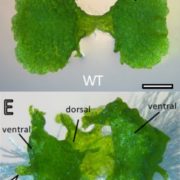
ALOG transcription factors influence the morphological diversity of plant lateral organs (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plants evolved from freshwater streptophytic algae over 450 million years ago and have since separated into morphologically diverse lineages. A key feature in the transition from aquatic to terrestrial life was the development of 3D body plans with lateral organs. In a new preprint, Naramoto and…
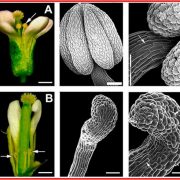
Review: Engineered male sterility by early anther ablation (Frontiers Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMale sterility in seed production could be used to increase crop yields, eliminate pollen allergies or avoid gene flow between genetically modified plants and other species. Here, Roque et al. developed a system to produce engineered nuclear male sterile plants using the pea Pisum sativum ENDOTHECIUM…

Review: Synthetic biology in photosynthetic microbes: present and future (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthetic microbes are emerging models for synthetic biology applications since they possess relatively simple physiology and cellular organization, fast growth in liquid culture, and facile genetic manipulation. In this paper, Vavitsas et al. review current synthetic biology tools and applications…
Critical residues for carotenoid biosynthesis by phytoene synthase (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCarotenoids are diverse structures that contribute to photosynthetic light harvesting and serve as pigments, photoprotectants, and precursors for vitamin A and signalling molecules. Phytoene synthase is the first committed enzyme for carotenoid synthesis, and in tomato it is encoded by two genes, PSY1…
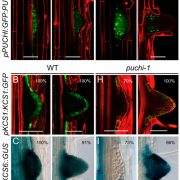
Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are involved in lateral root formation (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot branching determines the spatial organization of the root and its interaction with the soil. The emergence of lateral roots (LR) is controlled by a complex regulatory network, involving genetic, hormonal and mechanical factors. In this study, Trinh et al. got new insights about PUCHI, a transcription…
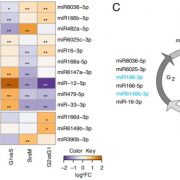
Cell cycle dependent regulation and function of ARGONAUTE1 in plants (Plant Cell) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRegulation of gene expression at transcriptional, translational and post-translation levels is crucial for proper plant growth. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by small RNAs like microRNA (miRNA), siRNA and phasi-RNAs is necessary for meristem maintenance in plants. Unlike in the mammalian system,…

A signal amplifier that regulates soybean root growth in response to salt stress (Plant Cell_
Plant Science Research Weekly
The balance between environmental stress tolerance and plant growth is an important research topic. Plant responses vary among species and varieties, but also with the growth environment. Soil, water, and environmental factors interact to affect plant growth responses to soil salinity. To engineer…
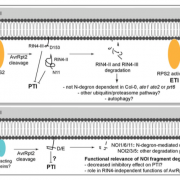
RIN4/NOI fragments utilize different N-end rules of degradation to fight off pathogens (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo fight off invading pathogens, plants such as Arabidopsis are intrinsically programmed with a subset of defense responses often known as pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). AvrRpt2, an effector secreted by the pathogen Pseudomonas syringe, is a protease that can…
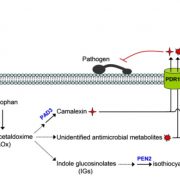
PEN3 and PDR12 secrete camalexin to the apoplast to limit pathogen growth in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytoalexins are important antimicrobial compounds that plants synthesize to fend off invading pathogens. In the Brassica family, the tryptophan (trp)-derived phytoalexin ‘camalexin’ provides broad-spectrum resistance against bacterial, fungal, and oomycete pathogens. The regulation of camalexin…

