PRC1 shapes local and long-range interactions in the Arabidopsis genome
Xiaochang Yin1, Francisco J. Romero-Campero2 3, Minqi Yang1, Myriam Calonje2, Yue Zhou1
1State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, School of Advanced Agricultural Sciences, Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Peking University, 100871, Beijing, China.
2Institute of Plant Biochemistry and Photosynthesis (IBVF-CSIC), Avenida Américo Vespucio 49, 41092, Seville, Spain.
3Department of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence (University of Sevilla), Avenida Reina Mercedes s/n 41012, Seville, Spain.
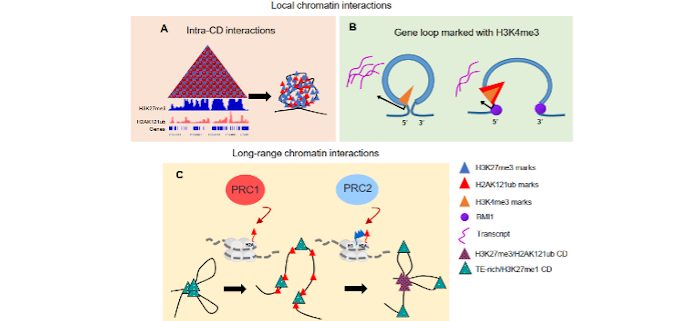
Background: How chromatin is organized in three dimensions (3D) within the nucleus has been proposed to be important for controlling biological processes. Post-translational histone modifications within chromatin, such as those mediated by the Polycomb Group machinery, seem to be involved in shaping this 3D organization, but their exact role is not clear. Recent studies have shown that the genome of animals and many plant species is partitioned into blocks of chromatin that self-interact. These topologically associating domains (TADs) or compartment domains (CDs) are usually enriched in specific histone modifications. Although Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) chromatin is also decorated with histone modifications such as histone H2A monoubiquitination on lysine 121 (H2AK121ub), TADs or CDs have not been detected.
Question: What is the role of Polycomb Repressive complex 1 (PRC1)–mediated H2AK121ub in Arabidopsis 3D chromatin organization? Are TADs or CDs really absent in Arabidopsis?
Findings: Our results showed that TADs or CDs are present in the Arabidopsis genome. We identified CDs dominated by specific histone marks, like trimethylation of histone H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3), which is mediated by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), H3K27me1 or H3K4me3. Interestingly, PRC1 mediated H2AK121ub could be found in combination with other modifications, displaying different roles. We found that H2AK121ub acting together with H3K27me3 is required to maintain the interactions inside H3K27me3 enriched CDs. In addition, PRC1 and H2AK121ub when acting independently of PRC2 prevent the formation of chromatin loops marked with H3K4me3. Likewise, we found that PRC1 affects interactions between distant CDs, participating in a higher order of chromatin organization. Our results reveal a versatile role of PRC1 activity in shaping 3D chromatin configuration in Arabidopsis.
Next steps: An interesting path to continue our findings would be to explore whether the 3D interactions observed to be dependent on PRC1 are key in defining the 3D structure genome associated with developmental phase transitions and environmental responses.
Reference:
Xiaochang Yin, Francisco J. Romero-Campero, Minqi Yang, Fernando Baile, Yuxin Cao, Jiayue Shu, Lingxiao Luo, Dingyue Wang, Shang Sun, Peng Yan, Zhiyun Gong, Xiaorong Mo, Genji Qin, Myriam Calonje, Yue Zhou. (2023). Binding by the Polycomb complex component BMI1 and H2A monoubiquitination shape local and long-range interactions in the Arabidopsis genome. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad112