Review: Plant science's next top models (Ann. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) has been the absolute star of plant science research for more than 40 years, being the ideal model organism for its ease of handling and transferable knowledge to crops. In this review, Cesarino and coworkers explain how advances in "omics" technologies, together with…
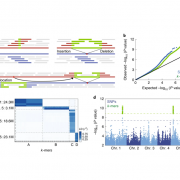
No-Genome-Required-GWAS (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyConventional approaches to connect phenotype to genotype, including genome-wide association studies (GWAS), are often limited by the quality of the species’ reference genome, and frequently neglect to detect structural variants that are common in plant genomes. Here, Voichek and Weigel present a “No-Genome-Required-GWAS”…
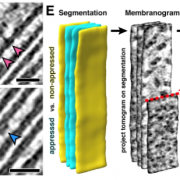
A close-up view of the thylakoids (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe thylakoid membranes inside the chloroplasts house the major protein complexes required for photosynthesis, including photosystems I and II (PSI/II), the b6f complex and ATP synthase. To optimize photosynthetic efficiency, the distribution and abundance of these complexes are dynamically regulated…
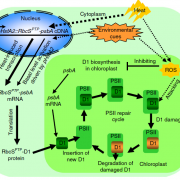
Nuclear-encoded synthesis of the D1 subunit of photosystem II increases photosynthetic efficiency and crop yield (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosystem II (PSII) is a protein complex located in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts that is involved in executing the initial reaction of photosynthesis in plants. When plants are exposed to extreme temperature conditions, PSII gets damaged. To repair the damage, one of the core proteins of…

Nitrate defines shoot size through compensatory roles for endoreplication and cell division (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this paper, Moreno et al. investigate how nitrate affects the balance between cell proliferation and cell expansion in shoots during early seedling development. They note that the cells in Arabidopsis cotyledons undergo considerable enlargement, and that the increase in cell size is correlated with…
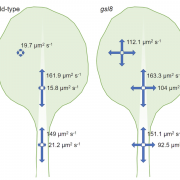
Symplastic auxin transport: Active, passive or both? (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdjacent cells in plants are connected by cytoplasmic connections called plasmodesmata (PD) and the movement through PD is called symplastic movement. Studies have shown that auxin transport between cells is protein-dependent, but it is not clear whether it can also move freely in the symplastic pathway.…

Aquaporins act in concert to regulate cold acclimation and freezing tolerance (Plant Cell Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAquaporins, also known as plasma membrane intrinsic proteins (PIP), are a large group of transporters that facilitate water transport through membranes. In this article, Rahman et al. explored the role of aquaporins in the cold stress response. They found that two aquaporin genes, PIP1;4 and PIP2;5,…
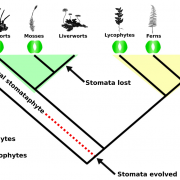
Phylogenomic evidence for reductive evolution of stomata (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyColonization of the terrestrial environment by land plants (embryophytes), a monophyletic clade that evolved from freshwater streptophyte algae, forever changed Earth by transforming biogeochemical cycles. The evolution of stomata was a key adaptation that allowed the colonization of terra firma. Present…
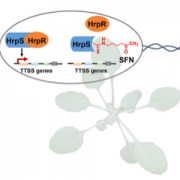
A plant secondary metabolite selectively targets bacterial pathogenicity (Cell Host Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have a variety of secondary metabolites that are associated with defense against pathogens, but the mode of action of such metabolites is poorly understood. Wang et al. revealed that the Arabidopsis secondary metabolite sulforaphane (SFN), which is derived from aliphatic glucosinolate, suppresses…

