A chromatin remodeler and a histone chaperone help repair DNA
Fan et al. investigate the proteins involved in DNA base excision repair
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae052
By Tianyi Fan and Yan Zhu
Background: DNA bases are susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as UV light or reactive oxygen species. Base excision repair (BER) can eliminate modified or damaged DNA bases. However, chromatin structures pose natural obstacles to the recognition and repair of DNA lesions. The mechanisms governing BER within the context of chromatin are imperative for maintaining genome integrity. However, the factors or mechanisms involved in facilitating chromatin mobility to aid BER remain poorly elucidated, particularly in plants, which experience extensive DNA base damage due to their stationary lifestyle and oxidative stress associated with photosynthesis.
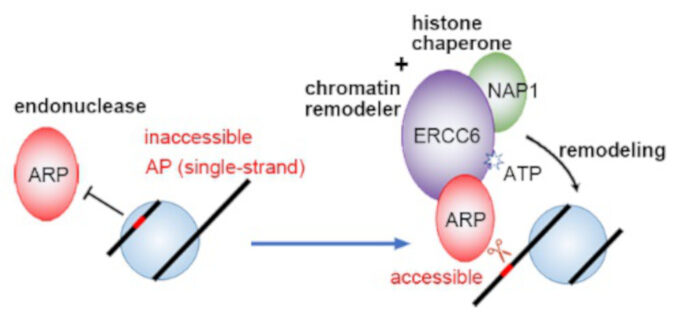
Question: APURINIC/APYRIMIDINIC ENDONUCLEASE REDOX PROTEIN (ARP) is the predominant enzyme responsible for cleaving apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in plants. Given its preferential endonuclease activity towards naked DNA, the question arises as to which chromatin-related proteins can be specifically recruited by ARP to enhance local chromatin mobility and facilitate efficient BER in plants.
Findings: We identified the plant chromatin remodeler ERCC6 and histone chaperone NAP1 as interacting partners with ARP. In a synergistic manner, ERCC6 and NAP1 contribute to the sliding of nucleosomes and exposure of hindered endonuclease cleavage sites. Loss-of-function mutations in Arabidopsis ERCC6 or NAP1 resulted in an arp-dependent hypersensitivity of plants to a toxic agent that induces BER, leading to the accumulation of apurinic or apyrimidinic sites. Furthermore, we showed that these proteins also interact with each other in yeast cells, suggesting a conserved recruitment mechanism employed by the apurinic or apyrimidinic endonuclease to overcome chromatin barriers during BER progression.
Next Steps: Future biochemical and molecular analyses will be imperative to unravel the intricate recruitment mechanisms of specific chromatin factors in distinct BER pathways at the chromatin level. This will advance our comprehension of the co-evolutionary dynamics between epigenetic machineries, their regulatory mechanisms, and chromatin architecture across diverse organisms for genome maintenance.
Reference:
Tianyi Fan, Tianfang Shi, Ran Sui, Jingqi Wang, Huijia Kang, Yao Yu, Yan Zhu (2024) The chromatin remodeler ERCC6 and the histone chaperone NAP1 are involved in apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease-mediated DNA repair. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae052