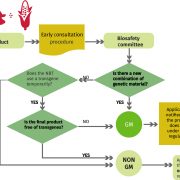
EU regulatory approach to directed mutagenesis: consequences for international trade and potential steps forward (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe seed sector, and particularly plant breeders, are responsible for providing farmers with new plant varieties able to overcome challenges such as climate change, water restrictions or plant pests. In order to do their job, breeders have a collection of tools at their disposal. Among these are traditional…
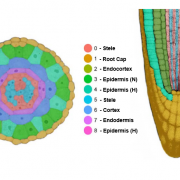
Single-cell RNA sequencing resolves molecular relationships among individual plant cells (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySingle cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has transformed our understanding of gene expression within and amongst individual cells. These techniques have been applied extensively to animal cell populations to discover the development of specific cell lines and identify rare cell types but are not commonly…
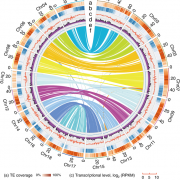
The genome of broomcorn millet: The fourth millet to be sequenced (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhole genome sequencing (WGS) unlocks the repertoire of genes encoded within the genome. From a structural genomics aspect, the sequence data enables the development of molecular markers and maps, and identification of novel QTLs/genes/alleles regulating the trait-of-interest. From a functional genomics…
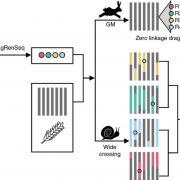
Tapping into the genetic diversity of wild crops for engineering disease resistance (Nature Biotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLack of sequence information makes harnessing the diversity of disease resistance (R) genes in wild crops highly challenging. Arora and Steuernagel et al. report AgRenSeq, a reference genome-free technique, for rapid cloning of nucleotide binding/Leucine-rich repeat (NLR) resistance genes from wild…
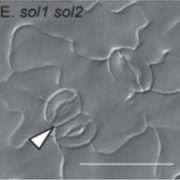
SOL1 and SOL2 regulate fate transition and cell division in stomatal lineage ($) (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata and pavement cell development in the leaves occur through programmed asymmetric cell division. In this paper the authors demonstrated the role of two CHC domain proteins, SOL1 and SOL2 that were identified previously by the same group to be downstream targets of a bHLH transcriptional factor…
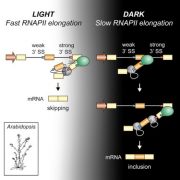
Light regulates plant alternative splicing through the control of transcriptional elongation (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight perception in plants generates a plethora of gene expression changes. Among them, it has been shown that light affects alternative splicing mediated by a chloroplast retrograde signal. Here, Godoy Herz et al. explore the different possible mechanisms possible involved in this regulation. Using…
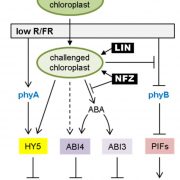
Chloroplast status can affect shade avoidance in plants ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFor optimal photosynthetic performance, plants utilize multiple strategies to compete with their neighbors. Especially when light supply is limited in the canopy, plants promote their own elongation to overgrow neighboring plants. This occurs as a response to a low ratio of Red to Far-Red light (R/FR),…

Lateral inhibition by a peptide hormone-receptor cascade during Arabidopsis lateral root founder cell formation (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The plant hormone auxin acts as a general coordinator of growth and development, transferring information over both long and short ranges. Among other roles, it promotes the formation of the founder cells in roots and it triggers the position of the lateral roots (LR). LR founder cells are determined…
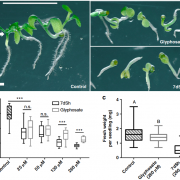
Natural Herbicide: Cyanobacterial antimetabolite inhibits the growth of prototrophic organisms (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe shikimate pathway synthesizes aromatic amino acids in microorganisms and plants, and its absence in animals makes the shikimate pathway a common target for the development of herbicides. Brilisauer et al. 2019 isolated a novel compound from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus—7-deoxy-sedoheptulose…

