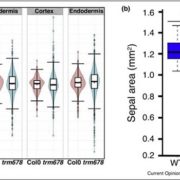
Review. Use it or average it: Stochasticity in plant development (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
In this interesting review, Roeder describes the importance of stochasticity in plant development. She starts off with an explanation: “A process that can be analyzed statistically but not predicted precisely is stochastic. Stochasticity does not imply the absence of regulation, just that the regulation…
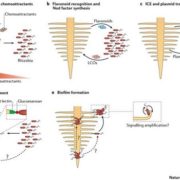
Review. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts (Nat. Rev. Microbiol.) ($)
One of the best characterized plant-bacteria interactions is that between legumes and rhizobia. This review by Poole et al. explores rhizobia in their non-plant associated state (as saprophytes that derive energy and nutrients from organic matter in the soil), through the complex signals that lead to…
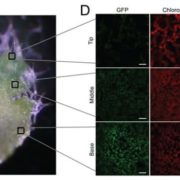
Control of retrograde signaling by rapid turnover of GENOMES UNCOUPLED 1 (Plant Physiol.)
Communication between chloroplast and the nucleus is crucial to accomodate changes in the environment as well as regulate development of the chloroplast itself. Five GENOMES UNCOUPLED (GUN2 to -6) genes were previously described to regulate plastid-to-nucleus communication by affecting the synthesis…
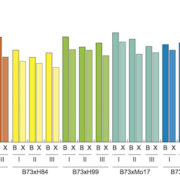
Single Parent Expression (SPE) of non-syntenic genes in maize hybrids (Curr. Biol.) ($)
In maize, it has long been known that the crossing of two inbred lines can produce a hybrid offspring with higher yield than the parents. Baldauf and collaborators have studied the gene expression of 6 hybrid lines coming from 7 distantly related inbred lines. One line, B73, was chosen as the common…
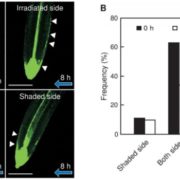
Asymmetric auxin distribution and root tropisms (Plant Cell Physiol.) ($)
The asymmetric distribution of the phytohormone auxin is essential for tropic responses of seed plants but it is unclear if this distribution is essential for root negative phototropism as well. To understand the role of auxin distribution in root negative phototropism in Arabidopsis, Kimura and colleagues…

A virus-targeted plant receptor-like kinase promotes cell-to-cell spread of RNAi (PNAS) ($)
Viruses can move from cell to cell through plasmodesmata. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are key components in the plant's arsenal against viruses. They function by harnessing the AGO system to target and cleave viral RNA, thus silencing the viruses. Like the viruses they target, siRNAs move from cell…
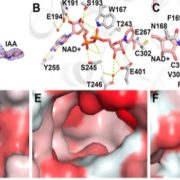
Auxin synthesis contributes to virulence of Pseudomonas syringae (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant pathogens have developed a large range of strategies to allow them to have successful interactions with their plant host, including physiological manipulation. For example, Pseudomonas syringae, the cause of speck disease in many plant systems, manipulates the auxin phytohormone physiology in its…
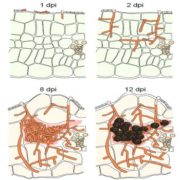
The biotrophic development of Ustilago maydis studied by RNAseq analysis (Plant Cell)
The corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis that causes tumorous symptoms on all aerial parts of maize has established itself as a model system to dissect host colonization strategies by biotrophic fungi. Transcriptional responses upon U. maydis colonization were previously demonstrated by several studies using…
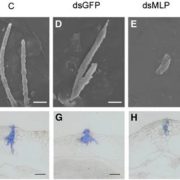
A mucin-like protein of planthopper is required for feeding and induces immunity response in plants (Plant Physiol.)
Piercing-sucking insects secrete saliva while feeding through specialized mouth parts called stylets. Saliva plays critical roles in insect digestion and nutrition, and regulates plant defense responses, but the specific metabolites involved have not been characterized. Shangguan et al. reported the…

