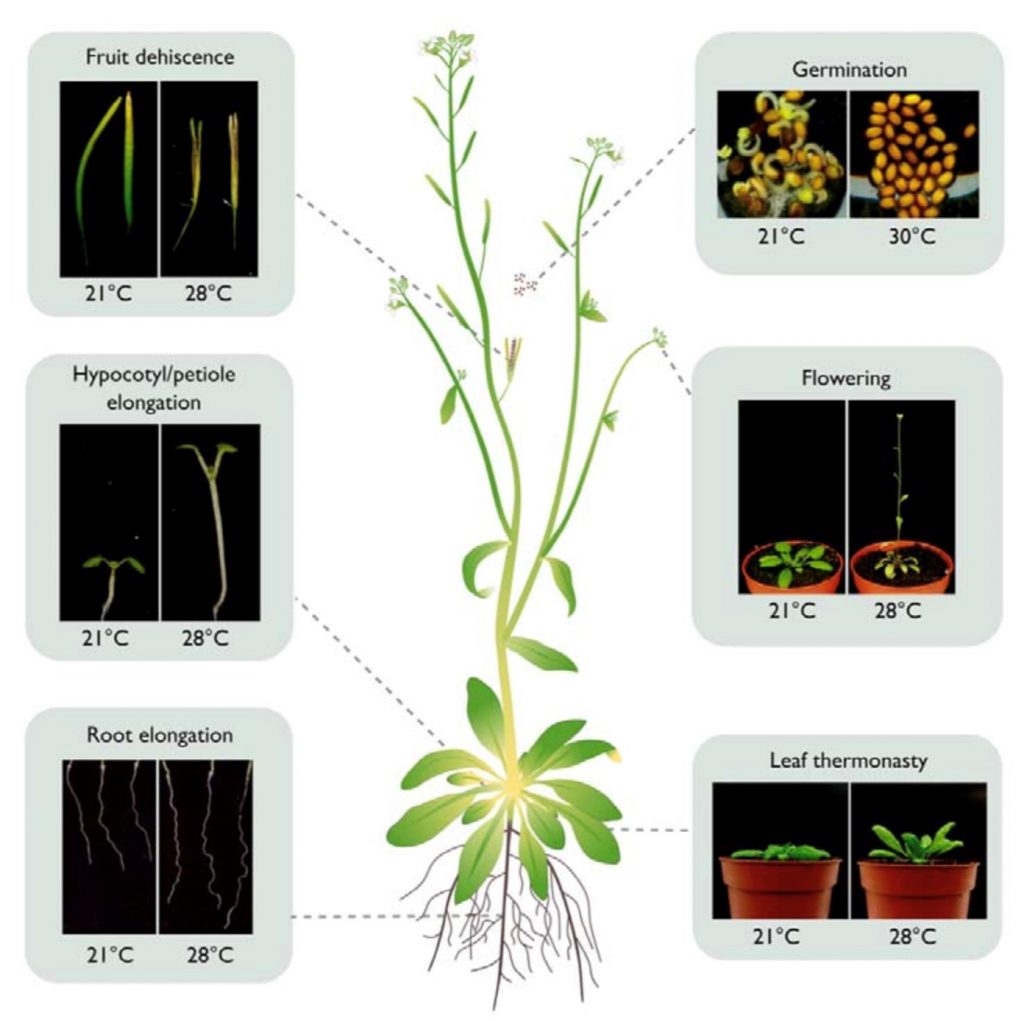
Review: Developmental thermal responses in Arabidopsis (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can modify their growth in response to environmental challenges. In a recent review, Vu et al. summarize the molecular mechanisms underlying high temperature responses during the Arabidopsis life cycle. At early stages, high temperature promotes abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis and decreases gibberellic…

