
Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Charlotte Volpe
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesCharlotte Volpe, co-first author of Loss of ALBINO3b insertase results in a truncated light-harvesting antenna in diatoms
Current Position: PhD candidate at the Department of Biotechnology and Food Science - Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) – Trondheim, Norway
Education: PhD…

Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Marianne Nymark
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesMarianne Nymark, co-first author of Loss of ALBINO3b insertase results in a truncated light-harvesting antenna in diatoms
Current Position: Research scientist at the Cell, Molecular Biology and Genomics group at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU)
Education: PhD in Biology from…

A modular cloning toolkit for genome editing in plants (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenome editing with the CRISPR/Cas system is now widely used in functional studies across biological sciences including plant biology. Typically, this system involves a DNA nuclease and a guide RNA that directs the nuclease to a specific location in the genome. Golden Gate (GG) is a cloning method that…
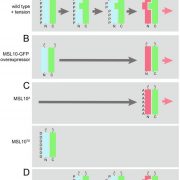
The N-terminus of AtMSL10 interacts with its own C- terminus (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are equipped with multiple mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels that respond to external and internal mechanical perturbations. When one of these, AtMSL10, is overexpressed it leads to a cell death phenotype, although there is no discernible phenotype associated with its loss of function. Recently…
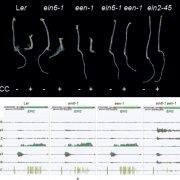
Epigenetic silencing of a multifunctional plant stress regulator EIN2 (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEIN2 is a key regulator of the ethylene response and a protein with a complex function and regulation. Zander et al. have uncovered an interesting and complex mechanism by which its expression is regulated. Many genes are regulated through histone modifications, with the histone variant H2A.Z and the…

Coordination of circadian times in Arabidopsis seedlings (PLOS Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPrecise temporal control is crucial for plant developmental processes, e.g., photosynthesis, leaf movement, and flowering. In this work, Greenwood et al. studied how rhythms are coordinated at the whole-organism level. The authors monitored the activity of GIGANTEA (GI), a core clock gene, using a LUCIFERASE…
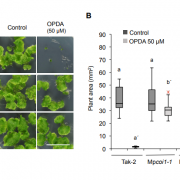
Jasmonate-related MYC transcription factors are functionally conserved in Marchantia polymorpha ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn recent years, studies in the model bryophyte Marchantia polymorpha have provided insights on how the Jasmonic Acid (JA) pathway works in early diverging land plants, starting from its biosynthesis (Yamamoto et al., 2015; Koeduka et al., 2015), followed by perception (Monte et al, 2018) and co-repressor…
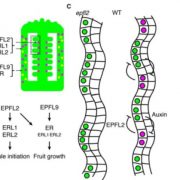
A peptide pair coordinates ovule initiation patterns with seed number and fruit size (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant peptide patterning is popping up everywhere! Now Kawamoto et al. show that a pair of peptides, interacting with receptor proteins, coordinates the placement of ovules in Arabidopsis. They started with a natural variation analysis, which highlighted that several varieties with mutations in the ERECTA…
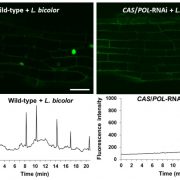
The ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor produces lipochitooligosaccharides and uses the common symbiosis pathway ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNutrient exchange during plant-fungal symbiosis allows assimilation of nutrients necessary for plant growth in a beneficial way. Several plants have evolved to form symbioses with mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia bacteria that allow the plants to efficiently take up nitrogen and phosphorous. In its interactions…

