
Male sterility in maize after transient heat stress (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe corn we eat is a seed, which is a product of fertilization. It is widely known that corn yields are highly susceptible to abiotic stress conditions that occur during the repdroductive stage of development. Begcy et al. used a metabolomic / transcriptomic approach to understand why transient heat…

TurboID-based proximity labeling reveals that UBR7 is a regulator of N NLR immune receptor-mediated immunity (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIdentification of protein- protein interactions helps understand the signaling cascade in multiple biological process including development, biotic and abiotic stress. Previously, a proximity-based labelling approach referred to as BioID had been used to identify proteins in close proximity to a protein…
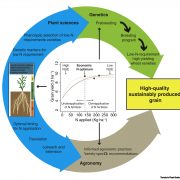
Opinion: Towards lowering crop N requirement (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCurrent and future food production demands a lot of nitrogen (N) fertilizers. Inefficient N fertilization leads to N losses to the environment and generates greenhouse gases that cause environmental problems. In a recent article, Swarbreck and colleagues discuss a strategy to develop crop varieties with…
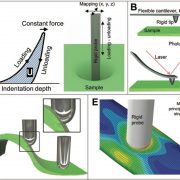
Review: Methods to quantify primary plant cell wall mechanics ( J. Exp. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant growth and morphogenesis are linked to cell wall properties, so a deep understanding of cell wall biochemistry and mechanics is essential for studying plant development. In a recent review, Bidhendi and Geitmann describe current and emerging techniques for the analysis of cell wall mechanics. Classic…
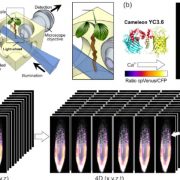
Review: Imaging technologies to uncover the role of Ca2+ signaling in plant nutrient homeostasis (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaintaining nutrient homeostasis is ridiculously challenging, in large part due to the tremendous effects individual nutrients have on other nutrients’ uptake and action, as well as the interactions between nutrient homeostasis and environmental conditions. In order to maintain the “right” amount…
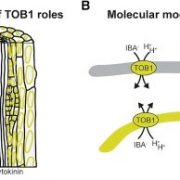
TRANSPORTER OF IBA1 links auxin and cytokinin to influence root architecture ($) (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIndole-3-butyric acid (IBA) is the precursor of the hormone auxin and it controls the formation of lateral roots. Evidence suggests that IBA is converted to IAA, endogenous active auxin. The major study material to distinguish between IBA and IAA was highlighted by the IBA-specific efflux carrier ABCG36/PDR8/PEN3,…
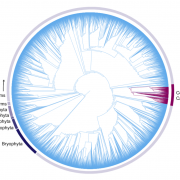
Review: The evolution of betalain biosynthesis in Caryophyllales (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the flowering plant order Caryophyllales (which includes beets), betalains substitute for anthocyanins, which are the most common form of pigmentation across the land plant phylogeny. Also found in the Basidiomycota fungal lineage, betalains are tyrosine-derived pigments that comprise of two groups…
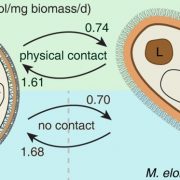
Algal-fungal symbiosis may account for the origin of basal land plant species (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight serves as the source of energy as well as an information signal for photosynthetic plants. During evolution, plants have acquired the ability to monitor environmental light radiation and adjust their developmental patterns to optimally utilize light energy for photosynthesis. However how the early-diverging…
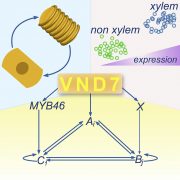
Molecular mechanisms driving switch behavior in xylem cell differentiation (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyXylem is involved in the movement of water and mineral nutrients through the plants from the roots to leaves; its cells are not totipotent and undergo programmed cell death. VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN (VND) transcription factors are master switches of xylem cell differentiation in Arabidopsis and much…

