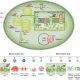
A key player in glutamate export from Arabidopsis chloroplasts
The et al. identified a chloroplast glutamate exporter in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell (2023).
By Samantha The and Mechthild Tegeder, School of Biological Sciences, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, 99164, USA
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad310
Background: Plants produce amino acids in chloroplasts, and membrane transporters are needed to move these amino acids to the cytosol. In the cytosol, the amino acids are used for protein production and other biochemical pathways within leaf cells and to supply nitrogen to growing sink organs, such as seeds. However, despite their importance, little is known about these plastidial exporters.
Questions: What is the role of chloroplast amino acid transporters in leaf metabolism and long-distance transport of nitrogen? What is their physiological importance?
Findings: We found that Arabidopsis thaliana USUALLY MULTIPLE ACIDS MOVE IN AND OUT TRANSPORTER 44 (UMAMIT44) localizes to the chloroplast envelope and regulates plastidial glutamate export and glutamate homeostasis within and outside of chloroplasts. Decreased export and subsequent cellular imbalances in umamit44 mutants impact the cellular redox state and affect both leaf nitrogen and carbon metabolism as well as the long-distance delivery of nitrogen and carbon to growing organs. Observed changes lead to decreased mutant growth and seed yield. Nevertheless, umamit44 plants adapt to some extent by accelerating alternative pathways for glutamate synthesis outside of chloroplasts and by producing other amino acids and antioxidants to alleviate oxidative stress. Overall, we demonstrate that UMAMIT44 is an essential player in plastidial glutamate export and vital for plant growth and development.
Next steps: Transcriptome, 13CO2 labeling and metabolic flux analyses are needed to determine the interrelationship between plastidial amino acid export, cellular metabolism and sink nitrogen supply. In addition, the identification of further chloroplast amino acid transport systems is a “must-do” as our understanding of the kind of transporters that mediate chloroplast efflux or influx of amino acids, and how they affect metabolic networks, metabolite levels and sink nitrogen nutrition, remains in its infancy.
Reference:
Samantha V. The, James P. Santiago, Clara Pappenberger, Ulrich Z. Hammes, and Mechthild Tegeder. (2023). UmamiT44 is a key player in glutamate export from Arabidopsis chloroplasts. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad310