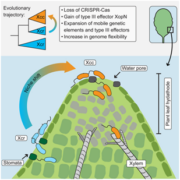
Shaping pathogenicity: How CRISPR-Cas loss fuels Xanthomonas evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved diverse infection strategies governed by virulence factors, often targeting specific host organs or tissues. Genome fluidity plays a crucial role in enabling microbial pathogens to adapt to the dynamic selection pressures imposed by co-evolution with their hosts. In a recent study,…
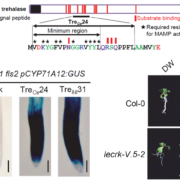
LecRK-V and trehalose-associated immunity: a conserved defense mechanism across kingdoms
Plant Science Research WeeklyMembrane-localized receptor-like kinases (RLKs) are essential for perceiving diverse signaling molecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, hormones, reactive oxygen species, ions, and damage-associated molecular patterns. Among the well-characterized RLKs, FLS2, EFR, and CERK1 are known to recognize…
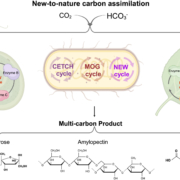
Review: Genetic engineering for carbon assimilation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme for photosynthesis, This enzyme poorly discriminates between CO2 and O2, which limits its efficiency. To work around this and make carbon assimilation more efficient, scientists have been employing different engineering…
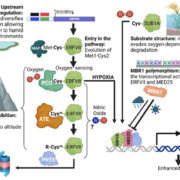
Review: Geography, altitude, agriculture, and hypoxia
Plant Science Research WeeklyHypoxia, or reduced oxygen availability, is a double-edged sword: while it disrupts metabolism and can cause cell death, it also plays a vital role in regulating development in animals and plants. With extreme flooding increasing due to climate change, understanding how genetic variation enhances hypoxia…
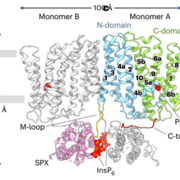
Structural insights into PHO1: A key regulator of phosphate translocation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient required for plant growth, development, and reproduction. It is primarily absorbed by plant roots in the form of orthophosphate (Pi). The root-to-shoot translocation of Pi depends on a crucial xylem-loading process mediated by PHOSPHATE 1 (PHO1), a Pi efflux…
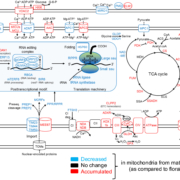
High-energy requiring pollen grains have specialized mitochondria
Plant Science Research WeeklyImagine you’re on a quest to deliver a package, racing against the competition. How do you prepare? Pollen grains and the pollen tubes that they form are essentially package-delivery systems. Their purpose is to deliver genetic information (sperm cell nuclei) to the ovule. Once the task is completed,…
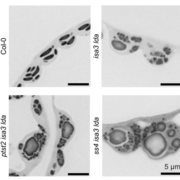
You’ve gotta starch somewhere: Evidence for an alternative starch granule initiation pathway
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarch is the major storage carbohydrate in plants, and in Arabidopsis leaves it forms granules in the chloroplasts to supply energy during the night when photosynthesis is inactive. These semicrystalline granules are made of glucose chains, which can be mostly unbranched (amylose) or highly branched…
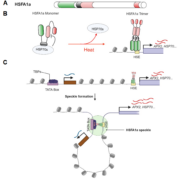
Prion-like domains of sensory HSFs remember heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe heat shock response, a rapid transcriptional response to heat, was first observed nearly 60 years ago, and has long been a paradigm for understanding gene responses to exogenous cues. The family of genes encoding heat shock factors (HSFs) is greatly expanded in plants. These HSFs serve as key regulators…

How a model C4 plant, Setaria viridis, copes with prolonged heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyDue to anthropomorphic global warming, 2024 was the first year during which the global mean temperature was more than 1.5° above pre-industrial levels. Clearly, understanding how high temperatures affect plant physiology is an urgent priority. In this new study, Zhang et al. did a multi-parameter study…

