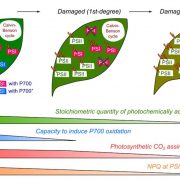
What quantity of photosystem I is optimum for safe photosynthesis? ($) (Plant Physiol)
Photosynthesis is one of the most vital and complex processes carried out by plants. During photosynthesis, Photosystem I and II (PSI and PSII) undergo photo-excitation. Excessive photo-excitation can damage and deactivate the PSI by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). This kind of photoinhibition…
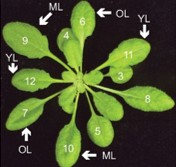
Leaf age dictates abiotic versus biotic stress signalling in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plants sense and respond to various external stimuli throughout their lifespan. During stress responses brought forth by abiotic or biotic factors, molecular and physiological adjustments mediated by distinct yet interconnected hormone pathways play critical roles in plant survival. Berens et al. investigate…
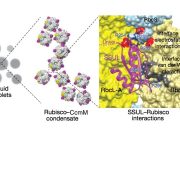
Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis (Nature) ($)
Cyanobacterial carbon-dioxide concentrating mechanisms elevate intracellular inorganic carbon as bicarbonate, and then concentrate it as carbon-dioxide around the enzyme Rubisco in specialized protein micro-compartments called carboxysomes. The formation of B-carboxysomes involves an aggregation between…
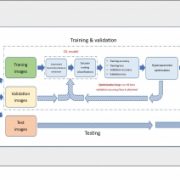
Review: Deep learning on image-based plant phenotyping (Trends Plant Sci)
The development of deep learning brings opportunities to train computers to solve complex questions. Self-driving vehicles are classic examples of an application of deep learning in the real world. However, the large amounts of data that are required for building accurate models and avoiding overfitting…

Nitrate transporter gene OsNRT1.1A/ OsNPF6.3 confers high yield in rice (Plant Cell)
In many ecosystems, nitrogen (N) is a limiting factor for plant growth. In agro-ecosystems, the application of synthetic N fertiliser has solved that issue. However, N fertiliser application is costly both to the farmers and the environment (in terms of N leaching and atmospheric release of greenhouse…
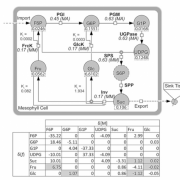
Mathematical modeling approaches in plant metabolomics
Mathematical modeling, as a series of useful methods for functional and causal interpretation of experimental high-throughput studies, enables us to explore the complex field of plant metabolism. The application of differential equations as a mathematical method has been developed and reviewed for decades…

Auxin efflux carrier ZmPGP1 mediates root growth inhibition under aluminum stress (Plant Physiology)
Acid soils (pH < 5.5) mobilize aluminum (Al) in the rhizosphere, which damages the root meristem and hinders exploration for nutrients and water. Zhang et al. demonstrate that a mutation in ZmPGP1, an auxin transport protein, imparts enhanced root growth under toxic Al conditions. The enhanced root…
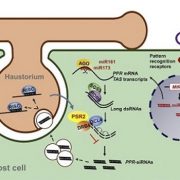
Plant-pathogen arms race: A pathogen effector protein inhibits trans-kingdom RNAi (Cell Host & Microbe)
Phytophthora spp. are highly aggressive fungus-like pathogens that cause various blight and rot diseases in many crops. Upon invasion of host cells, Phytophthora delivers thousands of effector proteins. Some of these effectors suppress the host RNA silencing pathway, which is mediated by a diverse…

Xylan and lignin deposition are independent of cellulose in the secondary cell wall (Plant Cell)
The secondary cell wall (SCW) plays an important role in the structural integrity of plants and is key to efficient water conductivity. Despite the important role of the SCW, little known about how and when SCW components are assembled. Currently, it is understood that cellulose deposition is a precursor…

